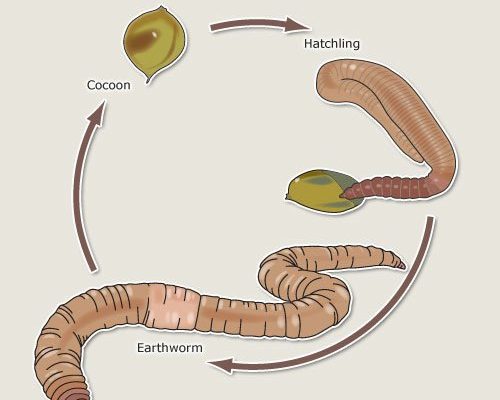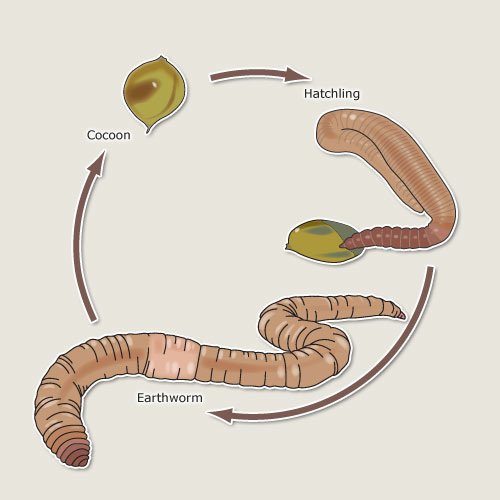
Let’s break down the earthworm’s reproduction process. It’s a bit like a secret life cycle, where the humble cocoon steps in as a vital component—sort of like a protective little house that holds all the potential for new baby worms. Don’t worry if you’re new to this topic. We’re going to dive into the journey from cocoon to hatchling, making this process as clear as mud (which, ironically, is where you’ll find these creatures most often!).
Understanding Earthworms’ Unique Reproductive System
Earthworms are classified as hermaphrodites, meaning each worm has both male and female reproductive organs. Here’s the thing: while they can technically fertilize themselves, they usually pair up with another earthworm to exchange sperm. It’s kind of like a dance, where two worms align their bodies and share genetic material.
During this mating process, earthworms produce a **sperm pouch**. After they exchange sperm, they separate and go about their wormy business. But don’t think that’s the end of the story. The magic really happens when they begin to create their cocoons!
The Cocoon: A Critical Stage in Reproduction
After mating, each worm creates a cocoon made of a sticky substance that hardens when exposed to air. Imagine it as a squishy little egg that protects future baby worms. The cocoon forms around the worm’s clitellum, a thickened band on its body. This clitellum is incredibly important, as it helps in the formation of the cocoon.
Once the cocoon is complete, the worm releases it into the soil. This isn’t just any soil; it needs to be rich and moist to offer the best chances for the little ones to thrive. The cocoon can be a home to several eggs, depending on the species of earthworm.
What Happens Inside the Cocoon?
Inside the cocoon, magic is happening! The eggs are fertilized by the sperm exchanged during mating, and they start to develop. You might picture the cocoon as a cozy little incubator, where the delicate baby worms are growing. Depending on the species and environmental conditions, the time it takes for the eggs to develop can vary. It can take anywhere from a few weeks to a couple of months.
This period is crucial because the baby worms are still in a vulnerable state. While they’re nestled inside the cocoon, they depend on the nutrients and protection that the cocoon provides. They’re literally growing and developing until they’re ready to emerge.
Emergence of Baby Worms
When the baby worms are fully developed, they break free from the cocoon. This is an exciting time in the life of an earthworm! Emerging from the protective casing, they are typically very small—about the size of a grain of rice. At this point, they’re not quite ready to set out on their own just yet. They’ll stay hidden in the soil to protect themselves and continue to grow.
You might wonder what happens next. Well, those tiny worms will start munching on decaying organic material and other nutrients in the soil. They’re not just floating around; they’re doing their part to aerate the soil and help it stay healthy—adding to the ecosystem like little heroes.
The Importance of Earthworm Reproduction
So, why should we care about how earthworms reproduce? Well, for starters, these creatures play an essential role in soil health. When they reproduce successfully, they ensure there’s a steady stream of worms to keep this process going. This is important for several reasons:
- Soil Aeration: Earthworms create tunnels in the soil, allowing air, water, and nutrients to penetrate deeper layers.
- Nutrient Cycling: By consuming organic matter and excreting nutrient-rich castings, they significantly enhance soil fertility.
- Supporting Plant Growth: Healthy soil filled with earthworms leads to stronger plants and crops, which is vital for food production.
If earthworm populations decline due to environmental changes or poor soil management, the consequences can ripple throughout ecosystems. So, the cycle of reproduction isn’t just about more worms; it directly impacts the health of our environment.
Challenges to Earthworm Reproduction
Unfortunately, earthworms face several challenges that can impact their reproduction rates. One of the biggest threats is habitat loss due to urbanization and agriculture. When their natural habitats are destroyed, it leaves them with fewer safe spaces to lay their cocoons.
Next, climate change plays a role, affecting soil moisture and temperature. Earthworms prefer moist conditions to thrive, and if their environment becomes too dry or too wet, it can impact their ability to reproduce successfully.
Finally, some human activities, like pesticide use, can also harm earthworm populations. These chemicals can disrupt their reproductive cycles and damage the delicate balance in the ecosystem.
Ways to Help Earthworms
If you’d like to support earthworms and help them thrive, there are some simple steps you can take:
- **Create a compost bin:** Composting not only provides rich nutrients for your garden but also offers a safe environment for earthworms.
- **Avoid pesticides:** Choose natural pest control methods to protect these essential creatures.
- **Plant native vegetation:** Native plants often support earthworm populations by promoting healthy soil.
These small changes can contribute to healthier ecosystems and encourage more successful reproduction among earthworms.
Wrapping It Up
So there you have it! The journey of an earthworm from cocoon to hatchling is both fascinating and vital for our environment. Earthworms might seem simple, but their life processes are intricate and essential for keeping our soil healthy. Every tiny worm working in the soil plays a part in a larger system, helping plants grow and keeping the earth fertile.
Next time you spot an earthworm wriggling in your garden, take a moment to appreciate the incredible journey it’s been on—from that little cocoon to a hardworking baby worm. Understanding their reproductive process not only shines a light on their importance in nature but also reminds us of how interconnected everything truly is. So, let’s do our best to protect these squirmy little partners of ours, ensuring they can continue their vital role in maintaining the earth’s health for generations to come.