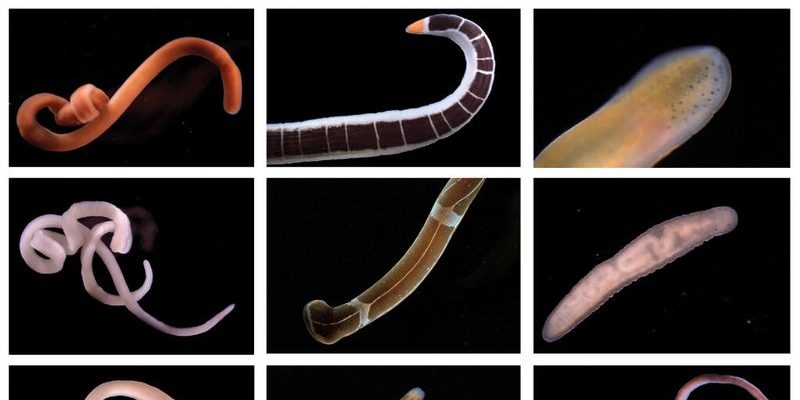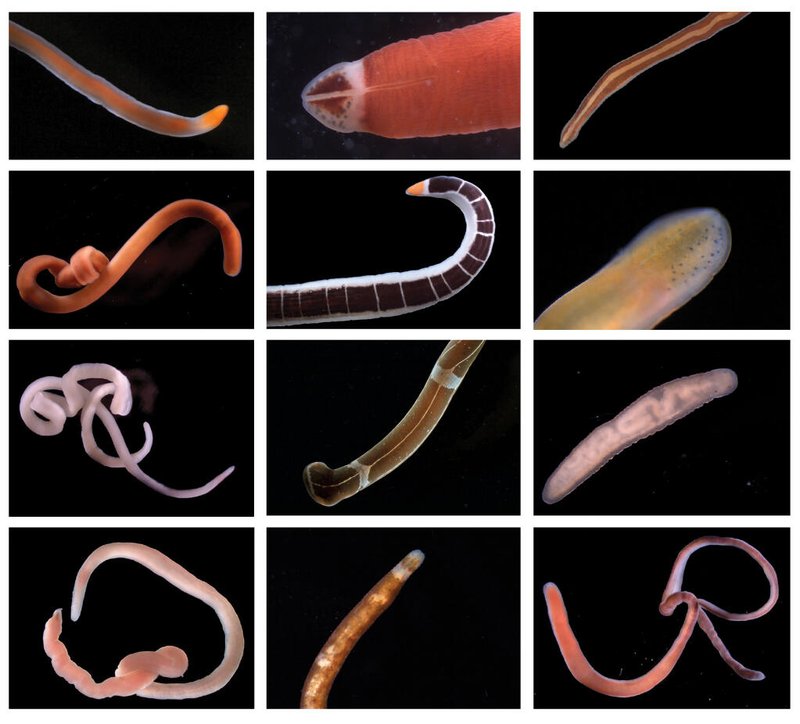
So, where exactly do these intriguing ribbon worms call home? That’s what we’re diving into! Picture a ribbon worm as a blend of a snake and a piece of spaghetti, slinking through the sea, often hiding in the sand or among rocks. They can be found in a variety of marine environments, each providing unique conditions that suit their lifestyle. Let’s explore the various habitats ribbon worms thrive in and why these places matter.
Coastal Waters: The Primary Habitat
When we talk about where ribbon worms are found, coastal waters often take the spotlight. These regions, where the ocean meets the land, are rich in nutrients and biodiversity. The shallow waters near shorelines provide perfect hiding spots for ribbon worms to crawl through sand and seaweed.
You might be wondering why these worms prefer coastal areas. Well, it’s simple. Coastal waters often have a variety of habitats, including estuaries and tidal pools, that offer the necessary food sources for ribbon worms. These creatures primarily feed on small invertebrates and organic matter found in the sediment. Think of them as scavengers, cleaning up the ocean floor while munching on anything that comes their way!
In California, for instance, you can find species like *Nemertopsis gracilis* in sandy habitats along the coast. Honestly, this diversity in habitat types showcases how adaptable ribbon worms can be. They can thrive in environments where other creatures might struggle, making them essential players in their ecosystems.
