When we think about the habitats of wild animals, it’s like thinking about each species having its own favorite coffee shop. Some prefer the bustling hubbub of the city, while others enjoy the serene spaces of a countryside café. For the Eurasian lynx, their “café” is made up of snowy mountains, thick forests, and, sometimes, rocky terrains. Let’s dive in and explore where these magnificent cats make their homes and what types of environments support their way of life.
The Range of the Eurasian Lynx
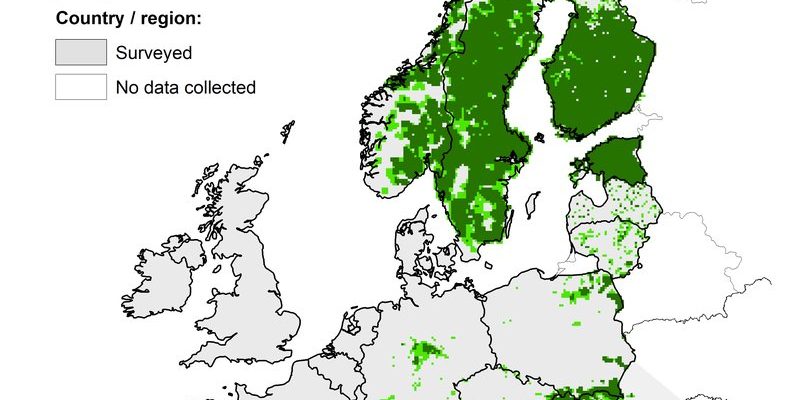
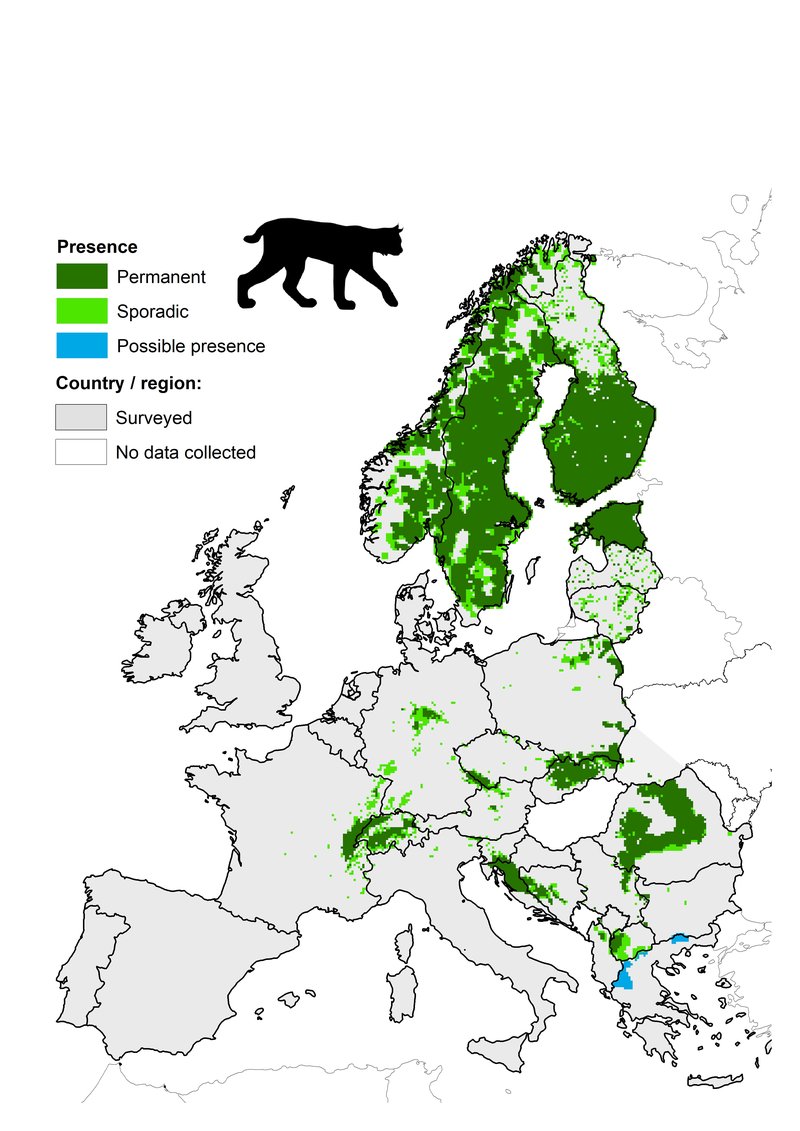
Eurasian lynxes are the largest lynx species and have a broad range that stretches across several countries. They can be found in many parts of Europe, particularly in the Scandinavian countries like Sweden and Norway, as well as eastern regions like Finland and the Baltic states. Beyond Europe, their territory extends into Siberia, reaching as far as Mongolia and northern China.
