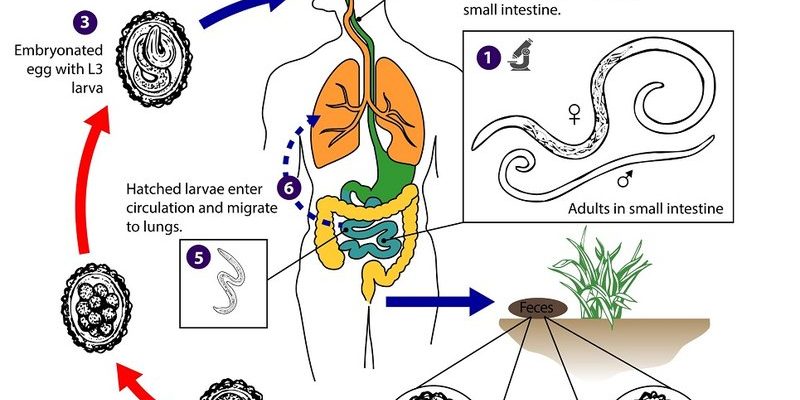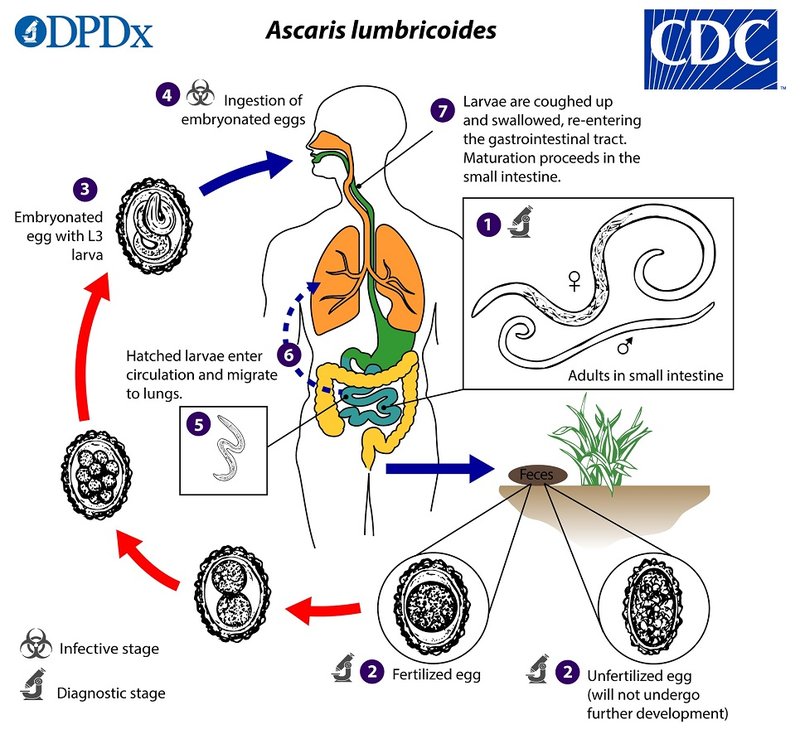
So, what’s the deal with pinworms? These small, white nematodes (basically a type of roundworm) find their home in the intestines of various animals, including humans. While we usually focus on the problems they cause—like itching and discomfort—it’s worth taking a moment to consider their ecological significance. Just as every ingredient in a recipe contributes to the final dish, pinworms play a part in the web of life, influencing soil health, nutrient cycling, and even helping scientists understand ecosystems better. Let’s dive into why these little guys matter in the grand scheme of things.
What Are Pinworms and Their Habitats?
Pinworms, or *Enterobius vermicularis*, primarily inhabit the intestines of humans, but they aren’t alone in the world. Many other animals, including rodents and some birds, host different species of pinworms. They all share a similar lifestyle, living in the intestines and laying eggs, but their habitats can differ significantly.
These worms are often found in places rich in organic matter, like gardens or areas where animals dwell. Imagine a bustling city where everyone is busy working—these parasitic worms thrive in environments where they can meet their hosts, helping to propagate their species effectively. By understanding their habitat, we can appreciate their role in the ecosystem as both a part of the food web and as indicators of environmental health.
The Role of Pinworms in Soil Health
Believe it or not, pinworms contribute to the health of soil. When an animal (like a rodent or bird) hosts these worms, they may help return nutrients back into the soil. It’s like when you use compost: you’re adding nutrients back into the earth to help your flowers bloom. Pinworms can contribute to this cycle in a natural way, breaking down waste materials and enriching the soil where they live.
By decomposing organic matter and recycling nutrients, pinworms help sustain the ecosystems they belong to. This process can enhance soil fertility, making it more hospitable for plants and, ultimately, for herbivores that depend on those plants for food. It’s a beautiful cycle that illustrates the interconnectedness of life.
Pinworms and the Food Web
Now, let’s think about the food web. Every species has a role, and pinworms are no different. While they primarily feed on the nutrients in their host’s intestines, they also serve as prey for larger organisms. Birds, for instance, may consume infected rodents, and in doing so, they help regulate the pinworm population.
This balancing act is crucial. If pinworm populations grow unchecked, they can lead to health issues in their hosts, which can then have ripple effects throughout the food chain. By being both a parasite and a food source, pinworms maintain a dynamic equilibrium that illustrates the delicate balance of ecosystems.
The Importance of Research in Understanding Pinworms
Scientists and researchers studying pinworms can provide valuable insights into broader ecological systems. These tiny creatures serve as model organisms—think of them as the “guinea pigs” of the ecosystem world. Observing how pinworms interact with their hosts and environment helps researchers understand host-parasite dynamics, disease spread, and even how organisms adapt to various conditions.
This knowledge is particularly crucial in veterinary medicine and human health. Understanding how pinworms operate can lead to better treatments for infestations and improve our overall grasp of parasite biology. It’s like having a cheat sheet for keeping our environment—and ourselves—healthy.
Pinworms and Biodiversity
Biodiversity is essential for a healthy ecosystem, and every creature, no matter how small, plays a part. Pinworms contribute to this diversity by co-existing with various species, from humans to animals. Their presence indicates a functioning ecosystem, where hosts and parasites interact, promoting biological diversity.
This complexity matters. The more diverse an ecosystem, the more resilient it becomes. Pinworms, as part of this mix, help maintain that resilience. The loss of even small species like pinworms can disrupt food webs, reduce nutrient cycling, and lead to larger environmental issues.
How Human Activity Affects Pinworm Populations
Given our influence on the planet, it’s essential to consider how human activities impact pinworm populations. Changes in land use, urbanization, and pollution can alter habitats, potentially threatening these organisms. For example, the use of antibiotics and antiparasitics can disrupt their life cycles, while habitat destruction can reduce their numbers.
As we become more aware of our environmental footprint, understanding the role of even the smallest creatures like pinworms can help us appreciate the intricate webs of life we’re a part of. It urges us to consider more sustainable practices that protect not just pinworms, but the entire ecosystems they inhabit.
Pinworms might not be the first creatures that come to mind when discussing ecological importance, but they are indeed vital players in the game of life. By understanding their habitat, role in soil health, contribution to the food web, and importance in research, we start to see the bigger picture. Just like the supporting cast in a play, these tiny, often overlooked nematodes help keep the ecosystem functioning smoothly.
So, the next time you hear about pinworms, take a moment to appreciate their role. They remind us that every creature, no matter how small, has a part to play in the intricate dance of life. Striving for a deeper understanding of pinworms can lead us to be more mindful stewards of our planet. After all, every piece of the puzzle counts.