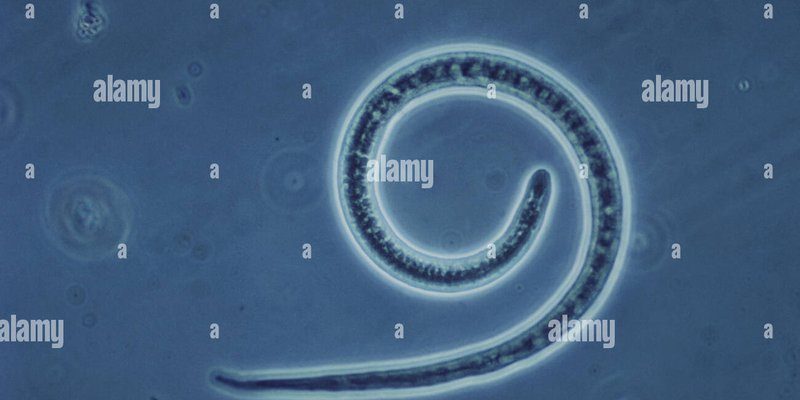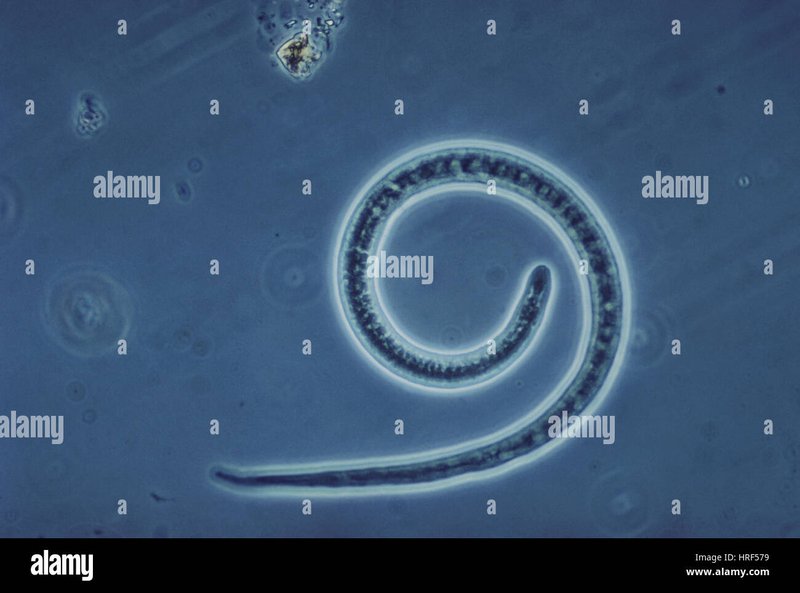
Imagine a delicate balance in nature, like a beautifully woven tapestry where every thread plays its part. Trichinella spiralis is one of those threads. In a way, it helps us understand greater ecological interactions. While it can lead to health issues in humans when we consume undercooked meat, especially pork, its role in wildlife and ecosystems is quite critical. Let’s go through how this little worm fits into the bigger picture.
What Is Trichinella Spiralis?
Trichinella spiralis is a type of roundworm that primarily affects mammals, including humans. These worms are transmitted through the consumption of meat containing encysted larvae. You might be wondering how this all works. Essentially, when a host animal eats infected meat, the larvae hatch in the intestines, mature into adults, and produce more larvae, which can then migrate to various tissues — often leading to muscular issues.
Now, you can find this parasite mainly in carnivorous and omnivorous animals. Think of animals like pigs, wild boars, or even bears, which can all carry the larvae. Infected meat might not seem like a big deal at first, but it’s crucial for us to be careful. Without proper cooking, we’re putting ourselves at risk for a disease called trichinosis, which can lead to various health issues, from gastrointestinal problems to muscle pain.
The Life Cycle of Trichinella Spiralis
To grasp the ecological importance of Trichinella spiralis, we need to understand its life cycle. It’s a remarkable process that starts when a carnivorous animal consumes infected meat. Here’s a simple breakdown:
1. Ingestion: An animal eats meat that contains cysts of the parasite.
2. Hatching: Once inside the intestines, the cysts release larvae that mature into adult worms.
3. Reproduction: Female worms produce new larvae, which then enter the bloodstream.
4. Migration: These larvae travel to muscle tissues, where they encyst and wait for another host to consume them.
This life cycle isn’t just a neat survival trick; it plays a big role in nutrient cycling within ecosystems. When animals consume infected meat, the Trichinella larvae can move up the food chain, impacting predators and prey alike. This cycle reflects the complexity of ecosystems and how each organism—no matter how small—has a significant role.
The Role in Ecosystems
Trichinella spiralis is often viewed through a negative lens because of the health risks associated with it. However, this species contributes to ecological balance in several ways. For starters, it affects the population dynamics of host animals. When a predator consumes an infected animal, it’s not just a meal; it’s a transfer of energy and nutrients through the food web.
By impacting the health and population sizes of hosts, Trichinella spiralis indirectly influences which species thrive in a particular area. For example, if a carnivore becomes less healthy due to excessive parasite loads, it may affect hunting behaviors and prey populations. This interplay keeps ecosystems in check, reminding us that even the less glamorous species have their roles.
Impact on Wildlife Health
Wildlife health is crucial for maintaining biodiversity, and parasitic infections like those caused by Trichinella spiralis can be a double-edged sword. On one hand, these parasites can lead to serious illness in animals, affecting their reproduction and survival rates. On the other hand, they can help regulate animal populations to prevent overpopulation.
In some cases, wildlife infected with Trichinella spiralis may show signs of disease, such as decreased mobility or weakness, affecting their ability to hunt or flee from predators. This can create a ripple effect throughout the ecosystem. For instance, if one species of predator becomes less efficient, prey populations may rise, potentially leading to overgrazing and a decline in vegetation.
Human Health Considerations
Let’s be honest: the connection between Trichinella spiralis and human health can be scary. Trichinosis can cause symptoms like diarrhea, fever, and muscle pain. It’s essential to understand how to mitigate these risks. The main way to prevent infection is by cooking meat thoroughly, especially pork and wild game.
Here’s a quick guide for safe cooking practices:
- Always cook pork to an internal temperature of 145°F (63°C) and let it rest for at least three minutes.
- Avoid consuming raw or undercooked meat, especially from wild animals.
- Check local regulations if you’re hunting for game.
By taking these precautions, you not only protect yourself but also contribute to the broader effort of managing the Trichinella population in the wild.
Future Research and Ecological Management
There’s still a lot to learn about Trichinella spiralis and its impact on ecosystems. Ongoing research can shed light on how climate change, habitat destruction, and animal husbandry practices might influence its prevalence.
Understanding these dynamics is essential for wildlife management and public health. By focusing on ecological management that considers the role of parasites like Trichinella spiralis, we can ensure healthier ecosystems and communities. It’s about finding that balance—remember the tapestry analogy? We have to recognize that every thread, even the unappealing ones, contributes to the overall design.
The Trichinella spiralis species might come with a few scary tales and health warnings, but don’t overlook its ecological importance. This tiny worm illustrates the delicate connections within our ecosystems, affecting wildlife populations and serving as a reminder of the balance between nature and human activity. So, the next time you hear about this parasite, think of it as one of nature’s curious creations, reminding us that every creature, no matter how small, has a role to play in the grand scheme of life. Stay informed, stay safe, and appreciate the wonders of our complex natural world!