Dung beetles have been around for a long time—way before dinosaurs roamed the earth. Their history is fascinating, filled with evolution, adaptation, and an unshakeable commitment to their ecological role. So, let’s dig into the evolution and history of these remarkable critters!
The Early Days of Dung Beetles
Dung beetles belong to a group called Scarabaeidae, which dates back to the Jurassic period, around 150 million years ago. Imagine life when giant reptiles ruled the land and lush forests surrounded them. Dung beetles thrived in this environment, breaking down the waste of herbivorous dinosaurs. In a way, they were nature’s first recyclers, turning what could be seen as trash into nutritious fertilizer for plants.
As they adapted to their surroundings, dung beetles developed various behaviors and body types. Some species became adept at tunneling, while others took to the surface, rolling dung into neat balls. This evolutionary diversity allowed them to occupy various niches in different ecosystems. You might be wondering how they even found dung in the first place. Well, dung beetles have an incredible sense of smell, allowing them to locate dung from miles away. Just think of them as tiny waste detection experts!
Types of Dung Beetles
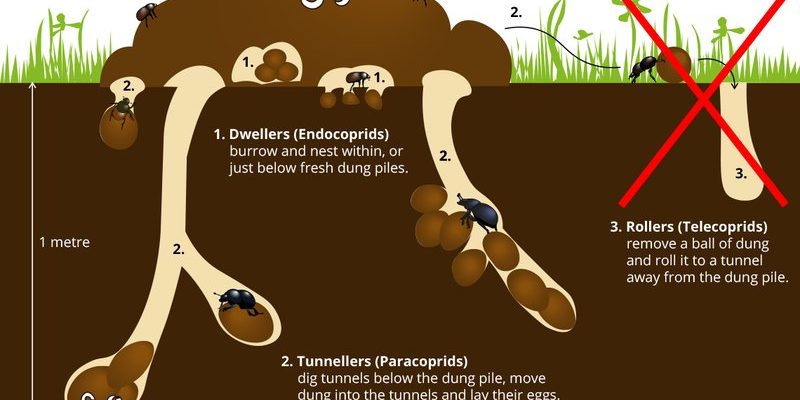
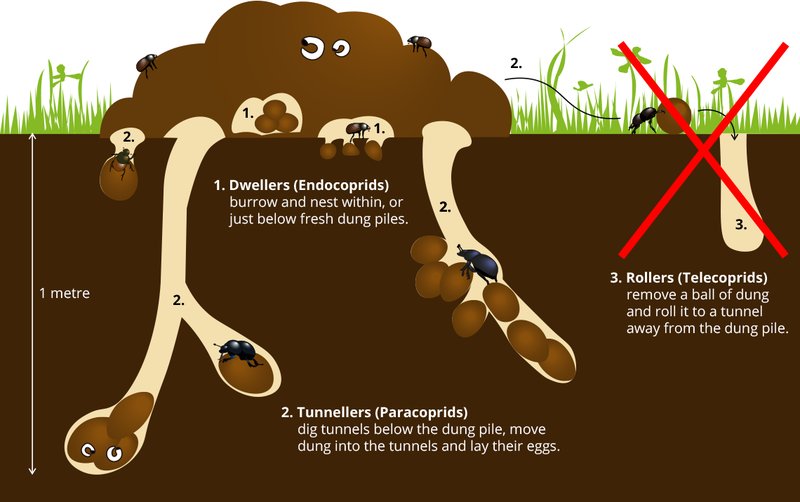
There are over 7,000 species of dung beetles, and they can be categorized into three main groups based on their behavior: rollers, tunnelers, and dwellers.
- Rollers: These beetles are like tiny bulldozers, rolling balls of dung back to their burrows. They can create balls that are several times their own body size!
- Tunnelers: Instead of rolling dung away, tunnelers dig directly into the ground to bury it. This behavior is vital for aerating the soil and enriching it with nutrients.
- Dwellers: These beetles live among the dung, not burying it but feeding on it directly. They help break the dung down, further contributing to nutrient recycling.
Each type plays a unique role in the ecosystem, assisting with decomposition and soil health. Honestly, without dung beetles, the world would be a lot messier!
Dung Beetles Through the Ages
Fast forward to today, and dung beetles continue to thrive, despite the many changes happening in our environment. Their resilience is remarkable. For millions of years, they’ve adapted to various climates and habitats, from tropical rainforests to arid deserts. And let’s not forget, they’ve even left their mark on human culture! Ancient Egyptians revered dung beetles, seeing them as symbols of regeneration and protection. They believed the beetle’s rolling behavior mirrored the sun’s journey across the sky.
In our modern world, dung beetles are still important. They help control parasites in livestock waste, which can be beneficial for farmers. By breaking down the manure, they reduce the number of harmful pathogens that could spread to animals and humans. Here’s the thing: their role in agriculture is vital, impacting food production and sustainability.
The Ecological Impact of Dung Beetles
So, why should we care about dung beetles? The truth is, they contribute tremendously to the health of our ecosystems. Dung beetles break down waste, returning vital nutrients to the soil, which supports plant life. The more dung beetles there are, the healthier and more robust the ecosystem becomes.
These little creatures also help control pests. When they bury dung, they’re not just cleaning up; they’re also disrupting the life cycles of parasites and flies that typically breed in animal waste. This behavior can reduce the spread of diseases in livestock, ultimately aiding in food security. If you think about it, dung beetles might just be the unsung heroes of agriculture!
Challenges Facing Dung Beetles
Despite their contributions, dung beetles face numerous challenges today. Habitat destruction, climate change, and pesticide use are all threats to their populations. With fewer natural habitats to call home, many species are at risk. You might be wondering what we can do to help. Supporting organic farming practices and reducing pesticide use can make a significant difference.
Conserving natural habitats is also crucial. By protecting grasslands and forests, we help maintain the environments where dung beetles thrive. Every little bit counts, and even small changes in our daily lives can contribute to the conservation of these amazing creatures.
The Future of Dung Beetles
Looking ahead, the fate of dung beetles largely depends on our actions. As we understand their significant ecological role, it’s important to increase awareness about preserving their habitats. Researchers continue to study these beetles to learn more about their behaviors, adaptations, and impacts on the environment.
One exciting area of research is the role of dung beetles in carbon sequestration, which is all about capturing and storing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. By breaking down dung and burying it, these beetles might help mitigate climate change. There’s still so much to learn about their potential benefits, and it’s clear that they have a lot to teach us.
From their ancient origins to their critical role in today’s ecosystems, dung beetles are truly fascinating creatures. They might not be the most glamorous insects, but they hold immense value in keeping our environment healthy and balanced. By recognizing their importance, we can take steps to protect them and appreciate their contributions to our world.
So next time you see a dung beetle rolling its little treasure, remember: they’re not just bugs; they’re nature’s cleanup crew, helping maintain the cycle of life! Let’s do our part to ensure they continue to thrive for generations to come.