Imagine a bustling city filled with workers, each performing essential jobs that keep everything running smoothly. That’s kind of like a fruit fly in the natural world. Beyond just being a nuisance, these creatures help with key processes like pollination, decomposition, and even scientific research. Let me explain how they do all this and why it matters more than you might think.
Understanding Pollination: What Is It?
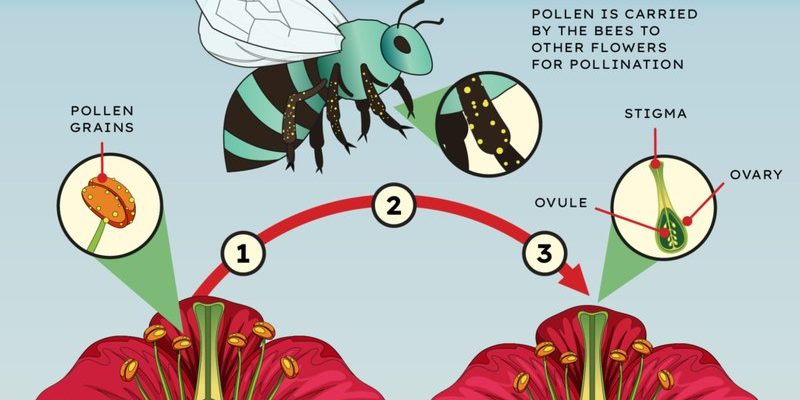
Pollination is like a matchmaking service for plants. It’s how flowers get fertilized so they can produce fruits and seeds. Most people think of bees when they hear the word “pollination,” but a lot of different species pitch in, including our friend, the fruit fly. These little guys are attracted to ripe and rotting fruits, which is like a buffet for them.
When fruit flies land on these fruits, they’re not just having a snack. They end up transferring pollen from one flower to another, helping plants reproduce. It’s a delicate dance that’s essential for the growth of many fruits and vegetables you might enjoy every day, like apples, strawberries, and tomatoes. Honestly, without pollinators like fruit flies, our diets would look pretty different!
The Role of Fruit Flies in Ecosystems
Fruit flies play a significant role beyond just helping plants reproduce. They contribute to the ecosystem in multiple ways, acting as a food source for various predators, including birds and spiders. This doesn’t just mean they’re food; it also means they help keep the balance in nature.
Think of fruit flies as tiny environmental technicians. They break down decaying organic matter, like fallen fruits and other plant debris. This decomposition is crucial because it recycles nutrients back into the soil, helping new plants grow. Without fruit flies doing their cleanup work, areas would become cluttered with waste, which could disrupt local ecosystems.
Fruit Flies and Scientific Research
You might be surprised to learn that fruit flies aren’t just important in the garden or forest—they’re also heavy hitters in the lab! Scientists have used them for decades in genetic studies because of their rapid life cycle and genetic similarities to humans. Fruit flies can reproduce in just a week, giving researchers a lot of data in a short time.
Let’s think about it in simpler terms: if you were conducting a study on inheritance, fruit flies would be like a fast track ticket. They allow scientists to observe genetic traits and mutations over multiple generations quickly. This research has led to breakthroughs in understanding genetics, diseases, and more. Who knew that the tiny pest flying around your kitchen could help us understand serious health issues?
Fruit Flies: The Good, The Bad, and The Ugly
Although fruit flies contribute positively in many ways, it’s also important to recognize the downsides. They can be pests, multiplying quickly in homes and kitchens, especially when there’s overripe food around. These swarming critters can be annoying, but there are effective ways to manage them.
If you’re dealing with an infestation, here’s the thing: don’t just reach for the pesticide. You might want to try some natural traps. A simple method is to pour a bit of vinegar into a bowl, cover it tightly with plastic wrap, and poke small holes in the top. The smell attracts the flies, but they get trapped inside. It’s a harmless way to deal with a bothersome problem.
How You Can Support Fruit Flies
Now that you know how important fruit flies are, you might be wondering how you can support them in your own garden or local environment. Thankfully, it’s pretty simple! Here are a few quick ways to help these little guys thrive:
- Plant flowers: Choose flowering plants that attract fruit flies, such as marigolds or daisies.
- Compost: Create a compost pile for organic waste, which can provide them with food and habitat.
- Avoid pesticides: Use natural methods for pest control that won’t harm beneficial insects.
By supporting fruit flies, you’re contributing to healthier ecosystems and promoting biodiversity. It’s a win-win!
The Intriguing Life Cycle of Fruit Flies
The life of a fruit fly is fascinating in its own right. They go through four stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. This journey is rapid, with complete development from egg to adult taking just about seven to ten days under the right conditions.
Imagine tiny eggs hatching into larvae, which then munch away on rotting fruit—it’s like a mini version of a nature documentary happening right in your kitchen. After a few days of feasting, the larvae find a safe place to pupate. It’s during this stage that they undergo amazing transformations, emerging as adults ready to carry on the cycle. This fast-paced life cycle is one reason they can quickly become a nuisance.
So next time a fruit fly buzzes past your ear, consider giving it a break. These tiny creatures do far more than annoy us; they play crucial roles in pollination, ecosystems, and even scientific advancements. By understanding their importance, we can appreciate them for the vital work they do.
Whether you’re managing them in your kitchen or encouraging them in your garden, remember that fruit flies are more than pests—they’re significant players in the natural world. Embrace their presence and the benefits they bring; after all, they help keep our environment, and even our research, thriving!