Just like a well-designed remote control can operate various devices, silkworms can shed light on complex biological processes. They grow quickly and have a metabolism that adapts to various environmental conditions, making them ideal subjects for scientific research. Not to mention, their short life cycle allows scientists to observe multiple generations in a relatively short time. So, grab a cup of coffee, and let’s dive into how these little critters are making big waves in research!
The Role of Silkworms in Metabolic Research
When we delve into the world of metabolism, silkworms offer a unique perspective. Their simplicity as organisms allows researchers to study metabolic processes without the complications seen in larger animals. Essentially, they act as a living laboratory. Researchers can observe how silkworms metabolize nutrients, which can help us understand broader biological concepts.
Here’s the thing: silkworms have a rapid growth rate, undergoing several stages from egg to adult moth in just a few weeks. During this time, they consume a lot of food—mostly mulberry leaves—which is where their metabolism comes into play. Their ability to convert food into energy and growth materials provides essential insights into metabolic rates and efficiency. For instance, scientists can manipulate their diets to see how changes affect growth rates, offering a glimpse into dietary impacts on metabolism.
Moreover, studying the metabolic pathways in silkworms can have crucial implications for agriculture and human health. By understanding how these insects process nutrients, researchers can apply those findings to improve food sources or develop new strategies for managing pests. Metabolism isn’t just about energy; it’s about survival and adaptation, and silkworms are perfect subjects for this intricate dance.
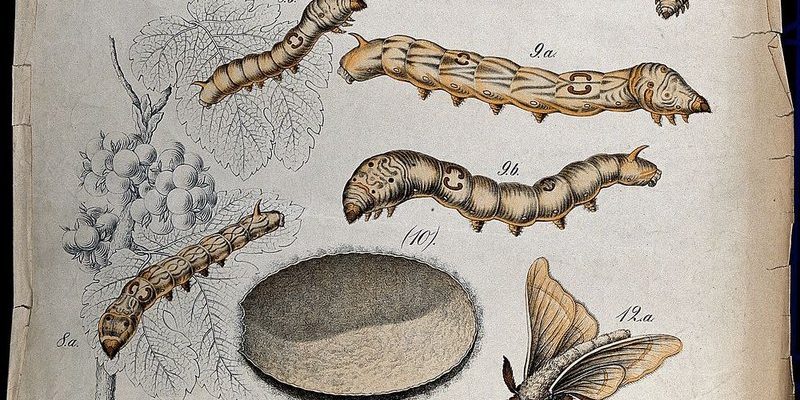
Growth Stages of Silkworms: A Lifecycle Overview
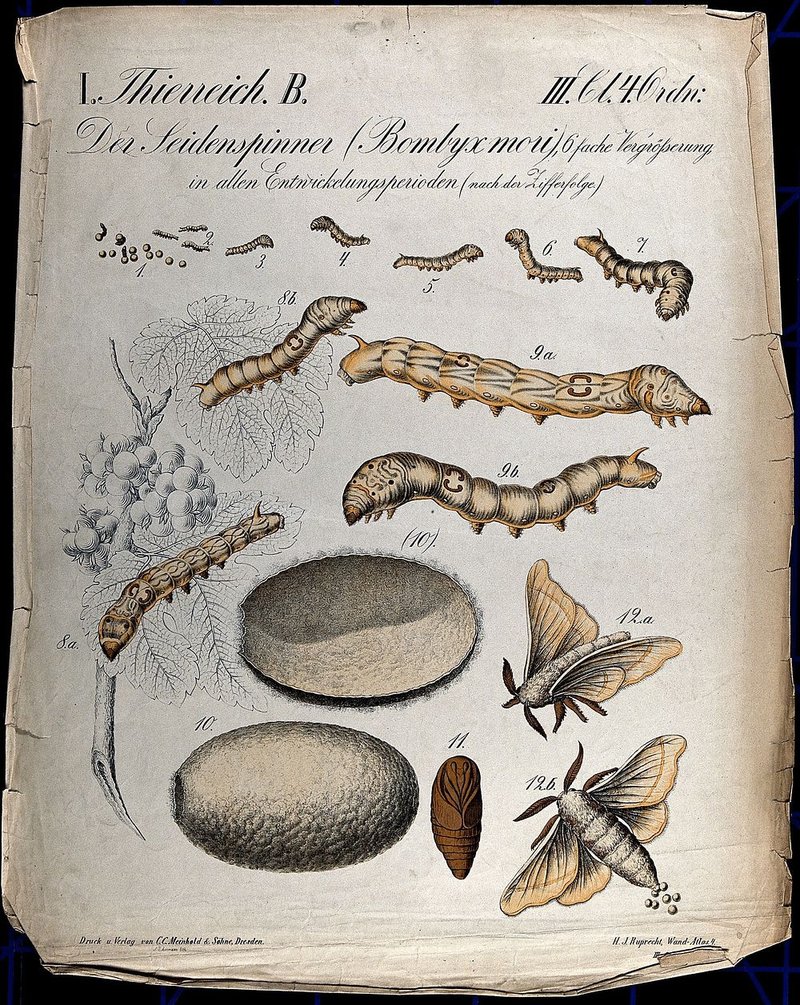
The growth stages of silkworms are nothing short of remarkable. They go through a series of transformations known as *instars*, each stage marked by molting. These stages include the egg, larva (or caterpillar), pupa, and adult moth, each with its unique characteristics. Let me explain: during the larval stage, silkworms can grow up to 10,000 times their original size!
