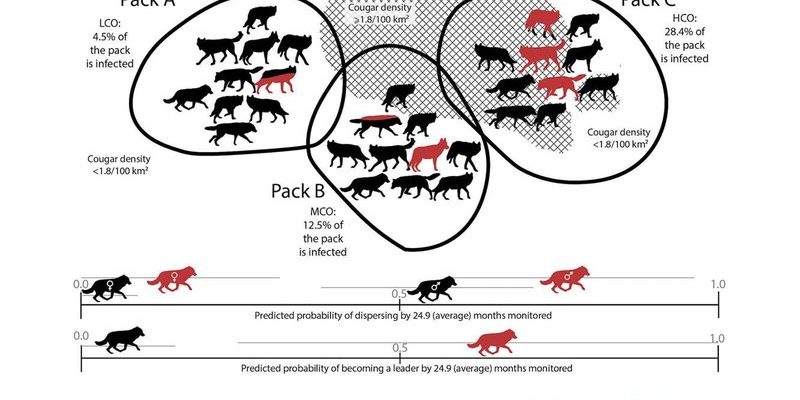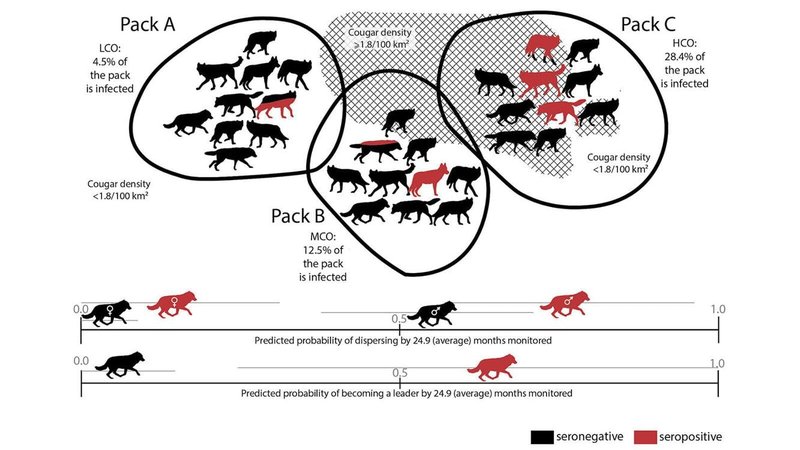
So, what exactly are wolf worms? These are larvae of a type of fly, specifically the **Cuterebra** species, and their life cycle involves invading small mammals, especially rodents. It’s a bit of a grim scene but stick with me—this relationship is crucial for understanding the delicate interplay of predator and prey in nature. Think of it like a game where each player has a significant role, affecting the score—and the broader environment—more than you might expect.
What Are Wolf Worms?
Wolf worms, or **Cuterebra larvae**, are fascinating creatures. They start their lives as eggs laid by the adult fly, often on the ground or on vegetation. When the eggs hatch, the larvae attach themselves to a host—most commonly small mammals like mice and squirrels.
Once inside the host, they create a small opening on the outside of the skin. This may sound pretty disturbing, but it’s all part of how they survive and grow. As they feed on the host’s tissue, they undergo several developmental stages before exiting the host to pupate and eventually emerge as adult flies.
This life cycle is pretty unique, and it allows for a close relationship between these parasites and their hosts. While it may seem one-sided, wolf worms can actually impact rodent populations in significant ways. They may weaken their hosts, making them more vulnerable to predators, thus influencing the overall population dynamics.
The Role of Rodents in the Ecosystem
Rodents play a vital role in ecosystems around the world. They’re not just cute little critters; they are key players in maintaining a balance in their habitats. By feeding on seeds and plants, they help control vegetation growth and also serve as a primary food source for many predators, including birds of prey, snakes, and, yes, even wolves.
Moreover, rodents are excellent at reproducing. A single pair of mice can produce dozens of offspring in just a year, which means their populations can swell quickly under the right conditions. This rapid reproduction is essential for supporting the food web, but it also means that their populations must be kept in check to prevent overpopulation and the depletion of resources.
Here’s the thing: the balance between predator and prey is crucial. If rodents thrive unchecked, they could decimate plant life, which would ultimately affect other species in the environment. This is where wolf worms come into play, impacting rodent populations and helping to maintain a healthier ecosystem.
How Wolf Worms Affect Rodent Populations
You might be wondering how a little parasite can influence the population dynamics of rodents. It all comes down to their effects on the host’s health and survival. When wolf worms invade a rodent, they can cause various health issues. Infected rodents often show signs of weakness and reduced activity, which makes them easy targets for predators like hawks and foxes.
Additionally, because wolf worms can be fatal if the infestation is severe, they act as a natural form of population control. This can prevent rodent overpopulation, which is essential for maintaining balance in the ecosystem.
In essence, by affecting the health and survival of their hosts, wolf worms help keep rodent populations in check. This relationship highlights how even the smallest creatures can have a massive impact on larger ecosystems.
Environmental Factors Influencing Wolf Worms and Rodent Interactions
Various environmental factors can influence the relationships between wolf worms and rodents. For instance, temperature and humidity play significant roles in the life cycles of both species. Warmer, wetter conditions might support higher rodent populations and, therefore, more opportunities for wolf worms to thrive.
Additionally, habitat quality matters. Areas with dense vegetation might support larger rodent populations, providing adequate shelter and food. However, this can also increase the likelihood of wolf worm infestations as they find more hosts to latch onto.
Here’s an interesting thought: in regions where habitat destruction or climate change alters the landscape, the balance between these species could be disrupted. This disruption might lead to either an explosion of rodent populations or a decline in their numbers, both impacting the overall ecosystem.
Implications for Wildlife Management
Understanding the dynamics between wolf worms and rodent populations has significant implications for wildlife management and conservation efforts. Effective management strategies take into account not just the larger predators and prey but also the roles of parasites like wolf worms.
For example, efforts to control rodent populations, such as using bait or traps, might also affect wolf worm populations. This could unintentionally lead to an imbalance, resulting in larger rodent populations that suffer less predation.
Conservationists need to consider the whole picture. By maintaining a healthy ecosystem where natural predators, prey, and even parasites coexist, they can help ensure stability in these populations. It’s like putting together a puzzle—every piece matters.
Taking Action for Ecosystem Health
So, what can we do to support a healthy ecosystem? First and foremost, we can promote biodiversity in our own backyards. Planting native flora, creating habitats for small mammals, and even encouraging natural predator species can all contribute to balanced population dynamics.
Also, educating ourselves and others about the delicate balance of ecosystems is crucial. The more we understand the roles of different species, including parasites like wolf worms, the better we can advocate for policies that protect these natural systems.
Ultimately, every creature plays a part in the grand tapestry of life. By respecting and nurturing the relationships within these ecosystems, we can help maintain their health and resilience for future generations.
In conclusion, the interactions between wolf worms and rodent populations showcase the complexity of nature. While these relationships might seem gross or odd at first glance, they’re essential for maintaining ecological balance. By understanding how these dynamics work, we can appreciate the intricate web of life that surrounds us—and do our part to protect it.