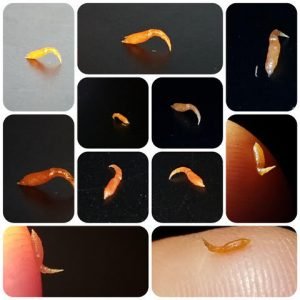
Wolf worms are known for their connection to wolves and other carnivores. They live a bit like tiny spies, waiting in the shadows until it’s time to strike. While this might sound gruesome, it’s all a part of the grand design of nature—a cycle of life where even parasites have a stake. Understanding wolf worms helps us appreciate the balance of ecosystems and how these little worms fit into the bigger picture.
What Exactly Are Wolf Worms?
Wolf worms, or *larvae of the botfly*, are parasitic insects that primarily target wolves and other canids. They might also infect coyotes and domestic dogs. They start their journey as eggs laid on the fur of their host. Once the eggs hatch, the larvae burrow into the animal’s skin. It’s a wild scene, if you think about it—a small worm taking a free ride in a larger creature!
These larvae develop inside the host, feeding on tissues and blood. While this process sounds horrifying, it’s important for wolf worms in their developmental stages. The host animal often shows signs of discomfort, like skin lesions and irritation. However, they typically don’t suffer severe consequences unless the infestation is severe.
You might be wondering why these worms are called “wolf worms.” The name comes from their primary hosts, but they aren’t exclusive to wolves. They can also infect other mammals, showing just how adaptable they can be. This adaptability plays a crucial role in how they interact within their ecosystems.
The Lifecycle of Wolf Worms
The lifecycle of wolf worms is quite fascinating and involves several stages. It all begins when a female botfly lays her eggs on the fur of a host animal. This might happen when the hosts are sleeping or resting—kind of like how some of us leave our shoes at the door without giving it a second thought. Once the eggs are laid, they hatch into larvae. Here’s where things get interesting.
1. **Egg Stage**: The journey starts with the female botfly laying eggs on the fur of a potential host.
2. **Larvae Burrowing**: Once the eggs hatch, the larvae will attach themselves to the host and start burrowing into the skin. They often create a small, open sore while they settle in.
3. **Development**: Inside the host, they grow and develop, feeding on blood and tissues. This stage can last anywhere from weeks to months, depending on the species and environmental conditions.
4. **Emergence**: When they’re ready, they’ll emerge from the host’s body to complete their transformation into adult flies, laying the next generation of eggs.
This cycle is an example of how life constantly thrives, even in the face of harsh conditions. Each stage plays a significant part in the larger ecological puzzle, contributing to nutrient cycles and the health of ecosystems.
How Do Wolf Worms Impact Their Hosts?
You might be curious about the effects of wolf worms on their hosts. Let’s be real: having tiny worms inside you sounds pretty uncomfortable! While many animals can withstand a small infestation, it can lead to various health issues.
For example, a heavily infested animal might exhibit:
– **Skin Lesions**: The entry wounds can become infected, leading to irritation and swelling.
– **Behavioral Changes**: Animals may become agitated or more aggressive as they cope with the discomfort.
– **Potential Secondary Infections**: A compromised immune system can make the host more susceptible to other infections or diseases.
Interestingly, while wolf worms can pose a threat to individual animals, their impact on larger populations and ecosystems can be nuanced. They can help regulate host populations by taking out weaker or sick individuals. This natural selection can be a key driving force in maintaining a balanced ecosystem, illustrating the role of predators and parasites in nature.
The Ecological Importance of Wolf Worms
Wolf worms might seem like a nuisance at first glance, but they play a vital role in ecological balance. Think of them as nature’s clean-up crew. By targeting weaker hosts, they inadvertently help maintain the health of animal populations. Here’s how:
– **Population Control**: By infesting weaker or sick animals, wolf worms help ensure that the strongest and healthiest individuals reproduce. This is a crucial part of natural selection and helps keep ecosystems stable.
– **Nutrient Cycling**: When wolf worms emerge from their hosts, they leave behind organic material that contributes to soil health. This breakdown of tissue returns nutrients to the ecosystem, benefiting plants and other organisms.
– **Food Source for Others**: Wolf worms can become a food source for various predators, contributing to the food chain. This interconnectedness highlights the importance of every species within an ecosystem.
So, while they may appear unpleasant, wolf worms aren’t just mindless parasites—they’re part of a larger web of life, demonstrating nature’s intricate balance.
Comparing Wolf Worms to Other Parasites
You might be wondering how wolf worms stack up against other parasites. There are plenty of other parasitic organisms out there, each with its own unique strategies for survival. Let’s compare wolf worms to a couple of well-known parasitic types:
– **Ticks**: Like wolf worms, ticks are blood-feeding parasites. However, they latch onto their hosts from the outside rather than burrowing inside. Ticks can transmit diseases, making them a significant threat to both humans and animals.
– **Tapeworms**: These parasites live in the intestines of their hosts, absorbing nutrients directly from what the host consumes. They can lead to severe health issues if not treated properly.
In contrast to these parasites, wolf worms have a more limited but fascinating role. They focus on specific hosts, while some other parasites can affect a wide range of animals. This specialization can influence how they are managed in wildlife and domestic settings.
Understanding wolf worms and their role in parasite ecology gives us a glimpse into nature’s complexity. While they might seem unpleasant at first, these little worms play crucial roles in maintaining the balance of life. They exemplify how every organism, no matter how small, contributes to the bigger picture of the ecosystem.
Next time you think about parasites, remember that they have their place in the grand scheme of life. Wolf worms, with their unique lifecycle and ecological impact, remind us that sometimes, even the tiniest creatures can have the most significant effects. By studying these fascinating organisms, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate dance of life unfolding all around us.
