Understanding silkworm mating behavior and egg laying is crucial not just for those in agriculture or textile industries, but it’s also a captivating topic for anyone intrigued by nature. Think of it as exploring a little romance story in the insect world. So, grab your coffee, and let’s learn more about how these critters ensure their lineage continues through some rather unique behaviors!
The Mating Ritual of Silkworms
Silkworms have a simple yet intriguing mating behavior. The male moth, after emerging from its cocoon, is on the lookout for a female partner. Here’s the thing: these little guys rely heavily on scent to find their mates. The female silkworm releases pheromones when she’s ready to mate, creating a sort of “come hither” call that the males can detect from quite a distance. Imagine a romantic dinner where one partner sends out sweet smells—only here, it’s all about the fragrance of attraction!
Once a male finds a female, he guides her through a process known as courtship. This is where things get a bit more hands-on. The male will often perform a little dance, vibrating his wings to attract her. If she’s receptive, they’ll eventually mate. This process, though fascinating, is quite quick. You might be surprised to learn that mating typically only lasts for a few hours before the pair goes their separate ways, which makes it a bit of a whirlwind romance!
The Act of Mating
During mating, the male silkworm transfers sperm to the female using specialized reproductive organs. This is crucial because the female needs the sperm to fertilize her eggs. After mating, the female will carry the sperm until she’s ready to lay eggs. It’s like having a precious cargo that she keeps safe for the next stage of her life cycle.
The timing of egg laying is essential. Female silkworms are usually more active at night, making them nocturnal when it comes to reproduction. After mating, she will search for the perfect place to lay her eggs, often preferring leaves or other surfaces that provide cover and safety. This instinctual behavior helps ensure that her offspring have the best chances of survival once they hatch.
How Egg Laying Works
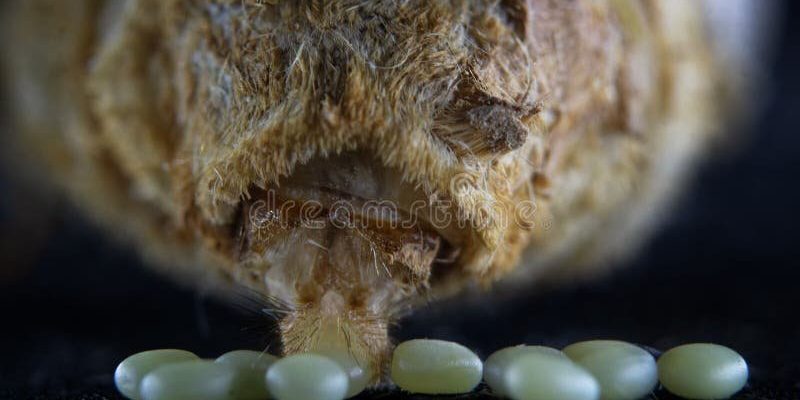
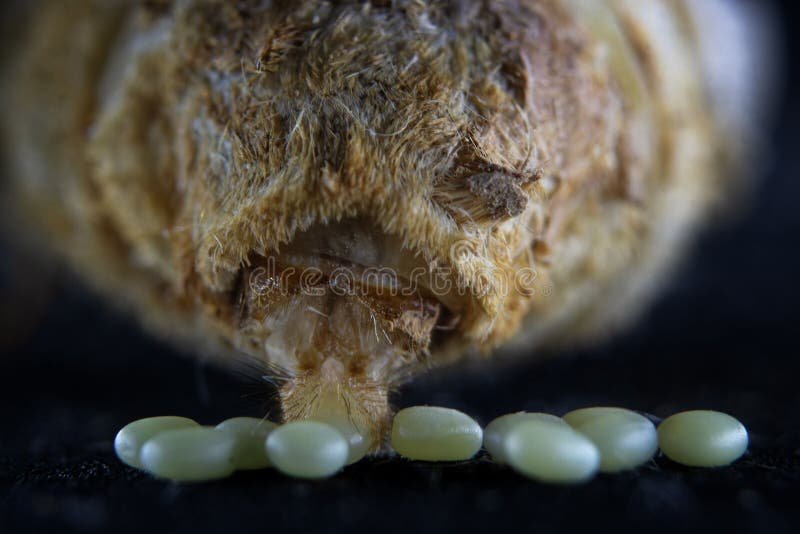
Once she finds a suitable spot, it’s time for the female to lay her eggs. Silkworms typically lay anywhere from 200 to 500 eggs in a single session. Now, this might sound overwhelming, but it’s a strategic move. The more eggs she lays, the higher the chance that some will survive predators or environmental challenges.
The eggs themselves are small, round, and come in various colors depending on the silkworm species. After laying, the female covers the egg mass with a sticky substance that helps protect them from potential threats. It’s a bit like a protective blanket, ensuring her future generation has a fighting chance right from the start.
Caring for the Eggs
After laying her eggs, the mother silkworm doesn’t stick around to care for them. Instead, it’s up to the eggs to fend for themselves. They usually hatch after about 10 days, depending on environmental conditions like temperature and humidity. Here’s where nature’s resilience shines: baby silkworms, also known as larvae, are born ready to eat.
Once they hatch, these tiny creatures begin munching on mulberry leaves, their primary food source. They have a voracious appetite and will grow quickly during this phase. The strong survival instinct in silkworms is fascinating—born to eat and grow, they’ll eventually metamorphose into those beautiful moths we admire.
The Role of Environment in Mating and Egg Laying
The environment plays a critical role in silkworm mating and egg laying. Factors like temperature, humidity, and light cycles can influence their behaviors. For instance, a warm, humid environment is ideal for mating and egg laying, while cold, dry conditions can hinder these processes.
Farmers and silkworm breeders often mimic these conditions to optimize reproduction. By providing the right environment, they can enhance the chances of successful mating and healthy egg production. It’s a careful balancing act that combines nature and nurture, ensuring that these creatures thrive and contribute to silk production.
Challenges Faced by Silkworms
Despite their remarkable life cycle, silkworms face numerous challenges. Predators, diseases, and environmental changes can devastate populations. For instance, if conditions aren’t right for mating or egg laying—like extreme weather or inadequate food sources—silkworm populations can decline.
Additionally, as interest in sustainable practices grows, the challenges of farming silkworms sustainably are at the forefront. Farmers are exploring new methods to ensure the health of silkworms while minimizing environmental impact. It’s a reminder of how interconnected nature is and how vital it is to respect these delicate ecosystems.
Understanding silkworm mating behavior and egg laying offers a peek into a world full of wonder. From the intricate courtship rituals to the challenges these creatures face, their life cycle is a testament to the resilience of nature. The next time you admire a silk garment, remember the tiny silkworms and the fascinating journey they undertake to fulfill their biological role.
By appreciating these little beings, we can connect more deeply to the fabric of our lives—literally and figuratively. Whether you’re a farmer, a fashion lover, or just someone curious about nature, silkworms have a story worth knowing. So, let’s continue to explore and protect the incredible tapestry of life around us, starting with these remarkable moths.

