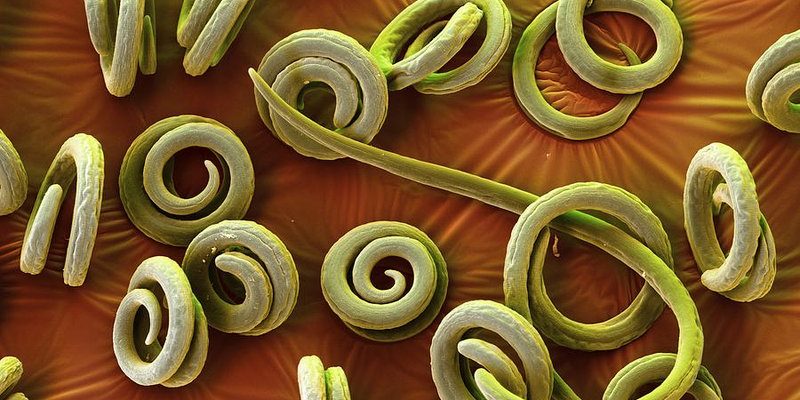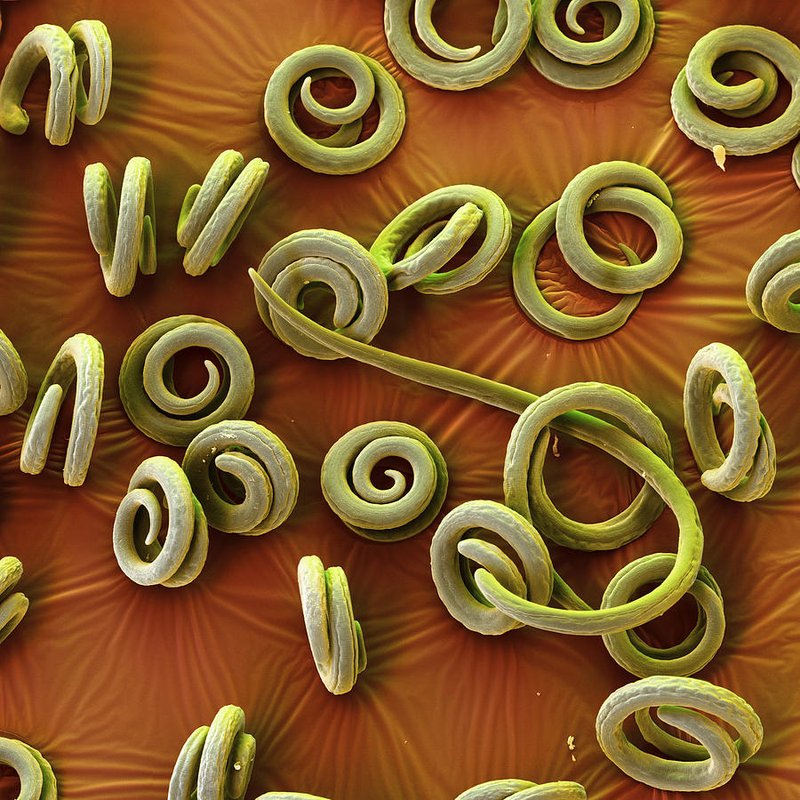
So, what exactly is Trichinella spiralis, and why should we care? Well, this pesky worm can hitch a ride into our bodies through undercooked meat, particularly pork. Once inside, it can create a lot of health issues if not managed properly. As we explore this microscopic entity, we’ll uncover not only its life cycle but also the risks it brings, how it’s diagnosed, and ways to prevent infection.
Understanding Trichinella Spiralis
To start, it’s essential to grasp what Trichinella spiralis really is. This roundworm belongs to a group called Nematodes, and it’s quite small—about 1 to 4 millimeters long. Think of it as a tiny spaghetti noodle that’s quite good at surviving in some extreme environments. But it’s not just about size; it’s about how it gets around.
Trichinella spiralis has a fascinating life cycle that involves multiple hosts. It generally begins when an animal, like a pig, eats food containing the larvae of the worm. These larvae then grow into adult worms in the intestines of their host. After mating, the female lays larvae that travel through the bloodstream to muscles, where they form cysts. This is where things get interesting. When another animal (or a human) eats undercooked meat from the infected host, they can become infected, and the cycle continues.
