First discovered in the late 19th century, fruit flies have become a staple in laboratories around the world. They’re like the trusty toolbox of the geneticist, offering insights into everything from basic biology to complex genetic disorders. Let’s dive into their history and evolution, exploring how these tiny flies have changed the way we understand genetics.
The Discovery of Drosophila
In the late 1800s, scientists were beginning to scratch the surface of genetics. In 1890, a young biologist named *Thomas Morgan* stumbled upon the fruit fly while working at Columbia University. He was searching for a model organism to study inheritance patterns, and fruit flies turned out to be a goldmine.
What makes them so appealing? For starters, they reproduce quickly—one fruit fly can produce hundreds of offspring in just a couple of weeks. Plus, they have a relatively simple genetic structure, making it easier to trace traits from one generation to the next. So, when Morgan saw the tiny flies hanging around some fermenting fruit, he knew he’d uncovered something special.
Morgan and his team soon discovered that fruit flies had distinct traits, like eye color and wing shape. Their experiments revealed how traits were passed down through generations, laying the groundwork for the field of genetics we know today. Honestly, it’s like finding a hidden treasure in your backyard!
The Role of Fruit Flies in Genetics
So, how exactly have fruit flies shaped our understanding of genetics? Well, they’ve played a huge role in demonstrating that the rules of heredity apply to all living things, not just plants or animals. Morgan’s pioneering work with fruit flies showed that genes are carried on chromosomes and that variations occur through mutations.
Here’s where it gets interesting: fruit flies have only four pairs of chromosomes. This simplicity allows researchers to easily identify mutations and track changes across generations. That’s like having a tiny science lab right on your kitchen counter!
Researchers have used fruit flies to study a variety of genetic concepts, including the workings of the X and Y chromosomes in sex determination. They’ve also been instrumental in identifying genes responsible for diseases. For instance, studies on fruit flies have provided insights into how genes might contribute to conditions like cancer and Alzheimer’s. This might seem a bit far-fetched, but it’s true!
Fruit Flies and Evolutionary Biology
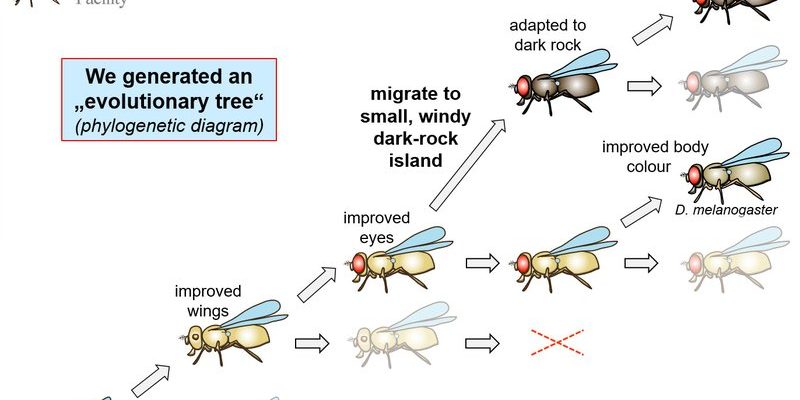
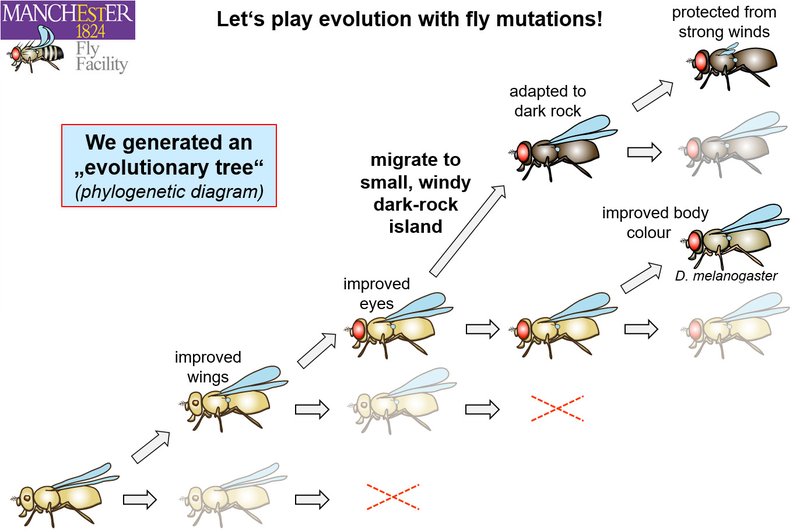
Let me explain something that might surprise you: fruit flies aren’t just important for genetic studies—they also offer a glimpse into the process of evolution. They have a fascinating ability to adapt to their environment, which researchers study to understand evolutionary mechanisms in other species.