– **Egg Stage:** The life of a silkworm begins as a tiny egg, which hatches into a larva after about 10 days, depending on environmental conditions.
– **Larval Stage:** This is where the magic happens. Silkworms are voracious eaters, and they munch on mulberry leaves to fuel their rapid growth. They go through five different instar phases during this time, growing larger each time.
– **Pupal Stage:** Once they’ve reached their full size, they spin a cocoon around themselves and enter the pupal stage. This is a crucial transformation period where they undergo metamorphosis.
– **Adult Stage:** Finally, they emerge as adult moths. Interestingly, these moths can’t eat; they rely on the energy stored during their larval stage to reproduce and fulfill their life’s purpose.
Studying these growth stages provides scientists with valuable insights into developmental biology. It’s fascinating to watch how a small egg can develop into a creature that makes silk—just like seeing how a tiny seed can grow into a towering tree.
Silkworms and Human Health: Applications in Biomedical Research
You might be wondering how silkworms relate to human health. It turns out that studying their growth and metabolism has significant implications in **biomedical research**. For instance, silkworms are often used as models for understanding various diseases, including obesity and diabetes. Their metabolic pathways can mirror those in humans, making them ideal candidates for testing new pharmaceuticals or studying metabolic disorders.
One exciting area is using silkworms to produce recombinant proteins. Scientists can introduce genes into silkworms that allow them to produce human proteins. This has promising applications in creating vaccines and therapeutic agents. Imagine silkworms serving as tiny factories producing life-saving medicines!
Furthermore, because silkworms have a robust immune system, researchers can study how they fight off infections and diseases. Insights gained from these studies can help us develop new strategies for enhancing human immunity.
Environmental Influences on Silkworm Growth and Metabolism
The environment plays a massive role in the growth and metabolism of silkworms. Factors like temperature, humidity, and the quality of food can significantly affect their development. For instance, if the temperature is too high or too low, it can lead to slower growth rates or even increased mortality.
Researchers often experiment with varying conditions to see how silkworms respond. This kind of research is vital, especially as we face climate change and its effects on agriculture. Understanding how silkworms adapt to environmental changes can inform us about resilience in other species, including our own crops.
– **Temperature Sensitivity:** Studies show that a rise in temperature can accelerate their metabolism, which sounds great, but it can lead to increased energy demands and nutritional needs.
– **Diet Variation:** The quality of mulberry leaves significantly influences their growth. Researchers are exploring different feeding strategies to optimize growth and silk production, which could lead to better silk farming practices.
Through these studies, we gain insights not just about silkworms but also about how organisms adapt to their environments. This knowledge is crucial as we navigate changing climates.
Future Directions in Silkworm Research
As science progresses, the future of silkworm research looks bright. With advancements in genetic engineering and biotechnology, researchers have the potential to unlock even more secrets of these remarkable insects. For example, genetically modifying silkworms to enhance specific metabolic traits could lead to strains that produce more silk or grow faster while requiring fewer resources.
Another exciting direction is the exploration of silkworms in sustainable practices. As climate change pushes us toward greener solutions, silkworms may offer a path to sustainable silk production. Their needs can be more easily managed compared to traditional livestock, leading to a lower carbon footprint and reduced environmental impact.
Moreover, researchers are increasingly using silkworms to study the effects of various chemicals and toxins. This can help in assessing environmental risks and developing better safety protocols for human and animal health.
Silkworms may seem like simple insects, but their role in research is anything but ordinary. From unraveling the complexities of metabolism to serving as models for human health, these little guys are making significant contributions to science. Their unique lifecycle and adaptability offer insights that extend beyond just their silk production.
Understanding silkworms allows us to appreciate the intricate connections between growth, metabolism, and our environment. As researchers continue to explore their potential, it’s clear that silkworms are more than just silk-spinners; they’re vital players in the ongoing quest to understand life itself. Who knew that these tiny caterpillars could hold the key to so many biological mysteries? So, the next time you think of silkworms, remember: there’s a whole world of research happening around them, revealing the wonders of life on Earth.