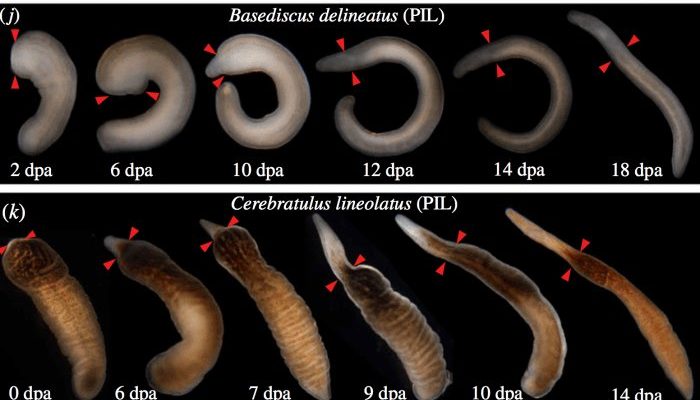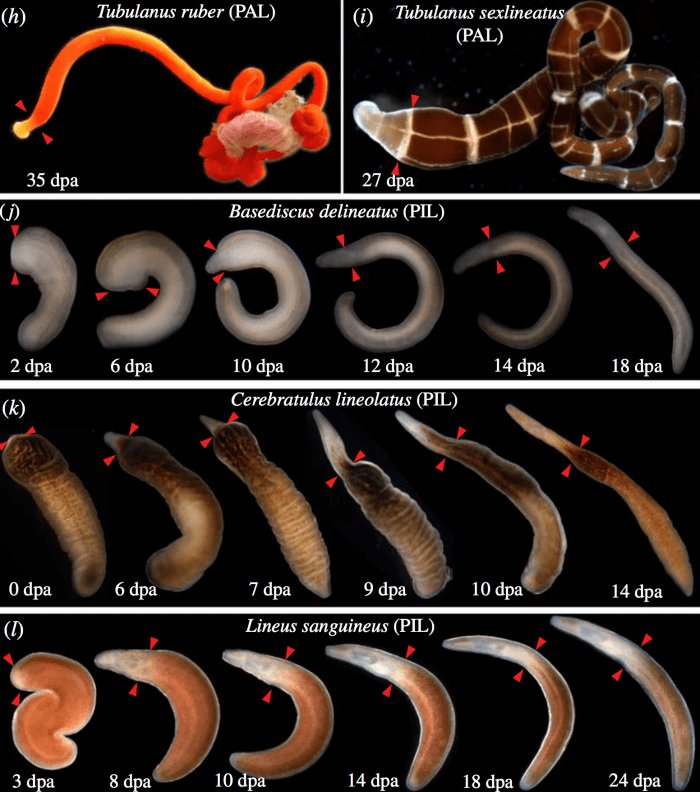
Studying ribbon worms is like peeking behind the curtain of nature’s own science lab. These creatures can regenerate not just limbs but entire sections of their bodies, making them a prime candidate for research. As we dive into the world of ribbon worms, we’ll explore how they grow, why they regenerate, and what it all means for science and medicine. So, grab a cup of coffee, and let’s unravel the mysteries of these remarkable organisms together!
What Are Ribbon Worms?
Ribbon worms are fascinating creatures that belong to the phylum Nemertea. They come in various sizes and colors, and some can grow up to 30 meters long—seriously, that’s longer than a school bus! They’re mostly found in marine environments, creeping along the ocean floor or hidden in the sand. You might be wondering why they’re called ribbon worms. Well, their long, slender bodies resemble ribbons, which makes sense when you see them in their natural habitat.
These worms have a unique anatomy that sets them apart from other invertebrates. They possess a **proboscis**, which is a tube-like structure they can extend and retract. This helps them capture prey like tiny shrimp and worms. Their bodies also contain a network of cells that play a vital role in their regeneration abilities. Understanding their biology is essential for studying how and why they can regrow lost parts.
What’s even more interesting is their method of locomotion. Unlike many other worms that crawl, ribbon worms can glide across surfaces thanks to a layer of mucus they secrete. This slime helps them move quickly and evade predators, making their survival a little easier.
