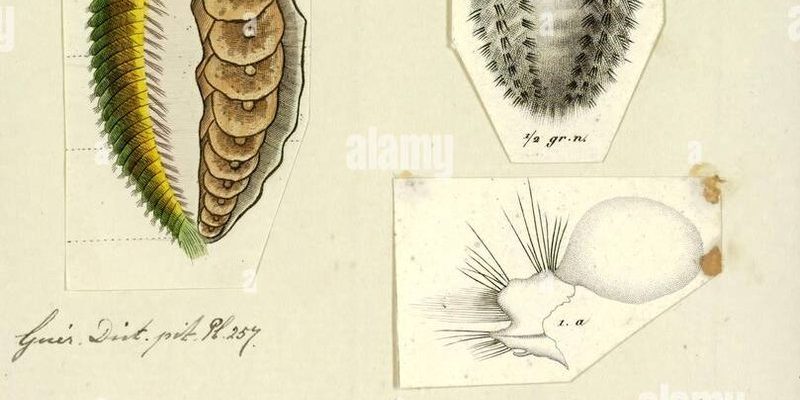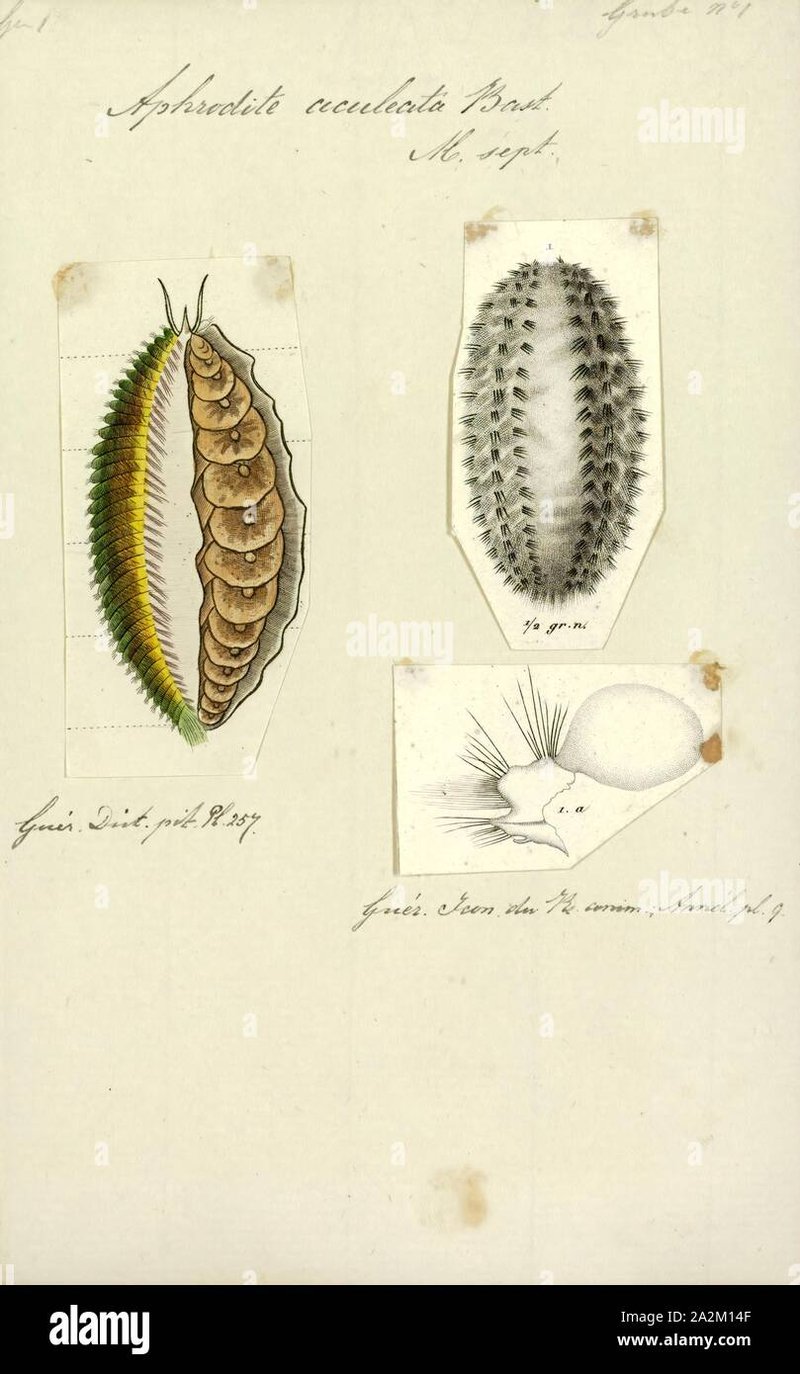
Imagine you’re sitting on the beach during a warm summer day, watching the waves lap against the shore. If you were to dig a little into the sand, you might find these worms, which look unassuming but are quite remarkable. They have unique adaptations that help them thrive in various conditions, changing their behavior as the seasons shift. This blog will dive deep into what field studies have revealed about the seasonal behavior patterns of *Aphrodite aculeata* and why these patterns matter.
