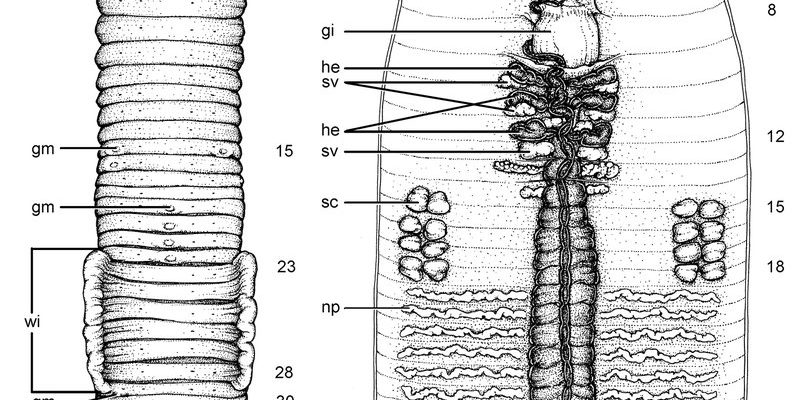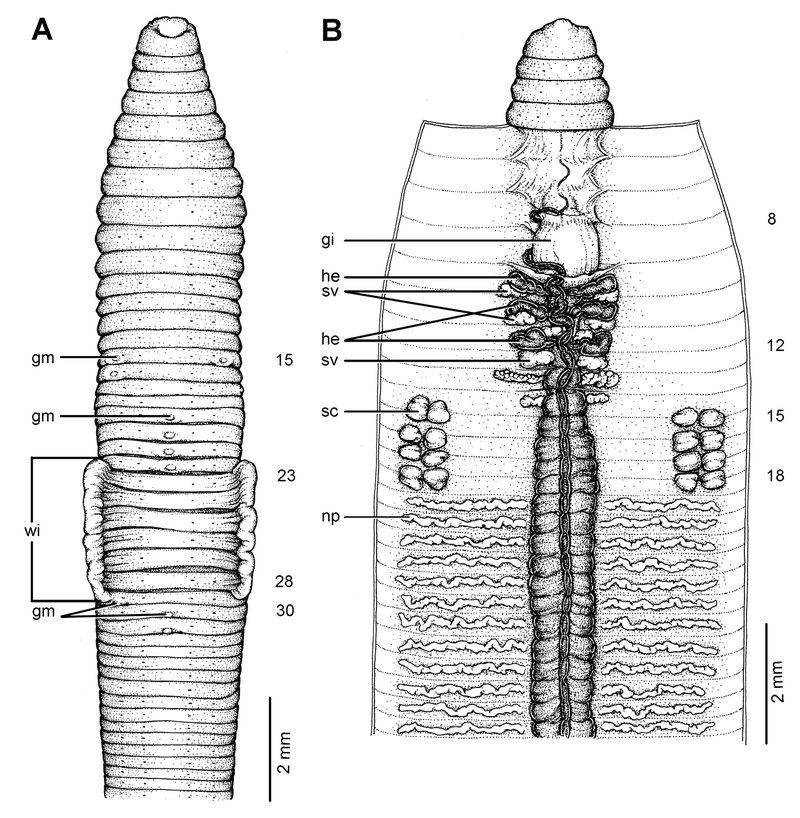
In this article, we’re going to dive deeply into how freshwater oligochaetes eat. We’ll break down their feeding mechanism step-by-step, so you can understand just how these creatures thrive in their underwater homes. Think of it as peeling back the layers of an onion—each layer reveals something new and interesting about their lives. So grab a cup of coffee, and let’s get started!
What Are Freshwater Oligochaetes?
Freshwater oligochaetes are a class of segmented worms, and they belong to the phylum Annelida. You might have heard of their well-known relatives, earthworms, but freshwater oligochaetes have adapted to life in lakes, ponds, and rivers. These worms are typically small, ranging from just a few millimeters to several centimeters in length.
Their bodies are divided into many segments, which are important for movement and feeding. These segments help them wiggle through the water and navigate their environment. You might be wondering, “What do they eat?” Well, that brings us to their impressive feeding mechanisms!
The Basics of How They Feed
Oligochaetes have a unique feeding strategy that varies slightly depending on their habitat and the availability of food. Generally, they are detritivores, which means they feed on decomposing organic matter. They help break down leaves, dead plants, and even tiny organisms into nutrients that are more accessible to other aquatic life.