The Magic of Regeneration
Regeneration is not just a cool party trick; it’s a vital survival strategy for ribbon worms. When they’re threatened, these creatures can lose portions of their bodies as a defense mechanism. Here’s the thing: instead of succumbing to injury, they initiate a complex process to regrow those lost parts. Imagine being able to replace your arm with a brand-new one, fully functional and ready to go!
So, how does this work? When a ribbon worm loses part of its body, it triggers a series of biological processes. Specialized cells called **neoblasts**, which are similar to stem cells, go into action. These cells multiply and differentiate into the various cell types needed to rebuild the lost structure. They can form muscles, nerves, and even skin layers. This is a highly coordinated process that shows nature’s brilliance.
Interestingly, scientists are eager to learn more about this regenerative process because it could hold keys to advancements in human medicine. If we can understand how these worms do it, maybe we can find ways to help humans heal better and faster too.
Factors Influencing Growth
You might wonder what influences the growth of ribbon worms. Just like us, their growth is affected by several factors, including environmental conditions, food availability, and even their genetic makeup. Let’s break these down.
**Environmental Conditions:** The habitat where ribbon worms live significantly impacts their growth. For example, water temperature and salinity can either foster growth or stunt it. Warmer waters generally boost metabolic rates, leading to quicker growth. However, if temperatures become too extreme, it could have the opposite effect.
**Food Availability:** These worms are predators that feast on smaller invertebrates. The more food they have, the faster they can grow and regenerate. Think of it like this: if you’re well-fed and happy, you’re more likely to flourish! A lack of food, on the other hand, can slow down their growth and recovery processes.
**Genetics:** Just like humans, each species of ribbon worm has its own genetic blueprint that influences how it grows and regenerates. Some species are better at regeneration than others, and this varies due to evolution and natural selection over time.
Research and Implications
Researchers are keenly interested in ribbon worms for several reasons. Understanding their growth and regeneration could lead to breakthroughs in regenerative medicine, which focuses on repairing or replacing damaged tissues and organs. For instance, scientists are investigating how the mechanisms in ribbon worms could inspire treatments for conditions like spinal cord injuries or severe wounds in humans.
In laboratories, scientists conduct experiments to observe these regeneration processes in real-time. They may remove parts of a ribbon worm and document how quickly and efficiently it regrows. This kind of research can provide insights into cellular behavior and regeneration pathways that might be applicable to vertebrates.
Moreover, studying the genetic factors that enable regeneration in ribbon worms could open doors to gene therapy and advanced medical treatments. The implications are vast, and as we learn more, who knows what wonders the future holds?
Challenges in Studying Ribbon Worms
Despite the exciting prospects, studying ribbon worms isn’t without its challenges. One of the significant hurdles is their habitat. Ribbon worms are often found in deep, murky waters or buried in the sand, making them difficult to observe. Collecting samples usually requires specialized equipment, and maintaining their health in a lab environment can be tricky.
Another challenge is understanding the full scope of their regenerative capabilities. While scientists have made strides, there’s still so much we don’t know about how these worms control their growth and regeneration at the cellular level. Moreover, the variability among different species adds another layer of complexity. Researchers must consider how environmental differences affect these processes before making broad conclusions.
Lastly, there’s the public perception of studying creatures like ribbon worms. Some people might not find them as appealing as other animals, which could affect funding and interest in research on them. Yet, as we’ve discussed, their unique traits could unlock answers to significant medical questions, making them worth the effort.
Studying ribbon worm growth and regeneration offers a glimpse into the marvels of nature. These creatures remind us that there’s so much more to learn about life beneath the waves. As researchers continue to explore their unique capabilities, we stand on the brink of discoveries that could transform our understanding of healing and regeneration.
Honestly, the potential applications of this research could revolutionize medicine as we know it. From improving wound healing to possibly regrowing damaged organs, the future is looking bright. Ribbon worms, with their ribbon-like bodies and incredible regenerative powers, may very well hold secrets that benefit us all—if we can just unlock those mysteries.
As we conclude our dive into the world of ribbon worms, remember that the journey of understanding these creatures is not just important for biology but could also shape the future of how we approach health and healing. So next time you hear about a ribbon worm, think of all the incredible science swirling around them—it might just inspire a new wave of curiosity!