In this article, we’ll dive into the world of ribbon worms, exploring how they grow, their unique abilities to regenerate, and why scientists are so interested in them. Think of it as a journey through a hidden underwater realm, where we’ll uncover the secrets these worms hold about life, healing, and resilience.
What Are Ribbon Worms?
Ribbon worms are fascinating, long, and soft-bodied animals that wiggle through the ocean and sometimes freshwaters. They can stretch several meters long, resembling a slimy noodle more than your typical worm. You might find them lurking in mud or under rocks, waiting to ambush their prey, which usually includes small fish and other critters.
One of the most intriguing things about ribbon worms is their unique body structure. Their bodies are made up of soft tissues and a complex system of muscles, which allow for amazing flexibility and movement. Imagine being able to squeeze through the tiniest gaps or stretch to great lengths—these worms truly showcase nature’s innovation.
Scientists believe there are around 1,300 species of ribbon worms, each one exhibiting some distinct characteristics. They come in various colors and patterns, making them not just interesting in terms of biology but also visually striking. The more you learn, the more you realize these creatures are full of surprises!
The Fascinating Process of Growth
When it comes to growth, ribbon worms go through several stages, from egg to adult. They start as tiny eggs that hatch into larvae, which are like miniature versions of themselves. As they grow, they undergo a series of transformations, eventually maturing into the elongated ribbons we recognize.
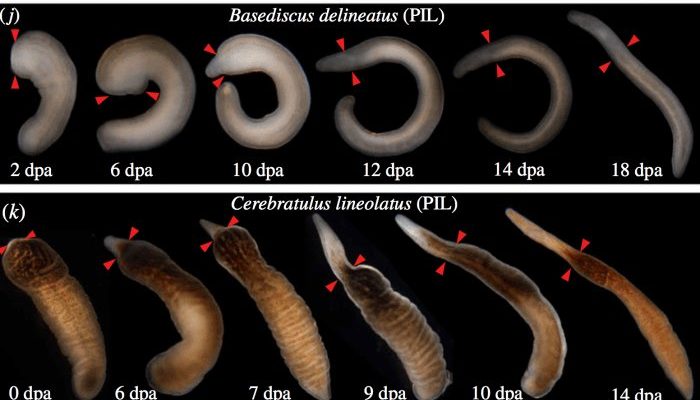
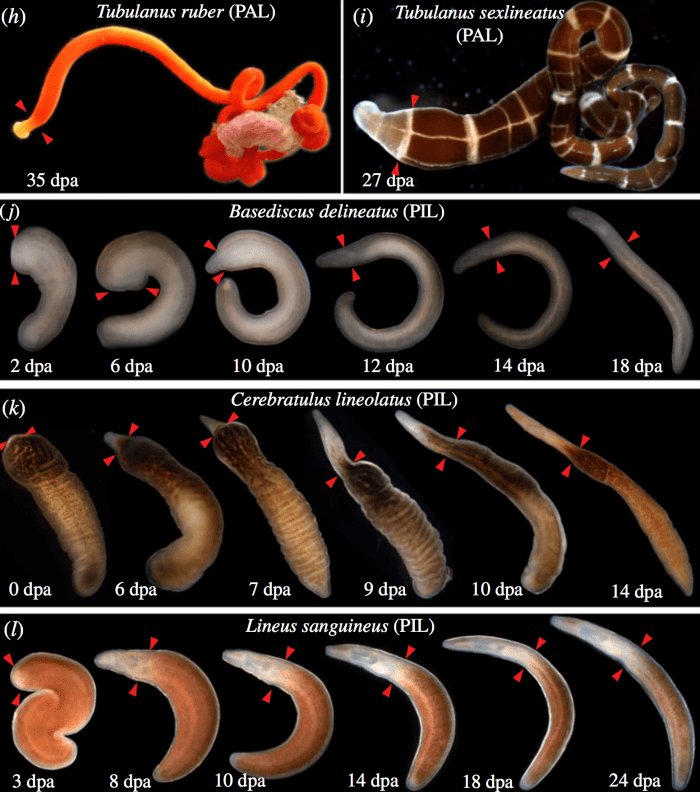
Here’s the thing: their growth isn’t just about getting bigger. Ribbon worms also regenerate body parts that may have been lost due to injury or predation. This ability is fascinating! It shows us how adaptable life can be. Growth in ribbon worms is influenced by factors like temperature, food availability, and habitat, meaning they are highly tuned to their environments.
