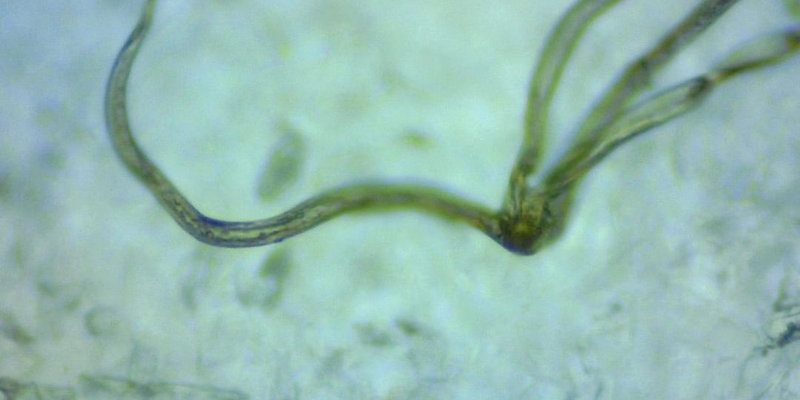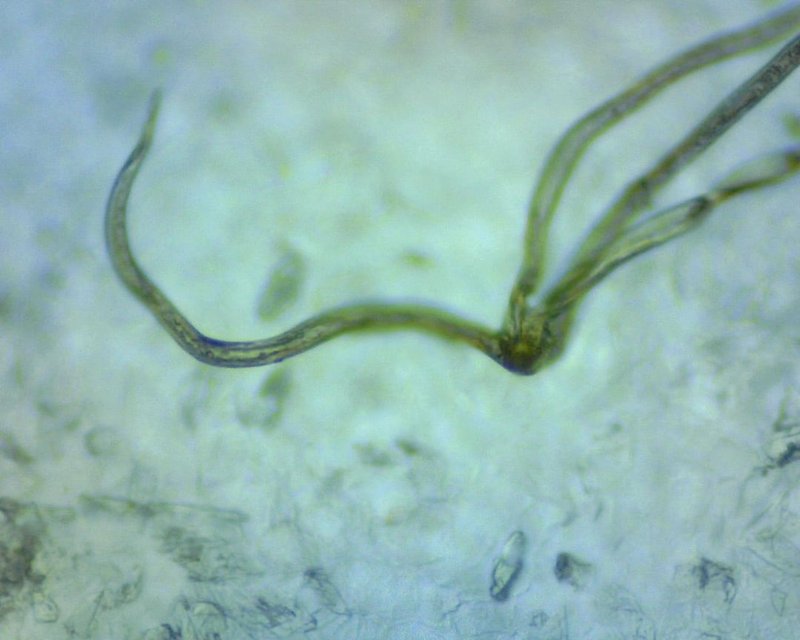
These worms have a unique life cycle that intertwines with various species in the ecosystem, making them key players in the natural world. You might be wondering how these unassuming worms influence their surroundings. Well, let’s break it down and explore their ecological importance in a way that’s easy to grasp.
What Are Nematomorphs?
Nematomorphs are a type of parasitic worm belonging to the phylum Nematomorpha. They’re mostly known for their long, slender bodies and their interesting life cycle. They begin their lives as eggs laid in water. When the eggs hatch, the larvae infect a host, usually insects like crickets or grasshoppers. This is where things get really intriguing.
As they grow inside their host, they manipulate their behavior. Imagine a puppet mastering its strings! When the worms are ready to emerge, they often force their host to jump into water. This dramatic exit isn’t just for show; it’s essential for their survival. Once in the water, the adult worms can reproduce and start the cycle all over again.
These life stages make nematomorphs a great example of parasitism, where one organism benefits at the expense of another. While this might sound harsh, it perfectly showcases the complex relationships found in ecosystems.
The Role of Nematomorphs in the Food Chain
You might be surprised to learn that nematomorphs play an important role in the food chain. As parasites, they can influence the population dynamics of their host species, like crickets. When these hosts become infected, it can lead to changes in their population. This, in turn, affects the prey and predator relationships within their habitat.
For example, if crickets become more common due to a decreased threat from predators, this can lead to an increase in the number of birds or other predators that feed on them. It’s like a domino effect in nature, where one small change can create a ripple through the entire ecosystem.
Furthermore, adult nematomorphs can also serve as prey themselves for species like fish and birds. This further cements their role in the food web, where energy is transferred from one organism to another, maintaining balance in the ecosystem.
Impact on Biodiversity
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life in a particular habitat. Healthy ecosystems rely on a rich tapestry of species working together. So, where do nematomorphs fit into this picture? Their presence helps maintain biodiversity by regulating host species populations.
When nematomorphs interact with insects, they can prevent any one species from becoming too dominant. Imagine a garden with a mix of flowers: if one type takes over, it can crowd out others. Nematomorphs act like nature’s gardeners, ensuring a balance that allows multiple species to thrive.
Additionally, the intricate life cycle of nematomorphs creates opportunities for other organisms to evolve. This adaptability and interdependence among species can lead to the emergence of new traits and behaviors, which are crucial for survival in a changing environment.
Nutrient Cycling and Soil Health
Now, let’s talk about something a bit less obvious: how nematomorphs contribute to nutrient cycling. When they die, their bodies decompose, returning nutrients back into the soil and water. This process enriches the surrounding environment, supporting plant growth and thus benefiting other animals.
Think of nematomorphs as tiny recyclers in nature. They help break down organic matter, returning it to the ecosystem. This process is essential for maintaining soil health and fertility, allowing plants to grow stronger and healthier.
Additionally, their presence in aquatic systems can enhance water quality. Healthy ecosystems rely on balanced nutrient levels, and nematomorphs contribute to this balance. By breaking down waste and organic material, they help keep waterways clear and support aquatic life.
Research and Conservation Efforts
Despite their importance, nematomorphs often fly under the radar in conservation discussions. Research on these worms gives us insight into their ecological roles and how they contribute to ecosystem health. Understanding their interactions with other species can guide conservation efforts, especially as we face environmental challenges like climate change and habitat loss.
Scientists are starting to recognize the need for including nematomorphs in biodiversity studies. By shedding light on their dynamics within ecosystems, we can better prioritize conservation strategies that protect not only these worms but the entire web of life they support.
So why should we care? As ecosystems continue to face pressures from human activities, keeping track of every piece of the puzzle, including nematomorphs, becomes more critical. Each species, no matter how small, contributes to the health and resilience of our planet.
In summary, nematomorphs may seem like simple worms, but they play a complex and crucial role in our ecosystems. From regulating host populations to promoting biodiversity and nutrient cycling, these creatures are unsung heroes of the natural world.
Honestly, the next time you encounter a tiny worm or learn about its life cycle, think about the web of connections it creates. Understanding how every species interlinks can deepen our appreciation for nature’s balance. By recognizing the ecological importance of nematomorphs, we can better understand the world we live in and help protect its wonders. So, let’s keep these tiny but mighty creatures in mind as we work towards a healthier planet.