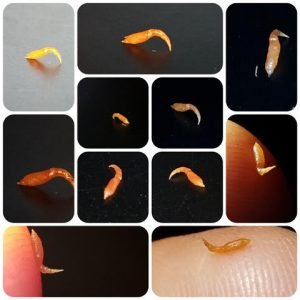
Imagine a tiny hidden world where all sorts of creatures are interacting, feeding, and living off one another. In this world, wolf worms come into play, keeping populations of certain species in check and contributing to the broader health of their habitats. If you’ve ever wondered how all these different life forms are linked, wolf worms offer a glimpse into that intricate balance.
What Are Wolf Worms?
Wolf worms are the larval stage of certain types of flies, specifically those in the *Cuterebra* genus. Think of them as the teenage stage of a fly’s life. Instead of being the typical little flies buzzing around your picnic, these larvae have a more dramatic beginning. They develop inside the bodies of mammals and are commonly found in wild animals like rabbits, squirrels, and even domestic pets. You might be wondering, why do they choose to live inside their hosts? Well, it’s all about survival.
These larvae burrow into their host to feed and grow. It’s a bit like living in an all-you-can-eat buffet – they’ve got everything they need right there. However, this relationship can be a double-edged sword. While wolf worms help control host populations, a heavy infestation can cause serious problems for the host animal, leading to illness or even death. This delicate balance is what makes the study of wolf worms so interesting.
The Life Cycle of Wolf Worms
Understanding the life cycle of wolf worms helps explain why they’re so effective in their role as parasites. Here’s a simple breakdown:
1. Egg Stage: The female fly lays eggs on the skin of potential hosts.
2. Larval Stage: Once the eggs hatch, the larvae penetrate the skin and find their way into the host’s body.
3. Growth Phase: Inside the host, they feed and grow for several weeks.
4. Pupation: Once fully developed, they exit the host to pupate in the soil and eventually emerge as adult flies.
This cycle is crucial for the health of both the worms and their hosts. As wolf worms thrive, they can help keep prey populations in check, which in turn allows ecosystems to flourish. It’s an example of how nature often has a much bigger plan in mind.
Wolf Worms in Parasite Ecology
In the grand scheme of things, wolf worms carry significant weight in parasite ecology. They serve a dual purpose: they act as both predators and prey within their environment. Here’s why this matters:
– Population Control: By infesting certain animal species, wolf worms naturally help regulate their populations. This prevents overpopulation, which can lead to resource depletion.
– Nutrient Cycling: As host animals die from heavy infestations, their bodies return nutrients to the soil, benefiting the ecosystem. It’s nature’s way of recycling.
These aspects are crucial for maintaining a balanced ecosystem, where every creature, large or small, plays a specific role. Just like in a well-orchestrated symphony, every player contributes to the overall harmony.
The Benefits of Wolf Worms
Although they may seem repulsive at first glance, wolf worms contribute positively to their environments. Here are some benefits they offer:
– Biodiversity: By controlling host populations, wolf worms help maintain a diverse range of species in ecosystems, allowing for resilience against diseases.
– Food Source: Adult flies and their larvae serve as food for various other wildlife, including birds and small mammals. This means they’re an important link in the food chain.
In many ways, wolf worms contribute to a sort of balance that keeps ecosystems healthy. It’s a reminder that even the most unappealing creatures have their place in nature’s design.
Common Misconceptions About Wolf Worms
You might have heard some rumors or misconceptions about wolf worms. Let’s clear a few up:
– Myth 1: Wolf worms are harmful to humans.
Truth: While they can certainly cause major issues for their host animals, they don’t typically pose a threat to humans. They are specialized feeders.
– Myth 2: They only exist in remote areas.
Truth: Wolf worms can be found in various environments, including urban areas, particularly if stray or wild animals are present.
Understanding these facts can help shift the narrative around these fascinating creatures. They’re a part of nature’s plan and shouldn’t be dismissed just because they make our skin crawl.
The Future of Wolf Worms in Ecosystems
As ecosystems change due to climate change and habitat loss, the role of wolf worms may also evolve. Some researchers suggest that as their host populations fluctuate, so too could the populations of wolf worms. Here’s what we might expect:
– Adaptation: Just like many species, wolf worms may adapt to changing environments, potentially finding new hosts or habitats.
– Disruption: If host animal populations decline drastically, it could impact wolf worm populations and their ecological role.
The future is uncertain, and that’s part of what makes studying these parasites so thrilling. They hold clues to how ecosystems function and adapt to change.
Wolf worms may not be everyone’s favorite topic, but their role in parasite ecology is crucial. They help maintain balance in ecosystems, control populations, and support biodiversity. Embracing the complexity of nature—including its less glamorous aspects—can lead to a better understanding of our world. So, the next time you hear about parasites, remember the wolf worm and the essential role it plays in the grand tapestry of life. After all, every creature, no matter how small or seemingly unappealing, has a story worth telling.
