Pumas have a rich history that stretches back to ancient times. They’re more than just a pretty face in the animal kingdom. Their evolution is a story of survival, adaptability, and a unique blend of traits that makes them one of the most skilled hunters on the planet. Throughout this blog, we’ll dive deep into their evolution, touch on their adaptations, explore their habitat preferences, and much more.
Understanding the Puma’s Ancestors
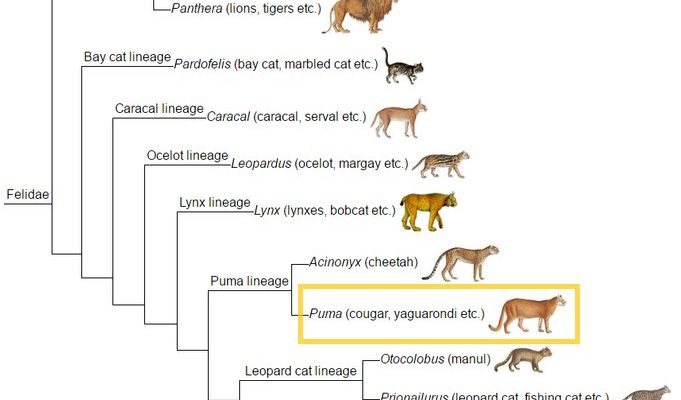
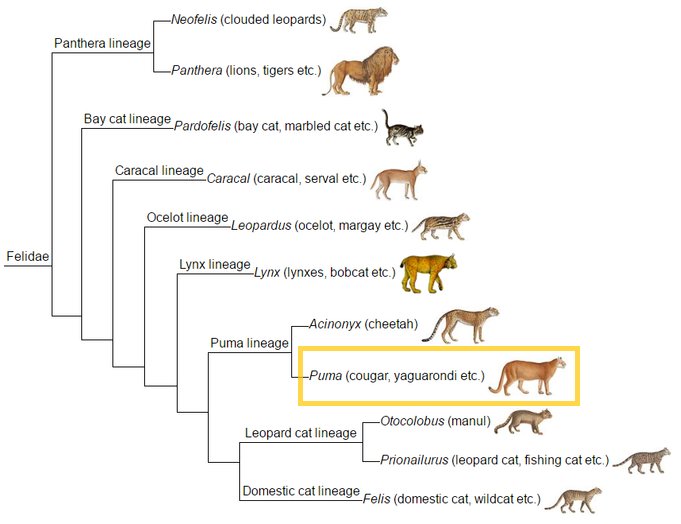
To truly grasp the evolutionary history of the puma, we need to travel back in time. Think of it like flipping through a family photo album, where each picture reflects a different era in the cat’s lineage. Pumas belong to the Felidae family, which includes all cats, big and small. They’re part of the subfamily Felinae, more specifically classified in the genus Puma.
The earliest members of the Felidae family appeared around 10–15 million years ago, during the Miocene epoch. Many of these early cats were quite different from the pumas we know today. They shared common ancestors with other modern cats, such as lions, tigers, and domestic cats. Over time, these ancient cats spread across the globe, each adapting to their unique environments. Isn’t that wild?
One particular branch of these ancestral cats led to the emergence of the puma around 2 million years ago. This lineage branched out from the Jaguarundi, a smaller cat that still exists today. The puma’s ability to adapt to various habitats has been key to its survival and success.
The Role of Ice Ages in Puma Evolution
Ice ages might conjure images of woolly mammoths and saber-toothed cats, but they played a crucial role in shaping modern pumas too. As glaciers advanced and retreated, they transformed landscapes and created various environments. This forced many species, including pumas, to adapt or migrate to survive.
During these periods, pumas expanded their range significantly. They adapted to both cold mountainous areas and warmer coastal regions. They developed traits like their incredible agility and powerful build, which helped them stalk and hunt effectively, whether they were in the snowy Rockies or the dense forests of South America.
Interestingly, some scientists believe that the puma’s adaptability during these climate shifts helped them survive when many other large mammals went extinct. Imagine being a puma, navigating through this changing world, figuring out how to hunt and thrive.