Estuaries: A Mixing Pot of Life
Estuaries are where fresh and saltwater mix, creating a unique environment that ribbon worms absolutely love. These areas are usually rich in nutrients and are teeming with life, from fish to crabs to various invertebrates. For ribbon worms, estuaries provide an abundance of food and shelter.
In these muddy, nutrient-dense waters, ribbon worms can often be seen burrowing into the mud or hiding among aquatic plants. They thrive in this soft substrate, which allows them to extend and retract their long bodies. Imagine a ribbon worm playing hide-and-seek, using the estuarine muck as its cozy blanket!
Moreover, estuaries serve as breeding grounds for many marine species. For ribbon worms, this means a wide variety of prey is available, making it a prime location for feeding. The blend of fresh and saltwater creates a dynamic ecosystem that is crucial not just for ribbon worms, but for countless other marine organisms as well.
Intertidal Zones: The Edge of Land and Sea
The intertidal zone can be considered the front line between land and sea. This area is exposed during low tide and submerged during high tide, creating a challenging yet rewarding environment for many marine creatures. Ribbon worms can often be found in the intertidal zones, hiding in crevices, under rocks, or in sandy patches.
Here’s the thing: the intertidal zone is filled with both opportunities and challenges. Ribbon worms must adapt to changing water levels and the varying salinity of the environment. They’re like seasoned adventurers, capable of thriving in conditions that might deter other species.
During low tide, these worms may maneuver their way into small pools, seeking food while evading predators. It’s fascinating to think about how these simple creatures navigate such dynamic environments. The intertidal zone truly showcases their resilience and adaptability.
Deep-Sea Environments: The Mysterious Depths
Now, let’s take a plunge into deeper waters. While ribbon worms are most commonly associated with shallower coastal regions, some species have been discovered in the depths of the ocean. Deep-sea environments are often dark, cold, and full of challenges, but they also hold a treasure trove of unique life forms, including ribbon worms.
In these deep waters, ribbon worms can be found in sediments on the ocean floor, where the conditions are stable, and food sources are available. Some species, like *Lineus longissimus*, are known to thrive in these deeper habitats. You might be surprised to know that these ribbon worms can grow incredibly long; some can even reach lengths of over 30 feet!
Being in such remote locations often means fewer competitors and predators for ribbon worms. However, survival in the deep sea comes with its own set of challenges, such as extreme pressure and limited light. Here’s a fun twist: it’s like living in a world of complete darkness but still finding plenty to eat and suitable places to hide.
Reefs and Coral Communities: A Hidden Gem
Coral reefs are often hailed as the rainforests of the sea, teeming with life and complex ecosystems. Ribbon worms can also be found in these vibrant habitats, where they play a role in the delicate balance of reef life.
Coral reefs provide ample food and hiding spots, making them an attractive home for ribbon worms. They can often be found tucked away in crevices or among coral formations, where they can feast on tiny invertebrates and organic debris that falls from the reef.
What’s remarkable is the interaction between ribbon worms and the reef ecosystem. These worms not only benefit from the reef’s abundance, but they also contribute to the health of the reef by helping to break down organic materials and recycle nutrients. Think of them as tiny recyclers of the ocean, ensuring the reef continues to thrive.
Climate and Environmental Changes: A Growing Concern
As we talk about where ribbon worms are found, it’s essential to touch on how climate change and environmental shifts are impacting their habitats. Rising water temperatures, pollution, and habitat destruction can seriously affect ribbon worm populations and their environments.
For example, warmer waters can lead to changes in food availability and overall health of marine ecosystems. Ribbon worms, being dependent on healthy habitats, are also impacted. If coastal waters become polluted, their food sources could dwindle, leading to potential declines in their populations.
It’s crucial to recognize these changes and work towards protecting marine environments. By understanding the importance of habitats where ribbon worms live, we can take steps to ensure these fascinating creatures continue to thrive for years to come.
In summary, ribbon worms inhabit a variety of marine environments, each with its unique characteristics and challenges. From coastal waters to deep-sea mysteries, these worms have carved out a niche for themselves in the ocean’s diverse ecosystems. They play a vital role in nutrient cycling and maintaining the health of their environments.
As we explore the world of ribbon worms, it becomes clear that these creatures, although often overlooked, contribute significantly to marine life. Understanding where ribbon worms are found only deepens our appreciation for the interconnectedness of life in our oceans. So, the next time you think about marine life, remember the ribbon worm and the hidden wonders of the underwater world!