These felines are incredibly adaptable, which is part of why their range is so extensive. From the cold tundra of the north to the milder forests in central Europe, they thrive in varying climates. You might picture them lounging under the shadow of tall pine trees or stealthily moving through a snowy landscape, hunting for their next meal.
Preferred Habitats of the Eurasian Lynx
Eurasian lynxes enjoy environments that provide both cover and hunting opportunities. Their preferred habitats typically consist of:
- Forests: Dense forests are ideal as they offer plenty of cover from potential predators and humans.
- Mountains: Lynxes often inhabit mountainous areas with rugged terrain, which gives them the ability to prowl and stalk.
- Tundra: In colder regions, they’ve adapted to thrive in the tundra, where they can find small mammals to hunt.
Honestly, the combination of these features makes perfect sense. The dense foliage allows lynxes to hide, while the open areas nearby let them catch sight of prey without being seen. It’s like having the best of both worlds—privacy and a prime spot for a meal.
Climate Adaptability
One of the most impressive traits of the Eurasian lynx is its ability to adapt to various climates. They’re comfortable in both cold, snowy regions and relatively warmer forested areas.
In regions with harsh winters, such as Siberia, these lynxes grow thicker fur coats for insulation. You might be wondering how they manage to find food during the winter months. They’re quite resourceful! Their primary prey includes small to medium-sized mammals like hares and deer, which they hunt even in deep snow. In milder climates, they can thrive on a diet with a bit more variety, adapting their hunting techniques as needed.
Impact of Human Activity on Lynx Habitats
As human developments expand, the habitats of these stunning creatures are increasingly put to the test. Urbanization and deforestation can fragment their living spaces, making it harder for them to find food and mates.
Many places in Europe have seen efforts to protect lynx populations and their habitats. For example, conservation programs focus on preserving forest areas and creating wildlife corridors. This is crucial because it allows lynxes to roam freely without the threat of roads or buildings cutting through their paths. Every time a lynx is spotted in a thriving environment, it’s like a reminder of nature’s incredible resilience!
Habitat Variation Across Regions
Interestingly, the specific type of habitat can vary significantly from one region to another. For instance, the Carpathian Mountains in Central Europe provide dense forests with rich prey populations. Here, lynxes have adapted to hunt in an environment filled with large deer populations.
On the other hand, in the boreal forests of Siberia, the lynx faces harsher conditions with a landscape that changes dramatically with the seasons. They rely heavily on snow cover to help them stalk their prey. So, depending on where they are, these lynxes can adjust their hunting strategies as per the available resources and environmental conditions.
Threats to Habitat and Conservation Efforts
Unfortunately, the Eurasian lynx faces several threats to its habitat. Besides direct human influence, environmental changes like climate change can significantly impact their ecosystems. As temperatures rise, the forest compositions may shift, making it tougher for lynxes to find suitable habitats.
Conservation efforts are vital to ensure that these cats have a future in the wild. Many countries have implemented protective measures to safeguard their habitats. For example, in some parks, hunting and logging are restricted to allow natural ecosystems to flourish.
Through community education and wildlife protection laws, humans can play an essential role in helping these majestic cats thrive. It’s like cheering for your favorite team from the stands, hoping they score the winning goal!
The Eurasian lynx is a symbol of nature’s beauty and complexity. Their habitats are as varied as the landscapes they roam, from thick forests in Europe to expansive mountains in Siberia. However, the pressures from human activity and environmental changes are challenges they face daily.
Understanding where they live and the types of habitats that support their survival is crucial. By working together to protect their environments, we not only help the lynxes but also preserve the rich ecosystems they are part of. So next time you’re exploring nature, take a moment to appreciate the intricate balance that allows creatures like the Eurasian lynx to thrive, reminding us all of the delicate web of life we share.