Wolf worms, also known as *Hyalomma* larvae, are not your typical creatures. In fact, they’re parasitic—but not in a way most people would assume. To clarify, these larvae often find a cozy home in the bodies of larger insects, like caterpillars or beetles. Their symbiotic relationship with their hosts can be puzzling. While it seems like one party is just taking advantage of the other, the reality is much more complex. In this article, we’ll peel back the layers on these intriguing creatures and how they fit into the wider ecosystem.
What Are Wolf Worms?
Wolf worms are the larval stage of a type of fly, specifically from the family *Braulidae*. These tiny creatures have a rather unsettling reputation for their parasitic lifestyle. They typically invade the bodies of unsuspecting host insects, getting the nutrients they need to grow. You might be wondering, “How do they do this without killing their hosts?” Well, here’s the thing: they strike a balance. While the host insect is essentially their living buffet, the larvae often don’t kill their hosts right away. This allows the larvae to develop while the insect carries on with its life, which can be quite a while.
The name “wolf worm” can be misleading. It sounds fierce, but these worms are small and often go unnoticed. They latch onto their hosts and can remain there for days, weeks, or even longer, feeding off of them gradually. This strategy ensures that the host doesn’t expire before the larvae have had enough time to mature. It’s a delicate dance between survival and predation, creating an intricate web of life and death in the insect world.
The Importance of Symbiosis
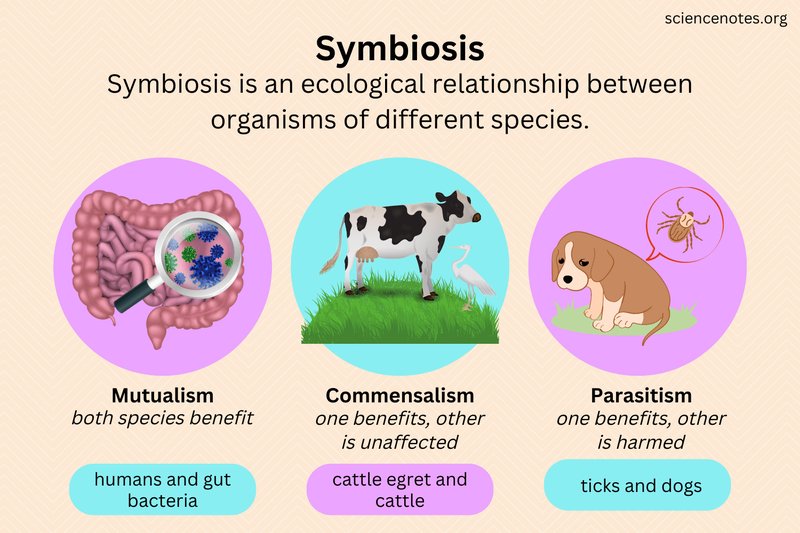
Symbiosis is a term you might have heard thrown around in biology classes, but what does it really mean? Simply put, it’s a close and often long-term interaction between two different species. In the case of wolf worms, the relationship can be classified as parasitism, where one organism benefits at the expense of the other. However, it’s essential to grasp that this relationship isn’t purely negative.
Wolf worms highlight an interesting aspect of nature: the idea that survival often requires collaboration—even among those who seem to be enemies. Just like that friend who always borrows your favorite shirt but ends up being there when you need a pep talk, wolf worms represent the complexities of life. They may take from their hosts, but they also play a role in regulating populations of other insects.
Additionally, understanding these relationships helps scientists and ecologists grasp larger ecological dynamics. Every species, no matter how small or seemingly insignificant, plays a role in its environment. Learning about them provides insights into how ecosystems function as a whole.
How Do Wolf Worms Impact Their Hosts?
Now that we know what wolf worms are and their symbiotic nature, let’s dig a bit deeper into how they impact their hosts. The interaction is unique: while the host insect is often exploited, there are cases where the presence of wolf worms can affect the host’s behavior. For instance, the infected insect may exhibit changes in movement or feeding patterns due to the larvae siphoning off nutrients.
This impact can have ripple effects throughout the ecosystem. When caterpillars or beetles are burdened by wolf worms, they can’t grow or reproduce as they normally would. A drop in the population of these insects can lead to changes in the food web. For example, if caterpillars are a primary food source for birds, fewer caterpillars could mean fewer birds, altering the entire community.
Moreover, host insects can sometimes develop a resistance to these parasites over time. This evolutionary arms race can create fascinating adaptations, showcasing how life continually evolves in response to challenges.
Examples of Symbiotic Relationships in Nature
To understand wolf worms better, it’s helpful to look at other types of symbiotic relationships out there. Nature is full of fascinating partnerships, each with its unique twist. Here are a few noteworthy examples:
- Mutualism: This is where both species benefit. For instance, bees and flowering plants have a mutualistic relationship; bees pollinate flowers while getting nectar for their food.
- Commensalism: Here, one organism benefits, and the other isn’t significantly harmed or helped. Think of barnacles on a whale; barnacles get a free ride in nutrient-rich waters, while the whale goes about its business.
- Parasitism: This is the category where wolf worms fit. In this situation, one organism benefits at the other’s expense. Other examples include ticks on mammals or tapeworms in the intestines of animals.
By comparing these different types of symbiotic relationships, we can appreciate the diverse ways life adapts and survives. Each type shows a different survival strategy and helps maintain the balance of ecosystems.
The Role of Wolf Worms in Ecosystems
Wolf worms, despite their unsettling lifestyle, serve an essential purpose in the ecosystems they inhabit. They help regulate insect populations, preventing any one species from overwhelming the environment. This is crucial because biodiversity is key to a healthy ecosystem. If one insect thrives unchecked, it can lead to imbalances that affect plants and other creatures.
Additionally, researchers study these parasitic relationships to learn about disease transmission and the dynamics of ecosystems. Understanding how parasites like wolf worms interact with their hosts can shed light on larger ecological trends, including how ecosystems respond to environmental changes.
Furthermore, wolf worms can act as bioindicators, helping scientists gauge the health of an environment. When populations of certain insects are affected, it signals potential problems in the ecosystem, prompting further investigation. So, even something that seems small and insignificant can tell us so much about the world around us.
The world of wolf worms and symbiotic relationships is like a spider’s web—intricate and beautifully complex. These tiny larvae may seem insignificant, but their interactions with their host insects tell a bigger story about life, survival, and balance in nature.
Understanding wolf worms’ role in ecosystems helps us grasp the delicate interplay between species, shedding light on the hidden dynamics of the natural world. So, next time you think about insects, remember that it’s not just about predators and prey; sometimes, it’s a fine dance of coexistence. By respecting and learning about these relationships, we can appreciate the wonders of nature and the roles each creature plays, no matter how small.

