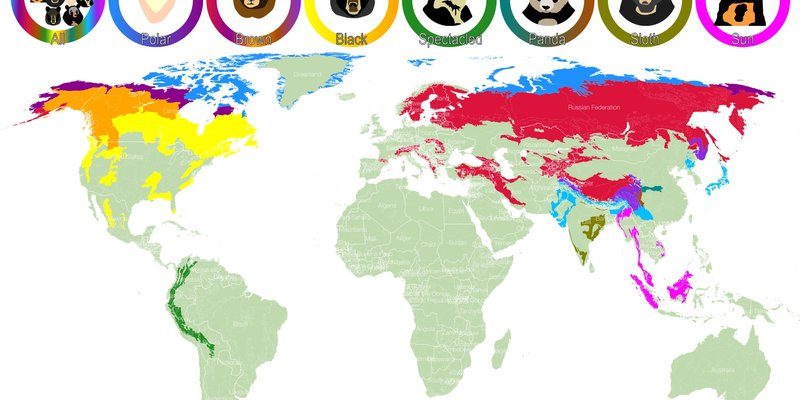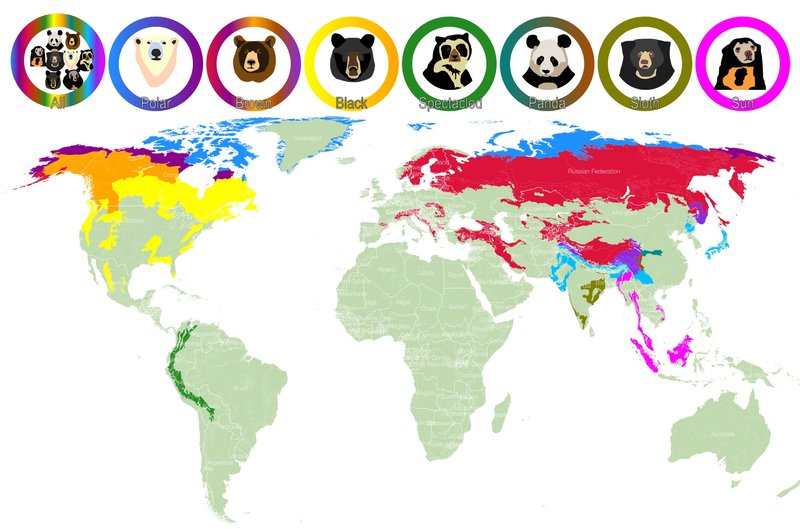
So, where do polar bears actually call home? These incredible animals primarily reside in the circumpolar Arctic, a term that sounds fancy but simply means the area around the North Pole. Picture a ring of ice, ocean, and land that stretches across several countries like Canada, Russia, Alaska, Greenland, and Norway. Let’s dive deeper into their habitats and distribution, discovering more about the environments they thrive in and the unique challenges they face.
The Icy Habitat of Polar Bears
Polar bears are deeply connected to the sea ice in the Arctic. This ice is crucial for their survival. Why? Well, these bears rely on sea ice to hunt for their primary prey, which is typically seals. Think of the sea ice as their hunting platform. It allows them to spot seals swimming beneath the surface and launch an energetic attack. Without this ice, polar bears struggle to find food.
Interestingly, polar bears don’t just hang out on ice all day. During the warmer months, when the ice melts, they adapt by spending more time on land. They can’t hunt like they do on ice, so they enter a sort of fasting period, living off their fat reserves. It’s a tough existence, and many bears can lose a significant amount of weight during these months.
Additionally, you might be surprised to learn that polar bears are excellent swimmers. When they cross expanses of open water between ice floes, they can swim long distances—some bears have been recorded swimming over 60 miles (96 kilometers) at a stretch! This ability helps them find new patches of ice or land when their usual habitats become too warm or ice-free.
Distribution Across the Arctic Regions
Let’s explore where exactly polar bears can be found. They inhabit five main countries, which means their distribution is quite wide. Here’s a quick rundown:
- Canada: Home to about 60% of the world’s polar bear population, especially in the northern territories.
- Greenland: The vast ice sheets here provide essential habitats.
- Norway: Particularly in the Svalbard archipelago, polar bears thrive on the surrounding sea ice.
