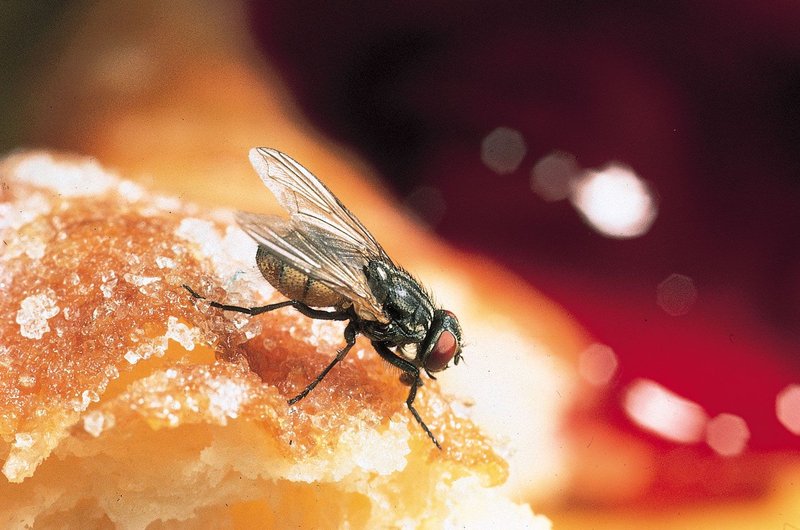
Houseflies are not just random pests. They are incredibly adaptable creatures that can be found in just about every corner of the world. From the warm kitchens of your home to the outdoors, they know how to make themselves at home anywhere. How do they do that? Let’s dive into their habitat preferences, survival strategies, and how they fit into our ecosystems.
Typical Habitats of Houseflies
Houseflies are like those friends who can crash at any party. They’re found in a variety of locations, but they prefer areas where food waste or organic matter is present. You might find them buzzing around:
- Kitchen counters
- Garbage cans
- Animal waste
- Farms and markets
These areas provide the essential food sources that houseflies need to survive and breed. They thrive in warm environments, generally between 70°F to 90°F (21°C to 32°C). You might notice them hanging around during summertime or in heated indoor spaces during winter.
Interestingly, houseflies can breed rapidly in ideal conditions. A female can lay up to 150 eggs at a time, often near food sources or waste. This ability to reproduce quickly helps ensure their survival even when facing predators or environmental challenges.
Adaptation: The Key to Survival
You might be wondering how houseflies manage to live in such diverse environments. Here’s the thing: they are masters of adaptation. Their bodies and behaviors have changed over time to help them cope with different habitats and food sources.
For instance, houseflies have specialized mouthparts called sponging mouthparts, which allow them to soak up liquid food. This is particularly handy when feeding on things like spilled soda or decaying fruits. Additionally, their compound eyes give them almost a 360-degree view of their surroundings, making it easier to spot potential threats and food.
Another significant adaptation is their life cycle. They can develop from egg to adult in as little as seven to ten days, depending on the temperature and food availability. This rapid life cycle allows them to quickly repopulate after any population drops due to environmental factors.
How Houseflies Contribute to Ecosystems
You might think of houseflies as just pests, but they actually play an essential role in our ecosystems. They are not just consumers of waste; they also help break it down. By feeding on decaying organic matter, they aid in decomposition, which is vital for nutrient cycling in the environment.
Moreover, houseflies serve as a food source for various predators, including birds, spiders, and even some mammals. This makes them a crucial link in the food chain. Without them, many of these predators would struggle to find enough food, potentially impacting the overall ecosystem balance.
Additionally, houseflies can help pollinate plants. As they move from one food source to another, they inadvertently transfer pollen, contributing to the reproduction of several plant species. It’s a small job, but it matters.
Challenges Houseflies Face
Despite their adaptability, houseflies encounter various challenges that threaten their survival. For starters, they have to deal with environmental changes. Pollution, habitat destruction, and climate change can affect their breeding sites and food availability.
Predators are also a major concern. While houseflies have some defensive behaviors, like quick flight and an acute awareness of danger, they are still vulnerable to birds, bats, and other insects. Increased use of pesticides can also pose a significant threat to their populations, disrupting local ecosystems.
On top of that, human intervention can sometimes create unfavorable conditions for houseflies. For example, cleaning up waste more efficiently can reduce their breeding sites, while changes in agricultural practices can limit their food sources.
How Houseflies Adapt to Urban Environments
Urban areas are often filled with opportunities for houseflies, but they also present unique challenges. Fortunately, they have adapted remarkably to thrive in these settings. Houseflies are often seen buzzing around restaurants, markets, and even homes because they have learned to exploit human waste and discarded food.
In cities, houseflies can find food in trash bins, compost heaps, and outdoor dining areas. They also flourish in warmer environments created by buildings and human activities. But living in urban settings also means they have to dodge cars, pedestrians, and various urban predators.
Interestingly, urban houseflies have been observed to develop slight behavioral changes. They may alter their feeding and breeding patterns based on human activities, making them incredibly resourceful insects. Their ability to thrive in these environments showcases their incredible adaptability.
So, where do houseflies live, and how do they adapt? These little creatures have an amazing ability to thrive in diverse environments, thanks to their adaptability and quick reproduction. While they can be pesky, they also play meaningful roles in ecosystems, contributing to decomposition and serving as food for other animals.
Understanding houseflies can give us a greater appreciation for the little things in our environment—even the ones that drive us a bit crazy. After all, every creature, no matter how small, has its place in the world. Whether you see them as pests or players in nature, houseflies are remarkable insects with a fascinating story to tell.