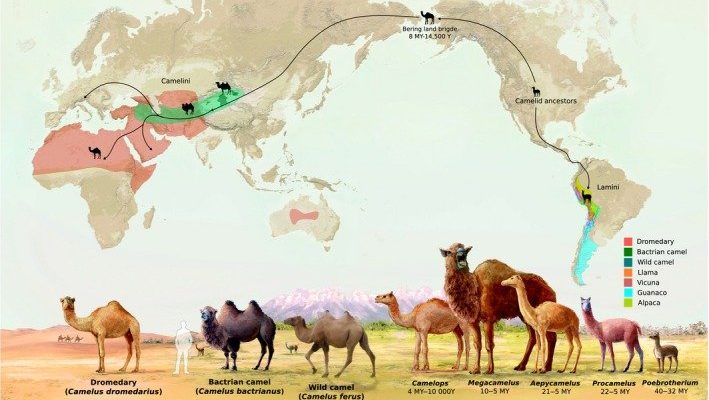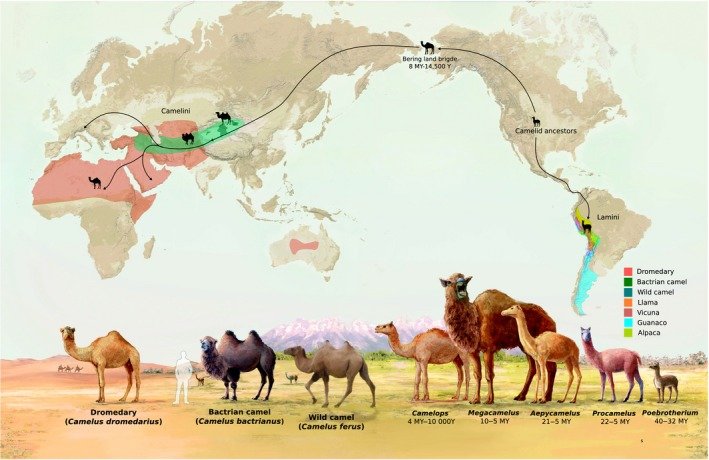
When we think of camels, we often conjure images of the Middle East or North Africa. But did you know that two distinct species of camels exist, each with its own unique habitat? The Dromedary, with a single hump, primarily inhabits regions like the Arabian Peninsula and parts of Africa. In contrast, the Bactrian camel, boasting two humps, roams the cold deserts of Central Asia. Understanding these habitats not only highlights the remarkable adaptability of camels but also sheds light on the environmental challenges they face.
The Dromedary Camel: A Desert Dweller
The Dromedary camel, known for its single hump, is predominantly found in hot, arid regions. You can largely find these camels in places like Saudi Arabia, Somalia, and other parts of North Africa. Imagine walking through a hot desert, where the sun blazes down, and there’s hardly a drop of water in sight. This is where the Dromedary thrives.
These camels are perfectly designed for desert life. Their long legs help them navigate sandy terrains, while their unique feet prevent them from sinking into the sand. Plus, they can go for several days without water. When they do drink, they can gulp down a staggering amount—in some cases, nearly 40 gallons in one go! This incredible ability allows them to endure the harsh conditions where other animals might struggle.
Another fascinating aspect of Dromedary camels is their social structure. They are often found in groups, which helps them stay protected from predators. Living in herds can also be beneficial for finding food and water sources as they navigate their arid homes. So, the next time you see a Dromedary, remember that it’s not just surviving; it’s thriving in an environment that would challenge most other creatures.
The Bactrian Camel: Thriving in the Cold
Now, let’s shift gears and talk about the Bactrian camel. Unlike its Dromedary cousin, the Bactrian camel is built to handle cold climates. You can find them primarily in Mongolia and parts of China. Picture the rugged, chilly landscape of the Gobi Desert; that’s the Bactrian’s playground.
