The story of the African bush elephant is like a giant tapestry, woven with threads of climate changes, migration patterns, and survival strategies. Each stitch tells us something important about how these animals have thrived across the African landscape. So, let’s dive into the past and explore the evolutionary history of these fabulous animals.
Understanding the African Bush Elephant
Before we get into the nitty-gritty of their evolution, it helps to know a bit about what makes African bush elephants unique. First off, they are the largest land animals on Earth. With their huge ears and long trunks, they not only look impressive but also have some serious skills. Their ears act like natural air conditioners, helping to regulate their body temperature in the hot African sun. Their trunks are versatile tools used for everything from grabbing leaves to showering themselves with water.
In terms of behavior, African bush elephants are social animals. They travel in herds led by a matriarch, usually the oldest female. This structure not only helps them protect their young but also means they have a wealth of knowledge about their environment. Each elephant in the herd has a role, making their social structure a fascinating topic in itself.
You might be wondering how these elephants came to be so adaptive and resilient. Well, their evolutionary tale is long and complex, involving ancestors that roamed the planet millions of years ago.
The Ancestry of Elephants
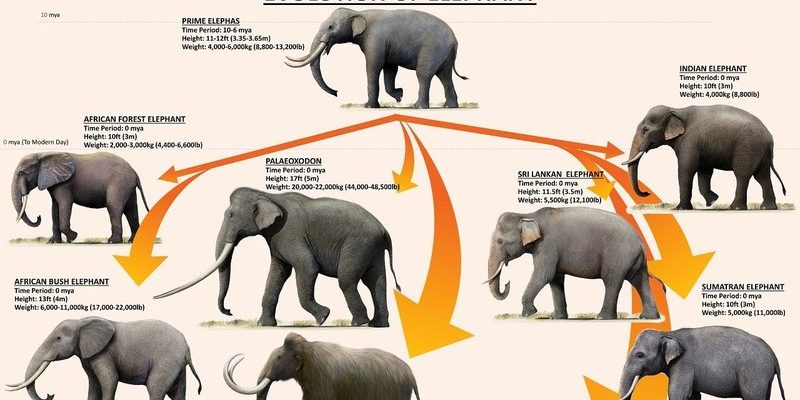
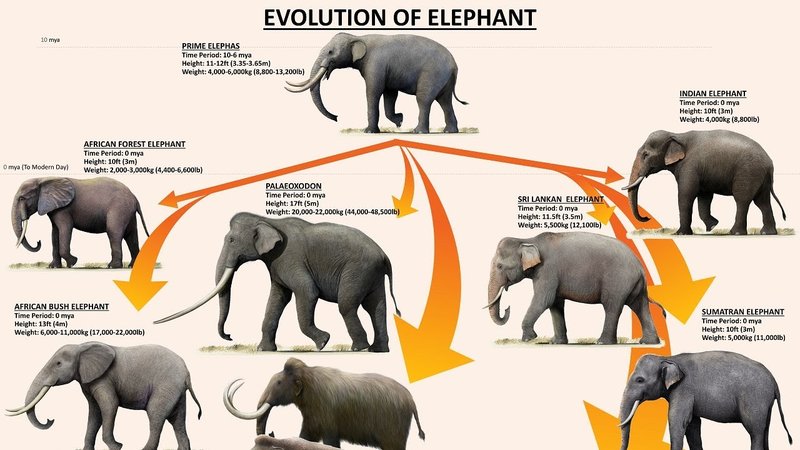
Elephants belong to a group called Proboscidea. Their early ancestors date back around 60 million years ago. If we go even further back, we find that elephants share a common ancestor with animals like manatees and hyraxes. Isn’t that wild? This ancestor was smaller and lived in a different environment, but it set the stage for what would become the mighty elephant.
Today, there are three recognized species of elephants: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. The African bush elephant is significantly larger, with males standing up to 13 feet tall and weighing as much as 14,000 pounds! This size advantage was crucial in their survival, especially in the open savannas where they roam.
As the climate changed over millennia, elephants adapted. For instance, during the last Ice Age, many species of large mammals went extinct. Elephants not only survived but thrived due to their ability to adapt their diet and habitat. Their impressive adaptability is a key reason they are still around today.
Adaptations to Environment
The African bush elephant’s evolution is closely linked to the diverse environments across Africa. These elephants are primarily found in savannas and grasslands where they can roam freely and find plenty of food. Their large bodies require a lot of sustenance, and these environments provide just that.
Their diet consists mainly of grasses, leaves, and fruits. Interestingly, they play a crucial role in their ecosystem by helping to shape it. As they feed, they knock down trees and create clearings that allow other plants to grow. This means they’re not just surviving; they’re actively contributing to their habitat.
The ability to adapt to different environments has also led to variations in their physical characteristics. For example, elephants living in dense forest areas have slightly different body shapes compared to those that roam the open savannah. This diversity showcases how evolution works: creatures change and adapt based on their surroundings.
Social Structure and Intelligence
One of the most fascinating aspects of the African bush elephant is their complex social structure. As mentioned earlier, they live in matriarchal herds. The matriarch is not just the leader but also the wise old sage of the group. She guides the herd to water sources and safe feeding grounds. This communal living enhances their survival, as they can protect one another from predators.
Elephants are incredibly intelligent. They display emotional behaviors such as empathy and grief. For example, when a member of the herd dies, elephants often return to the body, touching it with their trunks and showing signs of mourning. This emotional depth enriches their social bonds and is a testament to their advanced cognition.
Their intelligence allows them to solve problems and communicate with one another effectively. They use a variety of vocalizations and even body language to convey messages. This level of communication is essential for their survival and adds another layer to their evolutionary success.
The Impact of Humans
Unfortunately, the history of the African bush elephant is deeply intertwined with human activity. From hunting to habitat destruction, these elephants have faced numerous challenges over the years. In the past, they were hunted for their ivory, and their populations declined dramatically. Conservation efforts today aim to protect these magnificent creatures and their habitats, but the battle is ongoing.
The development of human settlements and agriculture has also changed the landscape of their habitats. Elephants often find themselves encroaching on farmland, leading to conflicts with humans. These situations can be dangerous for both parties, leading to efforts to create more harmonious co-existence strategies.
Interestingly, some communities have begun to recognize the value of elephants in tourism, seeing them as a vital part of Africa’s natural heritage. This awareness can help protect their future while providing economic benefits to local people.
Conservation Efforts and the Future
The future of the African bush elephant hangs in the balance. Conservation groups are working tirelessly to ensure their survival. They focus on protecting habitats, combating poaching, and raising awareness about the importance of elephants to ecosystems.
Education plays a vital role in these efforts. By involving local communities and educating them about the benefits of preserving elephants, we can foster a more positive relationship. Programs that share the economic advantages of tourism can also create incentives for people to protect these incredible animals.
In recent years, the use of technology has opened new avenues for conservation. Tools like GPS collars and drone surveillance help monitor elephant movements and protect them from poachers. This high-tech approach is just one part of a broader strategy to ensure that future generations can experience the wonder of African bush elephants.
The evolutionary history of the African bush elephant is a story of resilience, adaptability, and community. From their ancient ancestors to their role in today’s ecosystems, these animals remind us of the intricate web of life on our planet. As we continue to learn about their past and present, we must take steps to protect their future.
These magnificent creatures deserve our respect and admiration, and it’s our responsibility to ensure they thrive alongside us. The story of the African bush elephant is still being written, and with concerted efforts, we can ensure that it remains a tale of hope for generations to come.