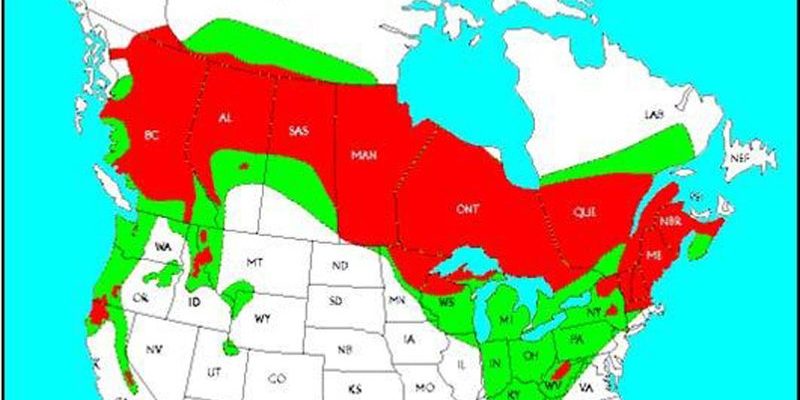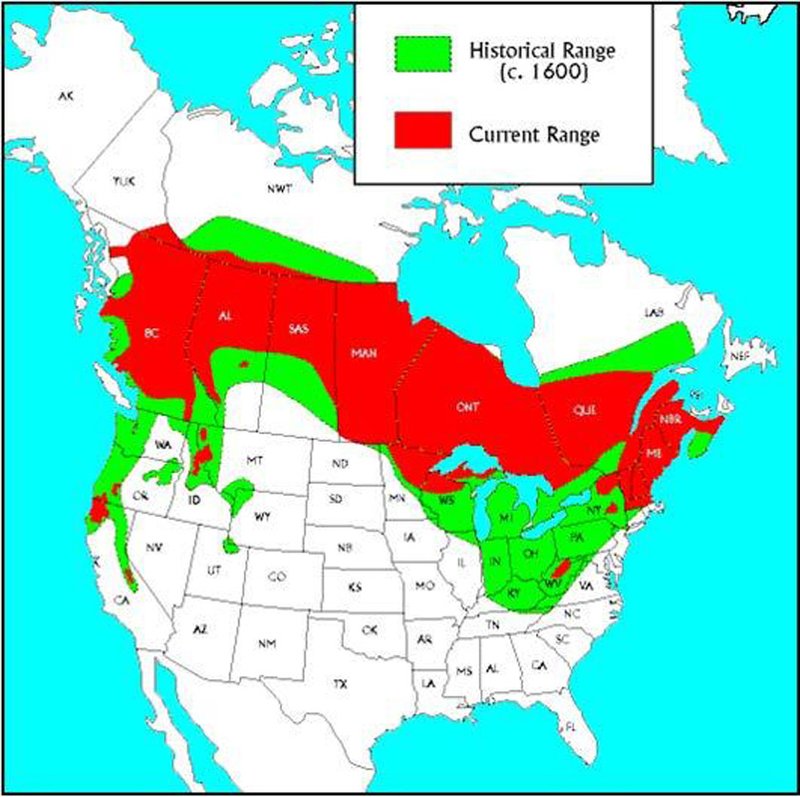
So, where exactly do these elusive creatures call home? To answer that, let’s explore the various environments where fishers thrive and what makes those spots just right for them. Think of it like peeling back the layers of an onion; each layer reveals a bit more of their world. You’ll start to see not only where fishers live but also why their habitats are crucial for their survival.
What Are Fishers?
Before we get into where fishers live, let’s clarify what they are. Fishers are medium-sized mammals that belong to the weasel family. They’re known for their slender bodies, dark brown fur, and long bushy tails. You might be wondering why they’re called fishers if they don’t primarily eat fish. Here’s the thing: these critters got their name from early European settlers who noticed that fishers often hunt in trees and might catch small rodents or birds, but they’re also adept at snatching up fish if the opportunity arises.
Fishers are agile climbers, which means they can navigate through dense forests and are often found in the canopy of trees. They weigh between 5 to 13 pounds and measure about 30 to 40 inches long, including their tails. This combination of size and skill makes them fascinating animals to observe, but they’re also pretty elusive.
Understanding the fisher’s biology and behavior helps set the stage for discussing their habitat and distribution. Now, let’s delve into where you’re likely to find these interesting creatures.