These camels are equipped with two humps, which store fat that they can use for energy during tough times. This fat storage is crucial for survival in their harsh habitats, where food can be scarce, especially during winter. When temperatures plummet, Bactrian camels have an incredible ability to adapt—growing a thick coat of fur to keep warm.
Much like the Dromedary, Bactrian camels also thrive in social groups. They often travel in herds, which helps them find resources and provides safety from predators. Plus, their strong, sturdy bodies make them ideal for carrying heavy loads across the challenging terrain of Central Asia. It’s a testament to how camels have embraced their environments, whether it’s scorching heat or biting cold.
Expanding Their Range: Domestic Camels
While wild camels are found in specific regions, domesticated camels have a wider distribution. Humans have been domesticated these creatures for thousands of years, primarily for transportation, trade, and even as a source of milk and meat. You might be surprised to learn that you can find domesticated camels in places far beyond their wild habitats.
Countries like India, Afghanistan, and even parts of Australia have populations of domestic camels. In these areas, they serve various purposes, from serving as pack animals to participating in festivals. For example, in Rajasthan, India, camels are decorated and showcased in vibrant parades, highlighting the cultural significance of these animals.
The adaptability of domestic camels is impressive. They can thrive in diverse climates, from deserts to semi-arid regions, showcasing their resilience. However, this also leads to challenges, as more people rely on them for work and livelihood, impacting their habitats.
Camels and Climate: Challenges They Face
As we explore where camels live, it’s essential to touch on the challenges they face. Climate change significantly impacts their habitats, especially in desert and semi-desert regions. Rising temperatures and fluctuating rainfall patterns threaten the delicate balance of their ecosystems.
For Dromedaries, increased heat can result in decreased water availability, drastically affecting their ability to survive in arid landscapes. Similarly, Bactrian camels face habitat loss due to industrialization and land development in Central Asia. As their environments change, food sources become scarcer, posing a significant challenge for these resilient creatures.
Moreover, human activities, such as overgrazing and land-use changes, further strain the natural resources camels depend on. As we become more aware of these challenges, it’s crucial to consider how we can help protect these magnificent animals and their habitats.
Conservation Efforts: Protecting Camel Habitats
With the challenges mentioned above, conservation efforts are more important than ever. Various organizations and groups work tirelessly to ensure the survival of these iconic animals and their habitats. These efforts often focus on preserving natural ecosystems and promoting sustainable practices among local communities.
For instance, some organizations help educate communities about the importance of camels and their role in the environment. By promoting sustainable grazing practices and supporting eco-friendly tourism, we can help reduce the pressure on camel populations and their habitats.
Additionally, breeding programs are being implemented to ensure the genetic diversity of both Dromedary and Bactrian camels. These programs aim to maintain healthy populations while also reintroducing camels to areas where they have become scarce. It’s a hopeful step toward preserving these remarkable creatures and the beautiful landscapes they inhabit.
The Cultural Significance of Camels
Finally, we can’t ignore the cultural significance of camels around the world. In many countries, these animals are more than just a means of transportation; they’re deeply woven into the fabric of local traditions, festivals, and folklore. For example, in the Middle East, camels play a vital role in various cultural celebrations and are even considered a symbol of status.
In addition to their practical uses, camels are often featured in art, literature, and songs, showcasing their importance to the communities that rely on them. In many regions, camel racing and beauty contests are popular events, drawing large crowds and highlighting the pride people take in their camels.
As we learn more about where camels live and their importance in different cultures, it becomes clear that these animals are much more than just creatures of the desert. They are an integral part of human history and continue to shape the lifestyles of many communities today.
In conclusion, camels have adapted to a wide variety of habitats, from the blistering heat of the deserts to the icy landscapes of Central Asia. Whether it’s the Dromedary roaming the hot sands or the Bactrian braving the cold, these incredible creatures have fascinating stories to tell. By understanding where they live and the challenges they face, we can better appreciate their role in our world and work toward ensuring their future.