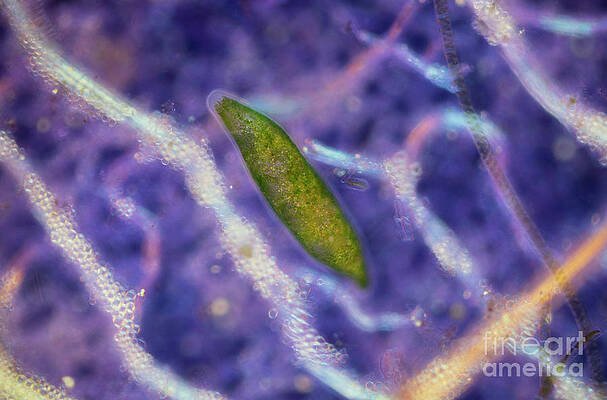
Imagine sitting in a classroom, and instead of just reading about how organisms regenerate or react to stimulus, students get to see it firsthand. Flatworms can illustrate these principles beautifully. They’re like tiny, living puzzles that reveal a lot about evolution, biology, and even neuroscience when observed under the right conditions. By incorporating flatworms into your lessons, you can transform mundane science topics into exciting, hands-on experiences that stick with students long after the classroom door closes.
In this guide, we’ll explore how to use flatworms effectively in school science demonstrations, covering everything from what makes them special to practical ways to incorporate them into your teaching. This isn’t just about memorizing facts; it’s about inspiring curiosity and a lifelong love for science.
What Are Flatworms and Why Use Them?
Flatworms, or Platyhelminthes, are simple yet intriguing creatures that play a crucial role in the ecosystem. They may lack complex organs like a heart or brain, but don’t underestimate their capabilities. These segmented wonders are known for their regenerative properties—some can regrow entire body parts, which makes them perfect for discussions about biology and evolution.
You might be wondering, what’s the big deal about using flatworms in demonstrations? Well, here’s the thing: flatworms can help students grasp complex concepts in a more tangible way. For instance, you can demonstrate how they respond to light and touch, making it a hands-on lesson in sensory biology.
Plus, flatworms are relatively easy to care for and breed in a classroom setting. They thrive in water, so you won’t need fancy equipment—just a simple aquarium setup. This accessibility opens the door for even the most novice teachers to dive into fascinating demonstrations without feeling overwhelmed.
Setting Up Your Flatworm Demonstration
Getting started with flatworms in your classroom is easier than you might think. First, you’ll need to acquire some flatworms. Many suppliers offer them specifically for educational purposes. Once you have your flatworms, the setup is simple. Here’s a quick guide to get you going:
- Choose a tank: A small aquarium or a plastic container will work. Aim for at least 5 gallons of water.
- Add water: Use dechlorinated water to fill the tank. If you’re unsure, letting tap water sit for 24 hours often does the trick.
- Include plants: Adding aquatic plants helps mimic their natural habitat and gives them places to hide and explore.
- Temperature: Flatworms do best in slightly warm water, around 20-24°C (68-75°F).
Have your students participate in setting up the environment. It encourages teamwork and gives them a sense of ownership over the project—and trust me, this will make them more engaged!
Demonstrating Regeneration and Adaptation
One of the most astonishing features of flatworms is their ability to regenerate. If you cut a flatworm in half, each half can regenerate into a complete worm! This is an amazing opportunity to discuss regeneration as a biological phenomenon.
Here’s how to conduct a simple regeneration demonstration with flatworms:
1. Preparation: Before the demonstration, ensure you have healthy flatworms.
2. Cut the Worms: Depending on your comfort level, you can use scissors to cut the flatworm into sections. Make sure to do this in a controlled environment where students can observe safely.
3. Observation: After a few days, ask students to check on the cut flatworms. Provide them with magnifying glasses to see the regeneration process up close. They can take notes on what they observe over time.
This isn’t just about seeing the process; it’s also a great moment to discuss cell division and stem cells. Students can share their thoughts and questions, fostering a classroom dialogue about how organisms adapt and survive.
Understanding Sensory Responses with Flatworms
Flatworms are also great for demonstrating sensory reactions. They might be simple creatures, but they respond to their environment in fascinating ways. For example, you can show how they react to light or changes in temperature.
To illustrate this, you can set up a basic experiment:
1. Light Introduction: Place the flatworm in a shaded area of the tank and gradually shine a light on it.
2. Observation: Students will enjoy watching how the flatworm moves away from the light source. This behavior is called negative phototaxis, and it’s a survival mechanism.
Encourage students to hypothesize why flatworms might avoid light. You can delve into discussions about evolution and natural selection here—why would avoiding light benefit these creatures? It’s exciting to watch students connect the dots between behavior and survival!
Exploring Flatworm Reproduction
Flatworms exhibit a range of fascinating reproductive strategies. Many flatworms are hermaphrodites, meaning they possess both male and female reproductive organs. This unique feature can spark interesting conversations about reproduction in the animal kingdom.
You can enhance this discussion by exploring the differences between asexual and sexual reproduction. To illustrate, here’s a quick activity:
– Group Discussion: Divide students into small groups and have them research different methods of reproduction in flatworms, including fission (asexual reproduction) and egg-laying (sexual reproduction).
– Present Findings: Each group can present their findings, promoting collaboration and public speaking skills.
This type of engagement allows students to explore how various organisms reproduce and adapt to their environments, deepening their understanding of biodiversity.
Safety and Ethical Considerations in Using Flatworms
Whenever we introduce live specimens into a classroom, safety and ethics should be at the forefront of our minds. Flatworms are low-risk organisms, but that doesn’t mean we should neglect proper care and handling.
Here are a few key points to keep in mind:
– Handle with Care: Teach students to handle flatworms gently to minimize stress on the animals.
– Hygiene Practices: Ensure that everyone washes their hands before and after touching the tank or any flatworms.
– Respect Life: Discuss with students the importance of treating all living organisms with respect, even simple ones like flatworms.
Having this conversation helps cultivate a sense of responsibility among students, preparing them for more complicated topics in biology and ecology down the road.
Wrap-Up: Creating Lifelong Learners
Using flatworms in school science demonstrations can be a game-changer in how students perceive science. They transform abstract concepts into tangible experiences, sparking curiosity and engagement. By taking these small but impactful steps, you can encourage your students to develop a love for science that lasts long after they leave your classroom.
Incorporating real-life examples, inviting participation, and fostering respectful practices are all part of creating a dynamic learning environment. Remember, the goal isn’t just to teach them what flatworms are; it’s about igniting their curiosity and making science come alive.
So, grab those flatworms, set up your aquarium, and watch your students’ excitement unfold. You’ll be amazed at how much they can learn from these simple little creatures!