- Russia: The Arctic coasts of Siberia offer a crucial environment for these magnificent creatures.
- United States: In Alaska, polar bears inhabit the coastal regions and surrounding islands.
Polar bears often roam vast areas, covering hundreds of miles in search of food and suitable ice. They typically stay within specific territories that meet their needs for hunting, breeding, and resting. This is why some regions are particularly important for their survival. Understanding their distribution helps in conservation efforts, especially in light of climate change.
The Impact of Climate Change on Polar Bear Habitat
Here’s the thing: polar bears are facing significant challenges due to climate change. As global temperatures rise, sea ice is melting faster than usual. This situation puts immense pressure on polar bears, who rely on stable ice platforms for hunting and breeding. When the ice melts earlier in the spring and forms later in the autumn, bears have less time to hunt for food, leading to malnutrition and lower cub survival rates.
Many scientists believe that if current trends continue, we could see major losses in polar bear populations. It’s not just about losing ice; it’s about the entire ecosystem being affected. As seals and other prey become harder to find, the entire food web shifts. This means that conservation efforts are more crucial than ever.
So, what can be done? Protecting the habitats polar bears rely on is vital. Initiatives aimed at reducing carbon emissions, preserving ice habitats, and creating marine protected areas can help ensure that these majestic animals have a fighting chance.
Polar Bear Migration Patterns
Migration is another fascinating aspect of polar bear life. These animals are not stationary; they often move in search of food and stable ice. During the late summer months, when ice is scarce, they might travel hundreds of miles to find a suitable habitat. This journey can be dangerous, especially with changing ice conditions and potential encounters with humans.
Interestingly, polar bears aren’t just wandering aimlessly. They often follow established routes that they or their ancestors have used for generations. These routes can lead them to areas rich in seals or safer ice. It’s like having a map that’s been passed down through the years!
However, as climate change alters their traditional pathways, polar bears may be forced into unfamiliar territories. This change can lead to increased competition for food as bears encounter one another more often. Understanding these migration patterns is key to protecting polar bears and ensuring they find the resources they need.
Polar Bear Denning Habits
Polar bears also have specific denning habits, particularly when it comes to giving birth. Female polar bears dig dens in snowdrifts to keep their cubs warm and safe during the harsh winter months. These dens are typically located on stable sea ice or land and are insulated from the severe Arctic cold.
Most females will head to their dens in the fall, where they will give birth to one to three cubs after about eight months of pregnancy. Inside the den, the mother and her cubs stay safe until the cubs are strong enough to venture outside in spring. This period is crucial for the survival of the young bears.
Sadly, because of climate change and decreased snow accumulation, some females are facing challenges in finding suitable denning sites. The loss of stable ice and shifting weather patterns can lead to inadequate snow cover, jeopardizing the safety of mothers and their cubs. Protecting these denning habitats is an essential component of ensuring polar bear populations remain healthy.
Human Interaction and Conservation Efforts
Human activity can have a significant impact on polar bears and their habitats. From oil drilling in the Arctic to increased shipping traffic due to melting ice, these interactions pose direct threats. You might be wondering how this affects polar bears specifically. Oil spills, disturbances from ships, and increased human presence can disrupt their hunting and breeding cycles.
Luckily, many organizations are working tirelessly to protect polar bears and their habitats. Conservation efforts include creating protected areas, conducting research on bear populations, and working with local communities to reduce human-bear conflicts. Innovative strategies, like using technology to monitor bear movements, are also being developed to help scientists understand their needs better.
It’s a challenging situation, but awareness is growing. Many people are realizing the importance of protecting these magnificent creatures and their icy homes. The more we learn about polar bears, the better we can advocate for their survival and the health of the Arctic ecosystem.
In summary, polar bears live in a crucial habitat defined by sea ice in the Arctic regions of Canada, Greenland, Norway, Russia, and the United States. Their survival relies on this delicate and rapidly changing environment. As we see the effects of climate change influencing their habitat and distribution, it’s essential to understand the challenges these remarkable animals face.
By recognizing the importance of their icy homes and advocating for their protection, we can help ensure that future generations get to experience the beauty of polar bears in the wild. It’s a shared responsibility, and every effort counts. Let’s keep the conversation going about these majestic creatures and work together to protect their habitats for years to come.