Think of the story of the elephant seal as a dramatic blockbuster. It has twists, turns, and characters that highlight the resilience and adaptability of nature. Initially, elephant seals were land-dwelling creatures, but environmental pressures have shaped them into the unique beings we recognize now. Their evolution tells us not just about their journey but also about how species adapt to survive in changing environments.
So, grab your favorite cup of coffee, and let’s explore the evolutionary journey of the elephant seal!
What Are Elephant Seals?
Elephant seals belong to the family Phocidae, which is commonly known as the true seals. Their name comes from the males’ large size and distinctive proboscis, which resembles an elephant’s trunk. The most well-known species are the Northern and Southern elephant seals, found along the coasts of the northern and southern hemispheres.
These animals can reach impressive weights, with males weighing up to 4,500 pounds (that’s about the weight of a small car!) and measuring over 20 feet long. Females are smaller but still hefty, averaging around 1,500 pounds. Their thick blubber provides insulation against the cold ocean waters and acts as a reserve for energy during fasting periods.
When you see an elephant seal lounging on a beach, it might look like a big, lazy blob—trust me, there’s a lot more going on beneath that blubber!
The Origins of Elephant Seals
Let’s rewind the clock a bit. The ancestors of modern elephant seals are believed to have originated around 30 million years ago during the Oligocene epoch. Back then, they were quite different from the seals we know today. The story starts with the migration of these ancestors to marine environments. It’s like they went on a long journey, gradually trading land life for the ocean’s bounty.
Interestingly, these early seals were more closely related to terrestrial mammals than we might think. They were adapted to life on land, somewhat like modern-day sea lions. However, as their environment evolved and they faced various challenges, they adapted to a life in the water. Natural selection played a crucial role here; the seals that were better at swimming and hunting in the ocean survived and thrived.
In this oceanic journey, their bodies transformed to become streamlined for swimming. Their limbs evolved into flippers, allowing them to navigate underwater with surprising grace. It’s a beautiful reminder that change is often necessary for survival.
Adaptations for Survival
One of the most remarkable features of elephant seals is their ability to dive deep into the ocean. They can reach depths of over 5,000 feet! To put that in perspective, that’s deeper than the height of Mount Everest! So, how did they become such extraordinary divers? It all comes down to a combination of physical adaptations.
First, let’s talk about their respiratory system. Elephant seals have a more efficient way of using oxygen than many other animals. They can hold their breath for up to two hours while diving, thanks to their large lung capacity and ability to store oxygen in their muscles. This adaptation allows them to hunt for food at great depths, where fish and squid are abundant.
Additionally, their thick layer of blubber acts as a thermal barrier, keeping them warm in icy waters. This means they can spend long periods at sea, feeding and growing without the need to return to shore frequently. Their size also helps deter predators like orcas, as the few things that dare to attack such a hefty animal often think twice when facing adult males.
Breeding and Social Structure
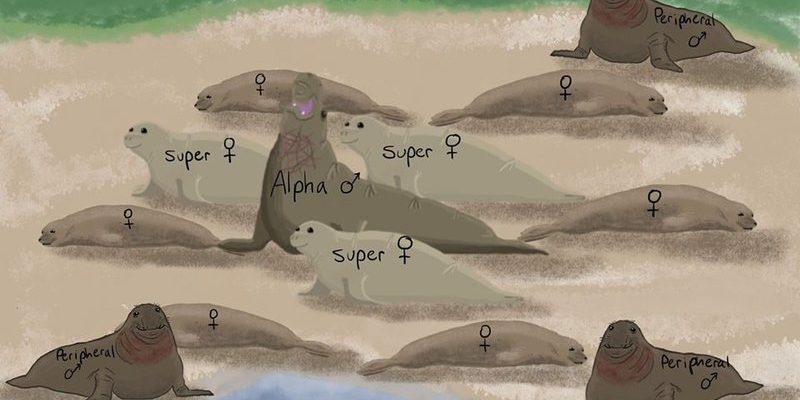
Breeding season is an exciting time for elephant seals—it’s like a reality show filled with drama! Male elephant seals can be fiercely territorial, engaging in intense fights for the right to mate with females. Dominant males often gather harems of females, and these harems can comprise dozens of individuals.
The female elephant seal typically gives birth to a single pup after a gestation period of about 11 months. These pups are born weighing around 60 pounds and start gaining weight rapidly, thanks to their mother’s rich milk. It’s an intense few months, as mothers fast while nursing their pups, relying on their blubber reserves.
During this time, communication is key. Mothers and pups recognize each other through unique vocalizations. Imagine the sweet sounds of a baby seal calling for its mom amidst the chaos of the beach!
Conservation Status and Challenges
Despite their impressive adaptations and remarkable resilience, elephant seals faced significant challenges in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Overhunting nearly drove them to extinction due to the demand for their blubber, which was used for oil. At one point, only a few hundred Northern elephant seals were left.
Thanks to conservation efforts and legal protections, their numbers have rebounded to over 200,000 today. However, they still face ongoing threats, such as climate change, entanglement in fishing gear, and habitat loss. It’s a stark reminder of how interconnected we all are and the responsibility we have to protect these magnificent creatures and their habitats.
The evolutionary journey of the elephant seal is a testament to the resilience of nature. From their humble beginnings as land-dwelling mammals to the majestic ocean-focused seals we see today, their story reflects not just survival but adaptation and innovation.
As we learn more about these incredible animals, it’s essential to support their conservation and ensure they thrive for future generations. So, the next time you see an elephant seal lounging on the beach or gliding through the water, think about their incredible journey. They are not just entertaining creatures; they’re a reminder of how life can adapt, change, and endure, despite the odds.
The elephant seal’s journey continues, and it’s a beautiful one worth following!