Forest Habitats: The Fisher’s Preferred Home
Fishers primarily inhabit mixed coniferous and deciduous forests. These areas provide the cover and food sources that fishers need to thrive. The mix of trees allows them to climb and hunt effectively. They are particularly fond of old-growth forests because these environments offer dense canopies, abundant prey, and a multitude of hiding spots.
You might be surprised to learn that fishers are quite adaptable. While they prefer mature forests, they can also be found in younger forests and areas that have been selectively logged, as long as there’s enough overhead cover. Their adaptability makes them somewhat resilient, which is vital when faced with changing environments.
Another interesting aspect of their habitat is the availability of water sources. Fishers tend to live near streams and rivers, where they can hunt for food and stay hydrated. These areas also tend to have a rich biodiversity, providing plenty of prey options.
Geographic Distribution of Fishers
Now that we know about their preferred habitats, let’s talk about where fishers are actually found. Fishers are primarily distributed across North America, with their range extending from southern Canada down into the northern United States. You’ll find them particularly concentrated in regions like the Appalachian Mountains, Great Lakes region, and the northern Rockies.
While fishers used to inhabit a broader area, they faced population declines due to over-trapping and habitat loss in the early 1900s. Thanks to conservation efforts and protective measures, their numbers are recovering, and their range is expanding again. It’s heartening to see these remarkable mammals reclaiming parts of their former territories!
Interestingly, you might find fishers in areas that have been recently reforested. Ecologists are studying how successful the reintroduction of trees impacts fisher populations and whether they can thrive in restored habitats.
Climate Influence on Fisher Habitats
The climate plays a significant role in the distribution and survival of fishers. They prefer cooler climates because these temperatures help them thrive, while warmer areas might not support their lifestyle. Cold, snowy winters benefit fishers by allowing them to hunt using their keen sense of smell to track prey beneath the snow.
You might be wondering how climate change affects these creatures. As temperatures rise and habitats change, fishers could become more restricted in their range. They’re sensitive to disruptions in their environment, which could alter their food supply or make it harder for them to find suitable habitats.
Understanding the effects of climate on fishers helps us appreciate their delicate place in the ecosystem. We need to consider how protecting their habitats can help these animals adapt to changing conditions.
The Importance of Connectivity in Habitats
Another crucial aspect of fishers’ habitats is connectivity. Fishers need access to various habitats to maintain healthy populations. Fragmentation due to human activities—like roads, cities, and agriculture—can isolate populations and hinder their ability to find mates or food.
Wildlife corridors are essential for facilitating movement between habitats. These corridors can help fishers and other wildlife traverse areas that would otherwise be barriers. For instance, preserves and conservation easements can create safe passages for these animals, allowing them to thrive.
You might think of it as ensuring that wildlife can move freely, like connecting dots on a page without drawing a line through barriers. Conservation efforts aim to maintain these vital connections, keeping populations healthy and robust.
Threats to Fisher Habitats
Despite their adaptability, fishers face several threats to their habitat and distribution. Deforestation is one of the most significant issues. As forests are cleared for agriculture or urban development, the natural habitats that fishers rely on diminish. It’s a tough situation because, without sufficient cover and food sources, fishers struggle to survive.
Additionally, climate change poses a serious risk. As temperatures rise, their habitats shift, meaning fishers could lose access to the areas they once thrived in. Invasive species can also disrupt the delicate balance of ecosystems, making it harder for native species like fishers to coexist.
Another threat comes from human activities, such as trapping and hunting. While regulations have improved, it’s crucial to continue raising awareness about responsible wildlife management. By understanding the challenges fishers face, we can better advocate for their conservation.
Conservation Efforts and Future of Fishers
Fortunately, there are many conservation efforts underway to ensure fishers continue to thrive. Wildlife agencies and organizations focus on habitat restoration, protection, and public education. This means creating more designated conservation areas and ensuring those areas connect effectively.
Programs that promote sustainable land use practices can also help. By working with local communities to promote conservation, we’re not just protecting fishers but also the entire ecosystem they rely on.
As you can see, the future of fishers depends on a collaborative effort between scientists, conservationists, and the general public. By understanding where they live and the challenges they face, we can better appreciate these incredible creatures and work together to secure their future.
Ultimately, knowing where fishers live isn’t just about finding them on a map. It’s about understanding the complex web of life they’re a part of. So the next time you think about these elusive mammals, remember the forests, streams, and conservation efforts that keep them thriving. Let’s work together to protect their homes!