Physical Adaptations of the Puma
When you think of pumas, you might picture a sleek, muscular animal. But their physical traits tell a deeper story of evolution. Pumas have developed a range of adaptations that make them exceptional hunters. Let’s break down some of these features.
First, their powerful legs allow for impressive leaps—often 20 feet or more in a single bound! This agility is crucial when they’re chasing down prey or escaping threats. Plus, their strong, flexible bodies enable them to climb trees and traverse rocky terrains.
Their unique coat color is another evolutionary adaptation. The tawny or grayish fur helps them blend into their surroundings, making it easier to stalk prey. It’s like nature’s camouflage, perfectly designed for a stealthy approach. Another cool detail is their retractable claws, which keep their claws sharp for hunting and climbing but retract when they walk, preventing wear.
Lastly, pumas have excellent vision and hearing. They can detect even the slightest sounds in their environment, which is super important for hunting. Imagine being able to hear a rabbit rustling in the bushes from a distance!
The Puma’s Diverse Range and Habitat
Pumas are incredibly versatile animals, and their ability to adapt to various habitats has allowed them to thrive across a vast territory. They roam from the snowy peaks of the Andes to the deserts of the American Southwest. This diverse range is a testament to their evolutionary success.
You might be wondering what factors influence a puma’s choice of habitat. Generally, they prefer areas that offer cover for stalking prey—think dense forests, mountain ranges, and even grasslands. They are solitary creatures, marking vast territories that can span hundreds of miles, depending on their food sources. Imagine living as a puma, staking out your territory, and making strategic decisions about where to hunt.
In urban areas, pumas have also shown remarkable adaptability. There have been increasing reports of pumas navigating suburban landscapes, finding ways to coexist with human populations. This ability to adapt to urban environments speaks volumes about their resourcefulness.
Behavioral Traits of Pumas
Behaviorally, pumas exhibit fascinating traits that are vital for their survival. They are known for being solitary animals, often preferring to stay away from each other unless it’s breeding season. This behavior helps reduce competition for food, which is particularly important given their large territories.
Pumas are also known to be crepuscular, meaning they are most active during dawn and dusk. This timing aligns with the hunting habits of many of their prey, such as deer. Think of it like planning a dinner party that aligns perfectly with when your guests are most likely to arrive.
Communication between pumas is mostly non-verbal. They use scent markings to establish territory and communicate with other pumas. Vocalizations like growls, screams, and chirps can also convey important messages, especially during mating season. It’s like having an entire conversation without saying a word!
Conservation Status and Challenges
Despite being incredibly resilient, pumas face various challenges in today’s world. Habitat loss due to urbanization and agriculture has significantly reduced their natural environments. As they lose their homes, conflicts with humans often increase when pumas venture into populated areas in search of food.
In some regions, they are also hunted for sport or out of fear. This has led to a decline in their populations in certain areas, making conservation efforts more crucial than ever. These efforts involve protecting their habitats, implementing coexistence strategies, and educating communities on the importance of these big cats in our ecosystems.
Strong conservation initiatives have made a difference in some regions, allowing puma populations to stabilize. However, there’s still a long way to go. Supporting local conservation efforts or wildlife corridors can make a big impact on ensuring these magnificent creatures thrive for generations to come.
The Future of Pumas
So, what lies ahead for the puma? Given their adaptability and resilience, there’s hope. As we learn more about their biology and ecology, we can ensure that conservation efforts are tailored to their needs. The key is balancing human activities and wildlife habitats.
Innovative solutions, like wildlife crossings and green corridors, can help. These strategies not only protect pumas but also other wildlife. With increasing awareness and global cooperation, we can foster environments where humans and pumas can coexist.
In the end, understanding the evolutionary history of the puma isn’t just about looking back. It’s a call to action for the present and future. Our choices today can shape the lives of these remarkable creatures tomorrow.
As we wrap up this exploration, next time you think about pumas, remember their journey—one filled with survival, adaptation, and a resilient spirit that persists even in the face of challenges. Isn’t it inspiring to learn how they’ve evolved, and how we can play a part in protecting their legacy?