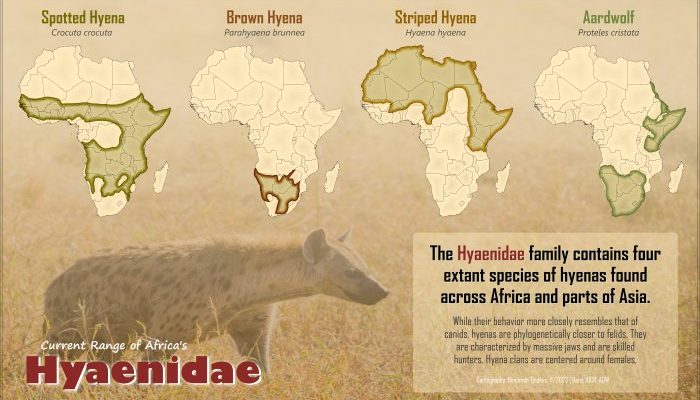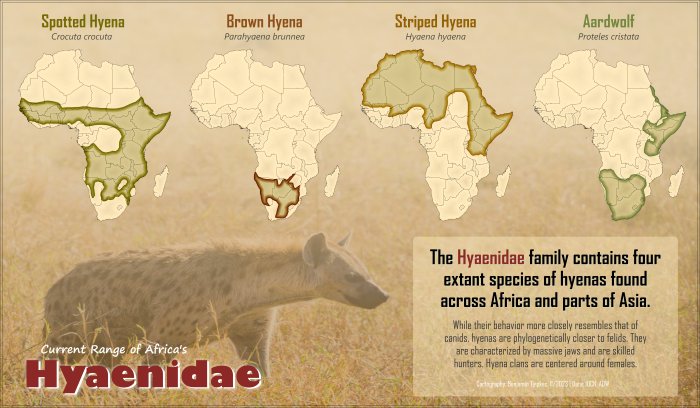
Honestly, understanding the habitats of hyenas is like piecing together a puzzle. You’ve got to consider their behaviors, their social structures, and how they interact with different environments. It’s not just about where they call home; it’s about how they thrive in those spaces. Let’s dive into the various types of hyenas and explore the places they inhabit.
Types of Hyenas: A Quick Overview
Before we get into where hyenas live, let’s take a moment to understand the different types. There are four species of hyenas, each with its own unique characteristics and habitat preferences:
- Spotted Hyena: The most well-known, famous for its laughing call.
- Brown Hyena: More elusive, they prefer to stay hidden.
- Striped Hyena: Smaller and found mostly in Asia and North Africa.
- Aardwolf: A lesser-known species that feeds primarily on termites.
Each species has specific needs when it comes to their living environment. For instance, spotted hyenas are generally social and thrive in open savannas, while brown hyenas are more solitary, often occupying semi-desert regions.
Savannas: The Spotted Hyena’s Playground
Spotted hyenas primarily roam the savannas of sub-Saharan Africa. These open grasslands are perfect for hunting and foraging, allowing them to take advantage of the wide spaces where prey is abundant.
Imagine a vast landscape dotted with acacia trees and tall grasses. Here, hyenas work in groups called clans, social structures that help them hunt and defend their territory. Their strong social bonds make them effective predators, and they can often be seen scavenging or hunting in packs.
Interestingly, their adaptability means they can thrive in varying conditions—whether it’s a dry season or a time filled with rain. This flexibility is key to their survival and population growth in these regions.
Forests and Woodlands: A Diverse Habitat
While savannas are the go-to for spotted hyenas, other species, like the brown hyena, prefer more wooded areas. These semi-arid environments provide cover and plenty of den sites for these shy creatures.
Brown hyenas are often found in southern Africa, in regions like the Kalahari Desert. Here, they tend to be nocturnal, avoiding the heat of the day while hunting for food. The dense underbrush and rocky outcrops offer perfect hiding spots from predators, including lions and humans.
You might be wondering why they prefer these environments. The answer lies in the abundance of scavenging opportunities available in these areas, coupled with less competition than in more open regions.
Mountain Regions: The Striped Hyena’s Choice
If you trek through the mountains of North Africa and parts of Asia, you might spot a striped hyena. These hyenas prefer rugged terrains where they can hide and hunt effectively. Unlike their spotted cousins, striped hyenas are more solitary and often forage individually.
Their habitat includes rocky slopes and scrublands, which provide both shelter and hunting grounds. They are highly adaptable and can survive in dry environments, often scavenging for food. Striped hyenas are known for their ability to thrive in less populated areas, which helps them avoid conflicts with larger predators.
Deserts: The Aardwolf’s Unique Habitat
Now, let’s talk about the aardwolf. This unique hyena species is quite different from the others, primarily feeding on termites instead of large prey. Aardwolves can be found in eastern and southern Africa, often in dry, open grasslands and savannas.
Their habitats are a mix of open areas and sparse vegetation, which is ideal for hunting insects. These nocturnal creatures rely on their keen sense of smell to locate termite mounds. The aardwolf’s ability to live in such dry habitats showcases how diverse hyenas can be in their adaptations and lifestyles.
Human Impact on Hyena Habitats
Of course, no conversation about where hyenas live is complete without discussing the impact of humans. As cities expand and agriculture pushes into natural habitats, hyenas face numerous challenges. Habitat loss is a significant problem, leading to declining populations in some areas.
Hyenas often come into conflict with farmers and ranchers, who see them as threats to livestock. This conflict can lead to negative perceptions of hyenas, despite the important ecological roles they play in their environments. Honestly, it’s crucial for us to recognize their value as scavengers and help develop strategies that allow humans and hyenas to coexist peacefully.
So, where do hyenas live? They inhabit diverse environments, from the grassy savannas of Africa to the rocky slopes of mountains and even deserts. Their adaptability is fascinating, and each species has carved out its niche in the animal kingdom.
Understanding their habitats is vital for conservation efforts. By recognizing the challenges they face and the importance of their roles in ecosystems, we can work towards a future where hyenas and humans share the land harmoniously. After all, these incredible animals deserve our respect and protection, don’t you think?