You might be wondering why this matters. The life cycle of Trichinella spiralis is not just an interesting biology lesson; it helps us understand how infections happen and why certain foods are risky. We’ll dive deeper into the health impacts in the next section.
The Health Risks of Trichinella Spiralis
Now, let’s talk about the health implications of Trichinella spiralis. When humans ingest this parasite, they can end up with a condition known as trichinosis. Symptoms can vary widely, but they often start with nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Imagine feeling like you’ve eaten something that just doesn’t agree with you, only for those feelings to escalate into a full-on battle inside your body over the next few days.
As the larvae migrate to the muscles, symptoms can become more severe. People may experience fever, muscle pain, swelling, and fatigue. In some cases, this can lead to serious complications, especially for people with weakened immune systems. Honestly, it’s not just a minor annoyance; it’s something that can genuinely affect your quality of life.
Prevention is key here. Avoiding undercooked meat, especially pork, is crucial. Sometimes people think they can just “eyeball” the doneness of meat, but this can lead to problems. Let’s look at cooking tips and safety measures next to keep everyone safe from this unwelcome guest.
How to Prevent Trichinella Infection
So, what can you do to avoid this sneaky parasite? The answer lies in proper food preparation and hygiene. Here are some practical steps:
- Cook meat thoroughly: Always cook pork to an internal temperature of at least 145°F (63°C). This is crucial. Using a meat thermometer helps ensure you’re not playing a guessing game.
- Freeze meat when possible: Freezing pork at a temperature of 5°F (-15°C) for at least three weeks can kill any Trichinella larvae that may be present.
- Avoid wild game: If you’re a hunter or love game meat, be aware that it can often carry Trichinella. Cooking it well is essential.
- Practice good hygiene: Wash your hands thoroughly after handling raw meat to avoid cross-contamination.
By following these guidelines, you can significantly reduce your risk of infection. Here’s the thing: being aware and proactive can make all the difference between a safe meal and a potentially serious health issue.
Diagnosis of Trichinosis
If you suspect you have trichinosis, getting diagnosed quickly is crucial. The symptoms can often mimic those of another illness, which makes it a bit tricky. The first step is usually a visit to your health care provider. They’ll likely start with a physical examination and take a detailed history of your symptoms and recent dietary habits.
In some cases, blood tests can help detect antibodies against the Trichinella larvae. However, these tests are not always definitive, especially early in the infection. Muscle biopsies can also be performed to check for the presence of the larvae. It might sound a bit invasive, but getting the right diagnosis can pave the way for effective treatment.
Once diagnosed, the good news is that most people recover well with proper treatment, which typically involves medication to kill the worms and manage symptoms. But again, prevention is far better than cure, so staying informed is key!
Understanding the Life Cycle of Trichinella Spiralis
Now that we’ve touched on health risks and prevention, let’s explore the life cycle of Trichinella spiralis in more detail. Understanding how this parasite thrives can give us better insight into its behavior and risks.
After the larvae are ingested by a host animal, they mature into adult worms in the intestines. This marks the beginning of a new generation of infection. The female worm produces larvae that enter the bloodstream and travel to the host’s muscles, where they encyst and wait for another host—often a predator or even a human.
This cycle isn’t just fascinating; it’s a survival strategy. Trichinella spiralis has evolved to be incredibly resilient, adapting to various environments and hosts. It’s like having a master key to different ecosystems, making it a formidable opponent for anyone planning to enjoy a nice pork dinner without the hassle of potential health risks.
At the end of the day, Trichinella spiralis is a reminder of how interconnected our food systems and natural ecosystems are. While this tiny roundworm might seem insignificant at first glance, its impact can be substantial. Understanding its life cycle, health risks, and prevention strategies not only keeps us safe but also highlights the importance of food safety and hygiene.
As naturalists and everyday people, we should remain aware of what we eat and how it’s prepared. This way, we can enjoy our meals with the peace of mind that we’re doing our best to protect ourselves from these lurking dangers in our food chain. So next time you’re getting ready to cook some pork, think about those little spaghetti-like worms and remember: cooking it right can make all the difference!