Moreover, ribbon worms can regenerate their bodies quickly. For example, if a ribbon worm loses part of its tail, it can regrow it in a matter of weeks. This process isn’t just a simple fix; it involves complex biological mechanisms that scientists are still unraveling. Each time they study these worms, they uncover more about how life can thrive despite adversity.
The Mechanics of Regeneration
So, how do these worms manage to regenerate? It all starts with their special cells known as *neoblasts*. These are like the body’s repair kit, capable of turning into different types of cells needed for regeneration. When a ribbon worm loses a part of its body, these neoblasts race to the injury site and begin to multiply, helping to grow new tissues.
Interestingly, the regeneration process isn’t just about healing a wound; it involves a whole orchestra of biological processes. This includes the formation of new blood vessels, nerve connections, and even muscles. Imagine building a new house after a storm; you don’t just replace the roof—you need to ensure everything inside is also strong and functional.
The ability of ribbon worms to regenerate parts of their body has drawn attention from researchers. If we can understand how they do it, perhaps we can unlock secrets to healing in humans and develop new medical therapies. It’s a thrilling field of study that blends ecology with human health.
Why Study Ribbon Worms?
You might be wondering, “Why all this fuss about ribbon worms?” Here’s the thing: studying these creatures can provide insights into broader biological concepts, like regeneration, plasticity, and adaptability in marine life. Their ability to regrow body parts can teach us about cellular biology and potentially lead to advancements in regenerative medicine.
For instance, researchers are investigating what makes ribbon worm regeneration so efficient. By studying their genetic makeup and the processes involved, scientists can learn how to apply these principles to human medicine. Just think of the possibilities: improved wound healing or even growing new organs in the future!
In addition, ribbon worms play a vital role in their ecosystems. They help maintain the balance of marine environments by preying on various organisms and recycling nutrients. Understanding their growth and regeneration can help us appreciate the larger ecological picture and inform conservation efforts.
Challenges in Studying Ribbon Worms
Studying ribbon worms isn’t without its challenges. For starters, they live in marine environments that can be difficult to access. Researchers often need specialized equipment to collect samples from deep waters or murky areas. Plus, many species are not well-documented, making it tough to gather comprehensive data.
Another challenge is the need for controlled environments to study them effectively. Since growth and regeneration can be influenced by environmental factors, replicating those conditions in a lab setting can be tricky. Researchers often have to experiment with different conditions, which can be time-consuming and costly.
Additionally, understanding the genetics behind regeneration requires advanced techniques like genome sequencing. While technology has made this easier, it still requires collaboration between various scientific fields, including ecology, molecular biology, and genetics.
The Future of Ribbon Worm Research
As science progresses, the future of ribbon worm research looks promising. With advancements in technology, including gene editing and biotechnology, researchers are excited about the potential to unlock new secrets. The insights we gain from studying ribbon worms could pave the way for breakthroughs in medicine, particularly in the areas of tissue regeneration and repair.
Moreover, ongoing conservation efforts are essential. Understanding how ribbon worms interact with their environments can help protect their habitats, ensuring these remarkable creatures continue to thrive. Biodiversity is crucial for maintaining healthy ecosystems, and every species, no matter how small, plays a part in that balance.
Finally, public engagement is vital. Educating people about the role of ribbon worms and their fascinating abilities can foster appreciation and support for marine conservation. The more we learn about these creatures, the more it opens our eyes to the wonders of nature. Imagine a future where we can harness the secrets of ribbon worm regeneration for humanity’s benefit—it’s an exciting prospect!
Studying ribbon worm growth and regeneration is a journey into the incredible resilience of nature. These unique creatures have so much to teach us about life, healing, and adaptability. From their astonishing ability to regenerate lost body parts to their crucial role in marine ecosystems, ribbon worms embody the wonders of biological diversity.
As researchers continue to explore their secrets, we may unlock new pathways to improving human health and environmental conservation. The next time you think about regeneration, whether it’s a lizard’s tail or a ribbon worm, remember the remarkable processes that make it all possible. Together, we can support ongoing research and foster a deeper appreciation for the incredible life forms that share our planet.