Wolf worms, often found in the larvae of certain moths, navigate a unique niche in this ecosystem. They don’t just show up uninvited; they rely on their insect hosts for survival, creating a relationship that’s both beneficial and, frankly, a little unsettling. Understanding this relationship not only fuels our curiosity but sheds light on how intricate and surprising the connections in nature can be. So, grab your coffee, and let’s dive into the world of wolf worms and the symbiotic relationships that define them.
Understanding Wolf Worms
Wolf worms, or *Hyalophora cecropia* in scientific terms, are essentially the larval form of the giant silk moth. You might find them in the wild, hanging out in trees, munching on leaves like they’re at an all-you-can-eat buffet. These worms, which are often a striking green or brown, are known for their large size—some can grow up to 4 inches long! What’s fascinating is how these worms use their size and unique appearance as a defense mechanism against predators.
The wolf worm’s life cycle is just as interesting. After hatching from eggs laid by adult moths, they go through several growth stages, known as instars. During this time, they’re not just eating and growing; they’re also engaging in a subtle dance of survival with their insect companions. Here’s the thing: while they might look like they have it all figured out, they heavily depend on their surroundings and the insects around them to thrive and survive.
Wolf Worms and Their Habitats
Wolf worms thrive in forests or areas with abundant greenery, as they feast on various host plants, primarily deciduous trees. These environments are rich in biodiversity, meaning lots of insects and potential hosts are hanging out. Now, imagine walking through a lush forest and stumbling upon a group of wolf worms, each nestled within the safety of the leaves. What you’re witnessing is nature’s cooperative strategy at work.
By living in these habitats, wolf worms not only enjoy a banquet of delicious leaves but also carefully curate who gets to hang around them. Their presence can attract other insects, including smaller creatures that provide protection and help keep the wolf worms safe from predators. It’s a surprisingly effective strategy that showcases the importance of why these worm-insect relationships matter.
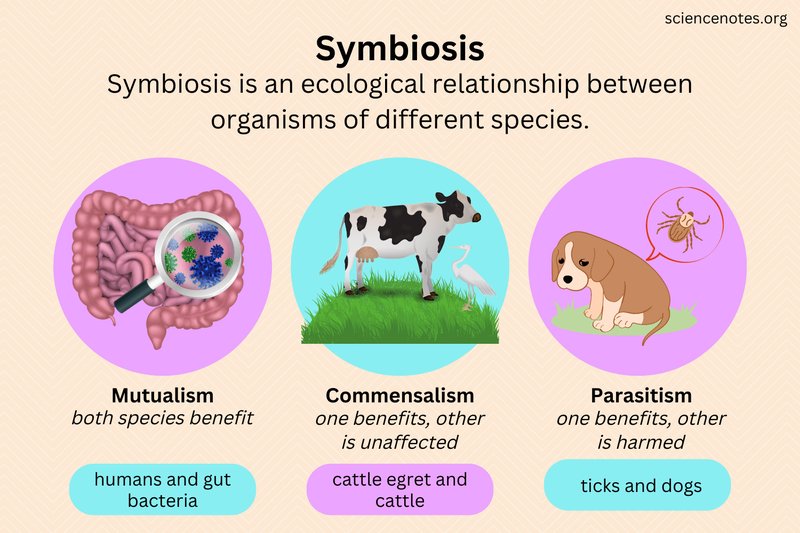
The Role of Symbiotic Relationships
Symbiotic relationships are nature’s way of highlighting teamwork. In the case of wolf worms, they exemplify a specific type of symbiosis known as commensalism, where one species benefits while the other isn’t significantly harmed. In this relationship, the wolf worms benefit immensely from their host insects, while the insects find safety and sometimes nutrients in the process.
For instance, when wolf worms latch onto certain moth larvae, they not only gain a cozy home but also access to food sources, as these larvae often move around and munch on different plants. This can be vital for their development, especially during the early stages of their life cycle. These little creatures are taught the art of survival through this mutualistic lifestyle, which can seem a bit gruesome but is essential for their growth.
Examples of Symbiotic Relationships
Let’s break it down with some real-life examples of symbiosis that you might find relatable:
- Cleaner Wrasse and Fish: These colorful little fish remove parasites from larger fish, providing a cleaning service while getting a meal.
- Oxpeckers and Mammals: These birds perch on large mammals like rhinos and giraffes, eating ticks and parasites while offering a pest control service.
- Clownfish and Anemones: Clownfish live among anemones for protection from predators, while anemones get nutrients from clownfish waste.
Each of these relationships shows how species can coexist and thrive together, just like wolf worms and the insects they partner with. It’s a beautiful reminder that in nature, teamwork often leads to success.
Impacts of Symbiotic Relationships on Ecosystems
Understanding these relationships goes beyond just curiosity—it has real implications for the health of ecosystems. Wolf worms and their insect partners play a role in the food web. When they flourish, they influence the populations of other species, including their predators. If wolf worms decline, the insects they rely on could face a domino effect, impacting everything from plant health to wildlife.
Here’s the key takeaway: every species, no matter how small or strange, contributes to the larger picture. It’s like a giant puzzle, and removing even a single piece can distort the entire image. By protecting these symbiotic relationships, we’re also safeguarding the ecosystems they inhabit.
Why This Matters to Us
You might be wondering, “Why should I care about wolf worms?” Well, beyond being fascinating oddities in nature, they serve as indicators of ecosystem health. When their populations are stable, it often means the overall environment is thriving. Conversely, if wolf worms start disappearing, it might signal issues like habitat loss or pollution.
As we think about conservation and how our actions impact nature, understanding these connections can drive home the importance of protecting our ecosystems. It’s a shared responsibility, and knowledge is the first step!
Challenges and Conservation
While nature has a way of self-regulating, human activities can tip the scales. Deforestation, pollution, and climate change pose threats to wolf worms and their insect kin. As forests shrink and habitats are disrupted, the delicate balance of the symbiotic relationships suffers.
Conservation efforts are crucial in protecting not just the wolf worms but the entire ecosystem. By promoting awareness about the importance of these relationships, we can help guide initiatives that protect these creatures and their habitats.
What Can You Do?
You don’t have to be a scientist to pitch in. Here are a few simple actions that can help support symbiotic relationships like those of wolf worms:
- Support Conservation Groups: Find local or national organizations working to protect habitats.
- Educate Others: Sharing knowledge about the importance of ecosystems with friends or family can create a ripple effect.
- Plant Native Plants: Creating habitats for local wildlife in your own backyard can help support many species.
These small efforts can lead to significant changes over time and help maintain the intricate web of life that includes wolf worms and their insect partners.
Wolf worms and their symbiotic insect relationships remind us of the complexities and wonders of nature. It’s a captivating world where tiny creatures play big roles in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. By understanding these connections, we can appreciate our environment better and take action towards its preservation. So next time you hear about wolf worms or stumble upon a symbiotic relationship in your own backyard, remember the significance behind it. Together, we can ensure these fascinating partnerships continue to thrive for generations to come.

