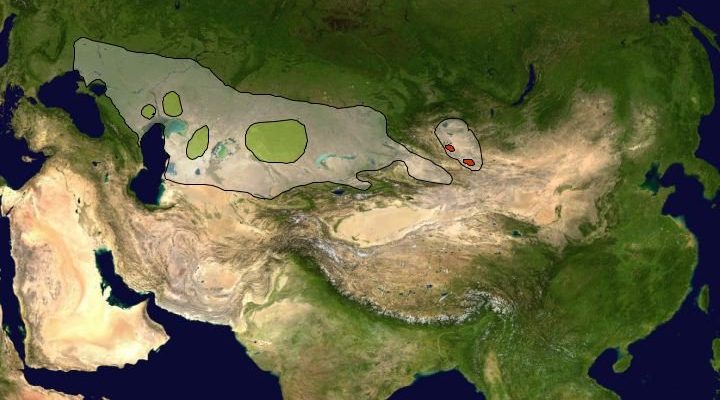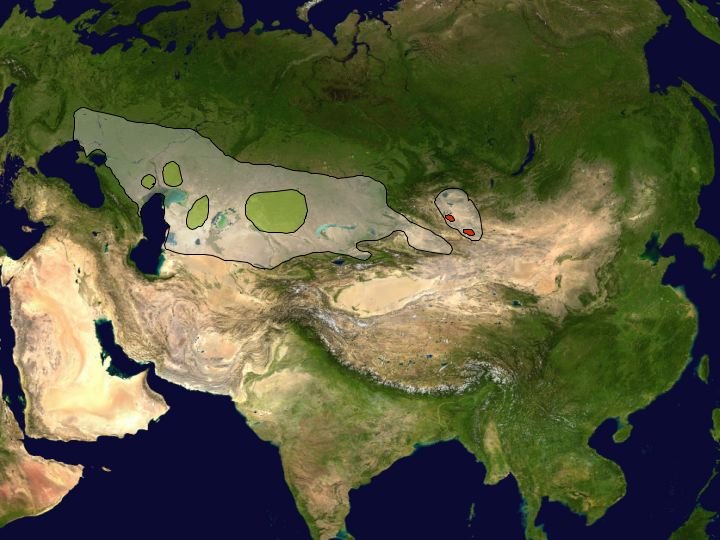
Imagine standing in a vast, open landscape where the only sounds are the wind whispering through the grass and the distant call of wildlife. Picture rolling steppes and arid regions—this is where the Saiga antelope finds its footing. Their habitats stretch across Central Asia, primarily covering parts of Kazakhstan, Mongolia, and the Russian steppe. In this article, we’ll explore not only their habitat but also their distribution, the challenges they face, and why all of this matters.
Understanding Saiga Antelope Habitat
The Saiga antelope is most commonly found in grasslands, steppes, and semi-desert regions. These habitats offer plenty of food sources like grasses, herbs, and shrubs which are essential for their survival. During the summer, they typically graze in areas with an abundance of green grasses. In winter, they migrate to regions with less snow and sparse vegetation. This adaptability is crucial for their survival in such harsh environments.
Interestingly, Saiga antelopes have a unique physiological trait that helps them thrive in these habitats. Their large, somewhat floppy noses aren’t just for show; they filter out dust and help regulate their temperature. This is particularly important in the extreme climate of their home regions, where temperatures can swing dramatically from freezing cold winters to scorching hot summers.
Geographical Distribution of Saiga Antelopes
So, exactly where do you find these remarkable animals? The Saiga antelope’s range primarily extends across the Eurasian steppe, primarily in countries like Kazakhstan and parts of Mongolia and Russia. Historically, they were much more widespread, but due to various factors, their numbers have dwindled significantly.
Currently, there are two main populations of Saiga antelopes: the Mongolian Saiga and the Steppe Saiga. The Mongolian population is more isolated, while the Steppe Saiga can be found in large groups migrating across their habitats in search of food and better living conditions. This migration is crucial. It allows them to find the best grazing areas throughout the seasons, showcasing their ability to adapt to changing environmental conditions.
Climate and Its Impact on Habitat
The climate where Saiga antelopes live plays a significant role in their daily life. These regions typically experience harsh weather, with cold winters and warm summers. The climate dictates where they can find food and water, which is essential for their survival.
During the hotter months, Saigas tend to migrate to areas with more abundant vegetation and water sources. In contrast, they tend to huddle together during the winter to conserve heat and find shelter from the cold wind. This behavior illustrates their adaptability and the dynamic relationship they have with their environment.
Unfortunately, climate change is putting pressure on their habitats, as shifts in temperature and precipitation patterns can affect food availability. As a result, we might see challenges for their survival unless we take action to address these changes.
Threats to Saiga Antelope Habitats
Here’s the thing: while the Saiga antelope is an incredibly resilient species, they face numerous threats. Habitat loss due to agricultural expansion and urban development is a significant concern. As humans continue to build and farm, they encroach on the Saiga’s grazing lands, leading to a decline in their population.
Additionally, poaching and illegal hunting remain serious threats to their survival. Saiga antlers are often sought after in traditional medicine and as trophies. This illegal wildlife trade puts immense pressure on already dwindling populations.
Environmental factors, such as climate change and the effects of industrial activities, also pose risks to their habitats. Changes in land use can lead to the degradation of essential grazing lands, making it increasingly difficult for Saiga antelopes to survive.
Conservation Efforts for Saiga Antelopes
Recognizing the threats to their survival, various organizations and governments are working hard to protect Saiga antelopes and their habitats. Protected areas have been established to safeguard their living spaces and migratory routes.
For instance, conservation programs focus on anti-poaching efforts and educating local communities about the importance of preserving these unique animals. You might be wondering, “How can I help?” Simple actions, like supporting wildlife conservation organizations or spreading awareness about Saiga antelopes and their plight, can have a positive impact.
Moreover, international cooperation is essential for the successful conservation of Saiga populations. Since these animals roam across various borders, working together can help ensure their survival in the long term.
The Importance of Saiga Antelopes in Their Ecosystem
You might not realize it, but Saiga antelopes play an important role in their ecosystem. By grazing on grasses and plants, they help maintain the balance of their habitats. This grazing can promote the growth of certain plant species and prevent the overgrowth of others, fostering biodiversity.
Additionally, as they migrate in search of food, they help disperse seeds and nutrients across vast areas. This process is critical for the health of their environment.
Overall, their presence is key to a thriving ecosystem, and losing them would have far-reaching consequences on the balance of their habitats.
In the grand scheme of things, Saiga antelopes are more than just a fascinating species to behold; they are indicators of the health of their ecosystems. Their habitats tell us about the climate and biodiversity of those regions, and preserving them is essential not only for Saigas but for countless other plants and animals that share their space.
The challenges they face are significant, but through conservation efforts and increased awareness, there’s hope for the future. By understanding where they live and the threats they encounter, we can support efforts to protect Saiga antelopes and ensure these remarkable creatures continue to roam the steppes of Central Asia for generations to come. Let’s work together to secure a future where these unique animals thrive in their natural habitats.