For example, scientists have observed that fruit flies living in different environments often develop unique traits that help them survive. This is a classic case of natural selection in action, where certain genetic traits become more common based on their advantages in a given setting.
Imagine a group of fruit flies on a rotting apple and another group on a pear. Over time, the flies adapting to the apple may develop preferences for that fruit and become more adept at surviving there. This ongoing study not only informs us about fruit flies but also paints a broader picture of evolutionary processes.
Modern Applications and Genetic Engineering
You might be wondering how fruit flies are still relevant today. Well, in the age of genetic engineering, they remain at the forefront of research. Scientists use them to understand genetic mechanisms that can be applied to other species, including humans. They’ve even played a role in groundbreaking advances like CRISPR technology, which allows for precise editing of genes.
This technology holds the potential to treat genetic disorders, enhance food crops, and even combat diseases like malaria. The simplicity of using fruit flies in lab settings means researchers can conduct experiments more efficiently, helping to accelerate discoveries and applications that benefit humanity.
Imagine a future where genetic diseases can be easily corrected or where crops can withstand harsh conditions. Fruit flies are helping to lead the way to that future, giving us hope for a healthier world.
Ethical Considerations in Fruit Fly Research
As with any scientific research, using fruit flies comes with its own set of ethical considerations. Animal welfare is a topic of discussion, and while fruit flies are significantly less complex than mammals, the implications of genetic research raise questions about the responsibility researchers have when manipulating life forms.
Here’s the thing: as scientists delve deeper into the genetic code of fruit flies, they must carefully navigate the moral landscape of their findings. What does it mean if we can change traits or eliminate certain genetic conditions? The balance between innovation and ethical responsibility is crucial in research.
It’s essential that researchers adhere to ethical guidelines while pursuing knowledge. Transparency, responsibility, and respect for all living organisms should be guiding principles as we continue to explore the depths of genetics.
The Future of Fruit Fly Research
Looking ahead, what’s next for fruit fly research? With the rapid advancements in technology, the future is bright. Researchers are continually discovering more about the genetic makeup of fruit flies, which could lead to novel therapies for human diseases.
Additionally, the use of fruit flies in studying complex behaviors is on the rise. Scientists are beginning to explore how genetics interact with environment and behavior, providing insights into everything from social structures in groups to learning and memory.
As we learn more about fruit flies, we can apply that knowledge to a broader context. Understanding how these tiny creatures live and thrive might help us tackle bigger issues, like climate change or public health challenges. It’s like finding the keys to a treasure chest of knowledge that could unlock solutions for many of our current problems.
In Conclusion
In a world where even the smallest creatures can leave a big impact, fruit flies stand out as remarkable allies in our quest for knowledge. Their journey from the laboratory to the dinner table has been woven into the very fabric of genetic research and evolutionary biology.
Through their story, we see a path from discovery to innovation, showcasing how tiny organisms can provide profound insights into the mysteries of life. So, the next time you see a fruit fly buzzing around your fruit bowl, remember—they’re not just pests; they’re tiny pioneers, helping us understand the world and ourselves a little better. By embracing the lessons they teach, we’re not just advancing science but also paving the way for a healthier, more informed future.