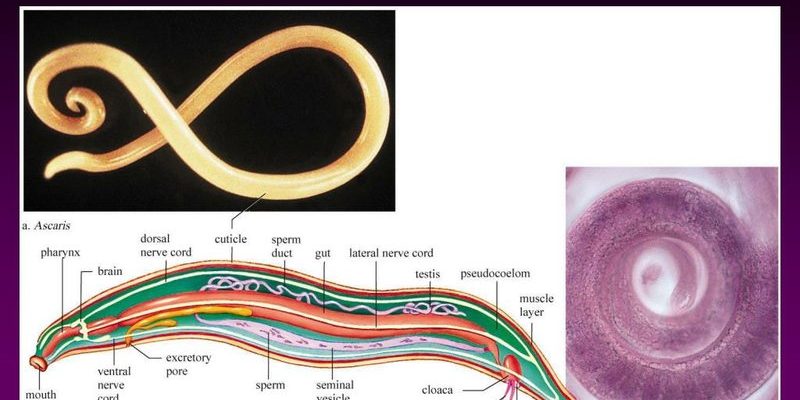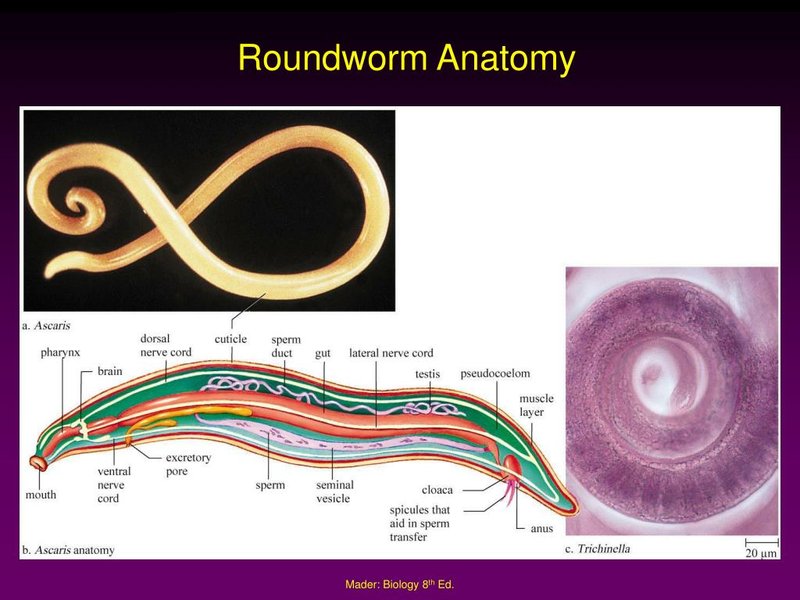
Imagine you’re at a buffet, trying to decide what to eat first. You could grab a little bit of everything, right? Roundworms operate on a similar principle, but instead of a plate, they have a specialized feeding structure. By understanding how roundworms eat, you’ll appreciate the complex systems in nature that allow life to thrive in different environments.
What Are Roundworms?
Before we jump into the nitty-gritty of their feeding mechanisms, let’s understand what roundworms actually are. Roundworms, or nematodes as they’re scientifically known, are among the most diverse groups of organisms on Earth. They can be found in a range of habitats, from the deepest oceans to the soil beneath our feet.
These worms are typically small and elongated, sporting a smooth, cylindrical body. They lack segments, which distinguishes them from other types of worms. You might be wondering how such simple creatures can play significant roles in ecosystems. Well, many roundworms are essential for soil health, while others can be parasitic, impacting plants and animals, including us!
How Do Roundworms Feed?
Alright, here’s where the fun starts! Roundworms use a unique feeding mechanism that allows them to consume organic matter, bacteria, or even host tissues in case of parasitic species. Their method primarily involves three steps: ingestion, digestion, and absorption.
1. Ingestion: Roundworms have a mouth opening, known as the buccal cavity, which acts like a vacuum. When they encounter food, they create a pumping action that draws the nutrients into their bodies.
2. Digestion: Once the food is inside, it moves into their gut, where it is broken down by digestive enzymes. This process allows the nutrients to be extracted by the worm.
3. Absorption: The final stage involves absorbing these nutrients into their body. Roundworms have specialized cells that take in the necessary components to provide energy and support their growth.
It’s a pretty efficient system, don’t you think? They’ve essentially mastered the art of nutrient extraction.
The Role of the Buccal Cavity
Let’s zoom in on that buccal cavity I mentioned earlier. You might think of it as a tiny, specialized mouth. It’s adapted to the type of food the roundworm consumes. For example, a plant-eating roundworm will have structures that can grasp onto plant material, while a predatory roundworm might have more complex features to catch prey.
Inside the buccal cavity, there are often small teeth or plate-like structures that help in tearing food apart. This makes the initial phase of feeding much more effective, allowing them to break down larger food items before they head deeper into the digestive tract.
Honestly, it’s amazing how these tiny creatures have evolved to feed in such diverse environments, all thanks to their specialized anatomical features.
Digestive Tract: A Continuous Process
The digestive tract of roundworms is straightforward—a tube-like structure that runs from the mouth to the anus. This design is pretty efficient because it allows food to move continuously through their body.
Once food is ingested through the buccal cavity, it passes through the pharynx (think of it as the gullet) and into the intestine. This is where the magic happens. Digestive enzymes break down the food, and nutrients are absorbed through the intestinal wall. Any waste left over is expelled through the anus.
What’s interesting here is that roundworms have a complete digestive system, which is more evolved than some other invertebrates that may have only a gastrovascular cavity. Having a continuous digestive tract allows for a more efficient processing of food.
Types of Food Roundworms Consume
Now, let’s talk about the diverse diet of roundworms. It’s not just a one-size-fits-all situation. Different species of roundworms have varying feeding habits based on their environments and needs.
– Decomposers: Many roundworms play a vital role in breaking down organic matter in the soil. They consume bacteria, decomposing plant material, and other microorganisms, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
– Predators: Some roundworms are predators, eating smaller organisms, including other nematodes. They can control the population of pests, making them beneficial for agricultural environments.
– Parasites: You might have heard of parasitic roundworms like hookworms or pinworms that can infect humans or animals. These roundworms latch onto their hosts and feed on blood or tissues, which can cause various health issues.
Isn’t it fascinating how these tiny creatures fit into multiple roles within their ecosystems? It shows just how interconnected life is.
How Roundworms Affect Ecosystems
You might be wondering why understanding the feeding mechanism of roundworms matters. Well, these tiny creatures have huge impacts on their ecosystems. By decomposing organic material, they help enrich the soil, supporting plant growth. This, in turn, benefits various animals, including humans, who rely on plants for food.
In agricultural settings, roundworms can be both friends and foes. Beneficial nematodes can help control pest populations, while harmful species can damage crops. Farmers often need to monitor and manage roundworm populations to maintain the health of their land.
Their presence can indicate the overall health of the environment. A diverse population of roundworms often means a thriving ecosystem, while a lack could signal problems.
So, the next time you think about roundworms, remember that they’re much more than just squiggly creatures in the soil. Their feeding mechanism is a beautifully adapted process that plays an essential role in our ecosystems.
From breaking down organic matter to maintaining the balance in food webs, roundworms contribute significantly to the earth’s health. Understanding them helps us appreciate the complexity of life, and it highlights the importance of every organism, no matter how small.
By unraveling the intricacies of their feeding system, we gain insight into the interconnectedness of life, allowing us to better appreciate the world around us. So here’s to roundworms—tiny yet mighty players in the grand scheme of nature!