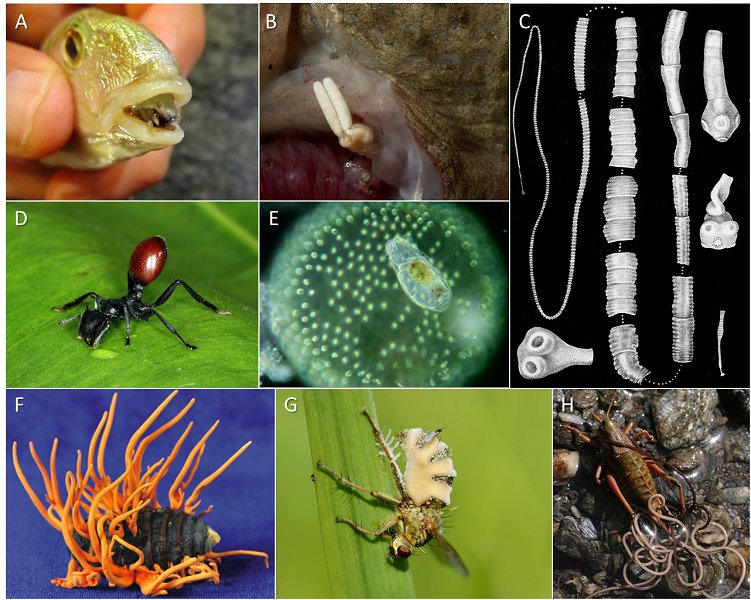
Picture this: you’re hiking through a dense forest, enjoying the sights and sounds of nature, when suddenly you stumble upon an animal that looks a bit off. It might have some unusual growths on its skin, and if you take a closer look, you might find a wolf worm nestled there. Now, you might be wondering why something so “icky” could be important. Let me explain. Wolf worms, scientifically known as *Cuterebra*, play critical roles in **parasite ecology**, helping control host populations and influencing the health of various species.
So, why should we care about these little parasites? For starters, understanding their role helps us get a clearer picture of how ecosystems function. In this article, we’ll dive deep into the world of wolf worms, their life cycle, their impact on wildlife, and what they can teach us about the great web of life surrounding us.
What Are Wolf Worms?
Wolf worms are a type of parasitic fly larvae, primarily belonging to the genus *Cuterebra*. These larvae are often referred to as **bots** due to their unique lifecycle. They mostly target mammals, especially rodents and rabbits. Imagine a tiny invader that starts its life as an egg laid by a female fly on a host animal. Once the egg hatches, the larva burrows into the host’s skin, embarking on a journey that can drastically affect the host’s health.
You might think this sounds terrifying, and you’re not wrong. Wolf worms must navigate the host’s immune system, which sees them as intruders. As they develop, they can cause a variety of health issues for their host, ranging from minor irritation to severe infections. This parasitic relationship is a natural occurrence, and it’s a crucial part of how nature balances itself.
Their lifecycle is captivating and much more complex than it might seem. After spending several weeks or even months inside their hosts, wolf worms eventually emerge, transforming into adult flies. This emerging process sometimes leaves behind noticeable wounds on the host, but many animals manage to heal. The entire process highlights a dramatic aspect of nature—life and death are intrinsically linked.
The Lifecycle of Wolf Worms
Understanding the lifecycle of wolf worms adds context to their ecological role. It begins when a female fly lays her eggs near potential host burrows or nests. The eggs develop quickly, depending on the surrounding environment. When a host brushes against the eggs, they can stick to the skin or fur, and that’s when the real adventure begins.
Once on the host, the eggs hatch into larvae, which then burrow into the host’s skin. They can spend anywhere from 30 to 60 days developing inside, feeding on the host’s tissue. It’s kind of like they’re throwing a long, unexpected party at someone else’s expense. During this time, they’re also inadvertently gathering valuable nutrients, which help them grow strong.
After their time inside the host, the larvae emerge, ready to transform into adult flies. This stage is crucial because it brings the cycle full circle. The emerging flies will go on to lay more eggs, continuing the lifecycle of these intriguing creatures. So, while the idea of parasites might make you squirm, they are a key component in the cycle of life in many ecosystems.
How Do Wolf Worms Impact Their Hosts?
You might be wondering what exactly happens to a host animal that falls victim to a wolf worm. The effects can vary, but generally, the presence of these parasites is more than just a nuisance. In some cases, they can lead to infections or severe reactions in the host, especially if the larvae cause tissue damage as they grow.
For smaller mammals, the presence of wolf worms can significantly impact their health. For example, a young rabbit might struggle to thrive with a wolf worm infestation. Symptoms can include lethargy, weight loss, and even difficulty moving. It’s not uncommon for these animals to succumb to other illnesses or predators, highlighting how these parasites naturally regulate animal populations.
On the flip side, not all hosts will be severely affected. Some animals have developed resistances or coping mechanisms, allowing them to live with the parasites without drastic consequences. This balance is essential, as it ensures that the populations of both the hosts and the parasites remain in check.
The Ecological Role of Wolf Worms
Wolf worms play a surprisingly important role in their ecosystems, acting as natural population control agents. By affecting certain species—usually those that are abundant—wolf worms help keep wildlife populations in balance. When one species becomes too numerous, it can lead to overgrazing or depletion of resources. Wolf worms can help mitigate this by reducing the survival rates of particular animals.
Additionally, the presence of these parasites can promote genetic diversity. When hosts face environmental pressures from parasites like wolf worms, it can encourage the survival of the fittest—those individuals that can cope with or resist such challenges. Over time, this results in populations that are healthier and more robust.
Furthermore, wolf worms also support the food web. When they emerge as adult flies, they become a food source for birds and other predators. This means that even parasites have their place in the grand scheme of things, contributing to the intricate web of life we see in nature.
Human Perceptions and Misunderstandings
Here’s the thing: people often have a negative view of parasites, including wolf worms. But it’s essential to remember that these organisms are part of nature’s design. While they may seem gross or even horrifying, they actually play integral roles in ecosystem health.
Many misconceptions stem from a lack of understanding about how these organisms function and their ecological importance. It’s easy to see them as just harmful pests, but their existence brings several benefits, including **population control** and enhancing the genetic health of wildlife. Their seemingly nasty behavior is just a part of the cycle of life.
Educating ourselves and others about creatures such as wolf worms can shift the narrative. Rather than fearing them, we can appreciate their role in maintaining the delicate balance of our ecosystems.
In a world where we often separate ourselves from nature, understanding the role of wolf worms shifts our perspective on what it means to coexist. These tiny parasites are not just unsightly invaders; they are essential players in the grand game of ecology. They remind us that every creature, no matter how small or strange, has a purpose.
So the next time you hear about wolf worms, think beyond the surface-level yuck factor. These fascinating organisms help shape animal populations, contribute to biodiversity, and uphold the balance of life in their habitats. Embracing the complexity of nature can lead us to deeper understanding and appreciation for all creatures, regardless of their role in the ecosystem. After all, nature thrives on diversity, and we can learn much from its intricacies.