Habitat and Environment
To understand how *Aphrodite aculeata* behaves throughout the seasons, it’s essential to consider its habitat. These worms typically inhabit sandy or muddy substrates in intertidal and subtidal zones. The conditions—such as water temperature, salinity, and food availability—vary with the changing seasons, influencing their behavior.
In summer, when temperatures rise, *Aphrodite aculeata* tends to be more active. The warmer water is rich in nutrients, making it a prime time for feeding and reproduction. The increased metabolic rate fuels their growth and encourages them to reproduce. During this time, you might observe them burrowing less and spending more time feeding near the surface, taking advantage of the abundant food sources.
As fall approaches, things shift. The temperature cools, and so does the activity of these worms. They start preparing for the colder months by conserving energy. They might retreat deeper into the substrate, becoming less visible and active. This behavioral shift is a smart survival strategy in response to the changing environment, showcasing how *Aphrodite aculeata* adapts to the seasonal rhythm of its habitat.
Feeding Behavior Throughout the Seasons
Feeding is a critical aspect of *Aphrodite aculeata*’s life, and it changes with the seasons, too. In warmer months, their preferred diet consists mainly of detritus and microorganisms abundant in the water. During this time, they can afford to be more active, hunting for food and engaging in mating behaviors.
In spring and summer, when food sources are plentiful, researchers have noted that these worms exhibit a more aggressive feeding strategy. They often come out to the surface more frequently, taking advantage of the increased abundance of phytoplankton and other microscopic life. This is like a buffet for them, and they really make the most of it!
However, as winter rolls in, food becomes scarce. With the cooler temperatures and less active microbial life, *Aphrodite aculeata* shifts its strategy. It becomes more selective with its feeding, focusing on whatever organic materials are still available within the sediment. This change highlights how adaptability is crucial for survival.
Reproductive Patterns and Timing
One of the most intriguing aspects of *Aphrodite aculeata* is its reproductive behavior, which is closely tied to seasonal changes. Field studies indicate that these worms generally reproduce in late spring to early summer when conditions are favorable.
During this reproductive window, they enter a phase called *epitoky*, where they transform into a more mobile form to spawn. Imagine them like butterflies emerging from a cocoon—suddenly vibrant and full of life. This transformation allows them to leave their burrows, swim freely in the water column, and maximize their chances of mating.
Once the eggs are released, the larvae are carried away by the ocean currents, which is a clever way to spread their genes. However, the timing of this process is critical. The larvae need to settle in a suitable environment that offers adequate food and protection. This is a delicate balancing act that highlights the interconnection between their reproductive timing and environmental factors.
Impact of Climate Change on Behavior
As our planet’s climate changes, the behaviors of many species, including *Aphrodite aculeata*, are also shifting. Rising sea temperatures and altered salinity levels can significantly impact their life cycles and habitat preferences.
For example, with warmer temperatures, the typical reproductive seasons might be affected. These worms may start breeding earlier in the year, leading to mismatched timing with food availability. Imagine planning a picnic in winter—without the right conditions, it just wouldn’t work!
Additionally, changes in ocean currents can influence the distribution of larvae, potentially leading to overcrowded areas or a lack of suitable habitats. Field studies have started to document these patterns, showing that *Aphrodite aculeata* may struggle to adapt to these rapid changes. Understanding these impacts is vital for conservation efforts and maintaining the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
Field Studies and Observations
Field studies play a crucial role in uncovering the seasonal behavior patterns of *Aphrodite aculeata*. Researchers often conduct observations during different times of the year to document changes in behaviors, populations, and habitats. These studies involve taking samples from various environments and analyzing the data collected.
For instance, scientists might deploy traps or sediment cores to capture worms during peak breeding seasons. These samples help them understand population dynamics and how environmental factors contribute to behavioral shifts. It’s like piecing together a puzzle where each observation reveals more about the intricate life of these worms.
Furthermore, these studies sometimes employ technologies like underwater cameras or sensors to monitor conditions in real-time. This innovative approach allows researchers to observe how *Aphrodite aculeata* responds to sudden changes, such as a storm or temperature fluctuations. The data collected helps build a comprehensive picture of their seasonal life and the challenges they face in a changing world.
Why Understanding Seasonal Behavior Matters
So, why should we care about the seasonal behavior patterns of *Aphrodite aculeata*? Well, understanding these patterns not only enriches our knowledge of marine biology but also helps us grasp the wider implications for marine ecosystems.
As key players in their environment, any changes in their behavior can ripple through the food web. For instance, if these worms start reproducing earlier due to warmer temperatures, it could affect predator-prey relationships and the balance of marine life. By studying *Aphrodite aculeata*, we can also learn more about the health of coastal ecosystems, as they often serve as indicators of environmental changes.
Moreover, insights gained from observing these beautiful creatures can guide conservation efforts. By knowing when and how they thrive, we can better protect their habitats and ensure that future generations can appreciate their role in marine life.
In summary, the seasonal behavior patterns of *Aphrodite aculeata* tell us a compelling story about adaptation, resilience, and the interconnectedness of life in our oceans. The more we learn, the better equipped we become to safeguard the delicate balance of our marine environments.
In conclusion, studying the seasonal behaviors of *Aphrodite aculeata* is not just an academic exercise; it’s a vital piece of understanding our marine ecosystems. Every observation and field study adds depth to our knowledge and highlights the importance of preserving these fascinating creatures and their habitats for the future.