Their feeding process begins with the worm extending its body to reach the organic matter, often found on the sediment at the bottom of the water body. They use their specialized mouthparts to scrape up this material. It’s a bit like using a vacuum cleaner to gather up crumbs from the floor.
Once they have gathered the organic materials, they transport it into their digestive system, where the real breakdown happens. This is crucial because it allows the nutrients to be absorbed not just by the oligochaetes, but also by other creatures that depend on these nutrients.
Feeding Structure: The Mouth and Pharynx
So, how do these worms actually grab their food? Let me explain the roles of their mouth and pharynx. The mouth of a freshwater oligochaete is located at the front end of its body. Think of it as the entrance to a charming little café. This is where all the delicious bites begin their journey.
Once the organic matter is inside, it moves to a muscular structure called the pharynx. The pharynx acts like a powerful suction pump, helping the worm grab and pull in even the tiniest food particles. It’s efficient and effective, almost like using a straw to drink your favorite smoothie.
The pharynx then breaks down the food further, making it easier for the nutrients to be absorbed as it passes through the digestive system. This step is crucial for ensuring the worm extracts as much nutrition as possible, which is essential for their energy and growth.
The Role of the Gut and Digestive System
Once the food is sucked in and passed through the pharynx, it moves into the gut, which is essentially the worm’s digestive tract. The gut is divided into specific sections, each with a unique function, working together like a well-oiled machine.
In the gut, the organic matter continues to break down, thanks to digestive enzymes and microbial activity. This process is crucial because it helps in breaking down complex organic materials into simpler compounds that can be absorbed by the oligochaete.
After the nutrients are extracted, the leftover waste moves toward the anus, where it’s expelled back into the water. This is important because it recycles nutrients back into the ecosystem, making them available for other organisms. It’s like a recycling program for nature!
How Feeding Supports Their Environment
You might be surprised to learn that the feeding habits of freshwater oligochaetes have a significant impact on their environment. By breaking down organic matter, they help maintain healthy water quality and promote nutrient cycling. This process supports the growth of aquatic plants and algae, which in turn provide oxygen and food for other organisms.
In addition, oligochaetes are an essential food source for various aquatic animals, including fish and amphibians. They contribute to the food web by providing sustenance for these predators, helping maintain biodiversity.
You could think of them as the unsung heroes of ponds and rivers, quietly doing important work behind the scenes. Without them, the aquatic ecosystem could face imbalances that might affect many species.
Adaptations for Feeding
Freshwater oligochaetes have developed several adaptations that make their feeding effective. For instance, many species have a highly sensitive sense of touch, allowing them to detect food particles in the sediment. This sensitivity is crucial, especially in murky waters where visibility is limited.
Another key adaptation is their ability to adjust their diet based on food availability. If organic matter is scarce, they can shift to consuming microbial biofilms, which are communities of microbes that form on surfaces in the water. This flexibility ensures they can survive in various environments and conditions.
These adaptations allow oligochaetes to thrive in both nutrient-rich and nutrient-poor waters. It’s like having a diverse menu that can cater to different tastes—no matter the conditions, they find a way to make it work!
The Life Cycle of Freshwater Oligochaetes
Understanding how freshwater oligochaetes feed wouldn’t be complete without mentioning their life cycle. It’s quite fascinating! They reproduce through a process called copulation, where two worms exchange sperm. Each worm can produce cocoons containing fertilized eggs, which later hatch into young oligochaetes.
Once they hatch, the young worms start their lives in sediment, feeding on organic matter just like their parents. As they grow, they continue to contribute to the ecosystem through their feeding habits. This cycle keeps the population stable and supports their vital role in healthy aquatic ecosystems.
In a sense, it’s a continuous loop of nutrients and energy that sustains not just the oligochaetes but the entire aquatic community.
Understanding the feeding mechanism of freshwater oligochaetes is not just an academic pursuit; it gives us better insight into the health of our aquatic ecosystems. These little worms may not seem important at first glance, but they play a crucial role in nutrient cycling and maintaining water quality.
So, the next time you’re near a pond or river, take a moment to appreciate these tiny creatures. Their work is vital, and it reminds us of the interconnectedness of all life. Just as we depend on healthy ecosystems, these unsung heroes rely on their feeding mechanisms to thrive and contribute to the larger picture. By recognizing their importance, we can better support and protect the environments they inhabit.