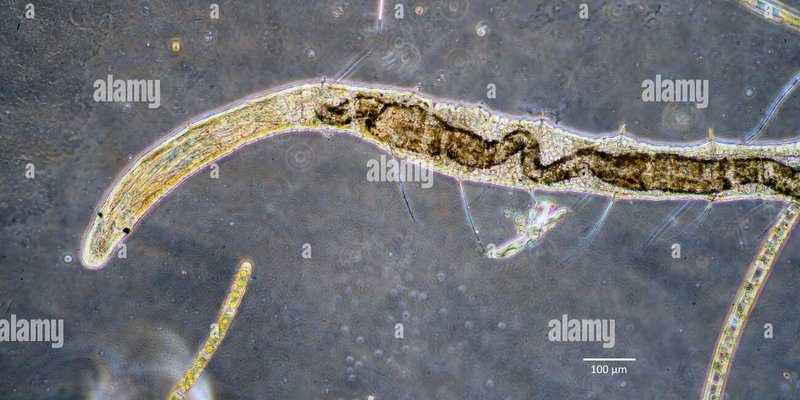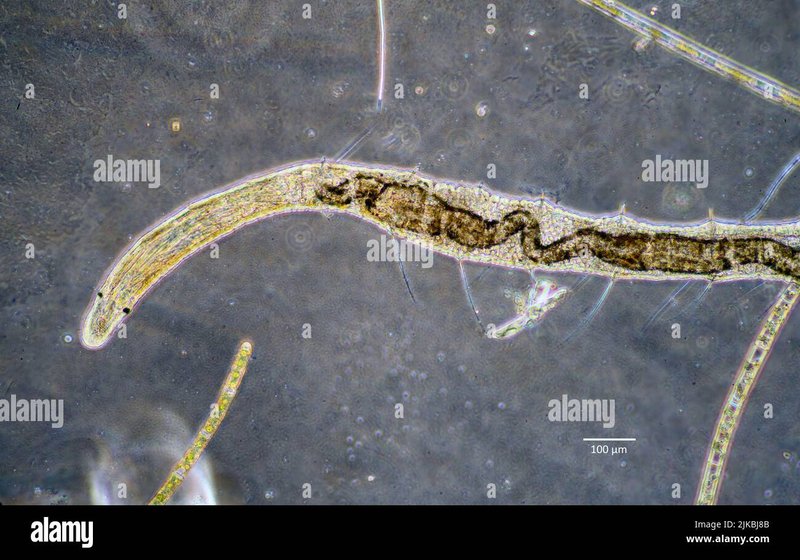
Bristle worms, belonging to the Annelida phylum, can be found in various marine environments, often buried in the sediment. They may look a bit like spaghetti with bristles, but they play a serious role in nutrient cycling. Imagine them as tiny workers in a bustling restaurant, taking leftover bits of food and turning them into delicious meals for others. So why should we care about these little guys? Let’s dive deeper and explore their essential role in maintaining the health of our marine ecosystems.
What Are Bristle Worms?
Bristle worms are fascinating creatures that come in various sizes, shapes, and colors. Most of them have long, segmented bodies adorned with bristles or setae that help them move through their underwater world. You may find them in mud, sand, or even on coral reefs. These worms can be either free-living or burrow in the sediment, making them incredibly adaptable.
There are many species of bristle worms, but some of the most common include *Nereis*, *Lumbricus*, and *Aphrodita*. While some species can grow quite large, others are relatively small, often measuring just a few centimeters in length. Their diversity is part of what makes them such an essential component of the marine ecosystem.
You might be wondering how these little critters manage to impact nutrient cycling so significantly. The secret lies in their feeding habits. Bristle worms are scavengers that consume organic material from dead plants, animals, and other detritus. As they munch away, they break down these materials, making nutrients more accessible to other organisms in the ecosystem.
How Do Bristle Worms Contribute to Nutrient Cycling?
Nutrient cycling is a natural process that involves the movement and transformation of nutrients within an ecosystem. Bristle worms contribute significantly to this cycle by breaking down organic material into simpler compounds that can be used by other organisms. Here’s how it works:
1. **Decomposition**: When plants and animals die, their bodies become a source of organic matter. Bristle worms feed on this matter, breaking it down into smaller pieces. This process not only recycles nutrients but also helps to reduce waste in the ocean.
2. **Nutrient Release**: As bristle worms digest organic material, they release nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus back into the sediment. These nutrients are essential for plant growth and can also be taken up by microorganisms. This, in turn, supports a wide range of marine life.
3. **Habitat Modification**: As bristle worms burrow through the sediment, they change the physical structure of the environment. This activity increases oxygen levels and promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria, further enhancing nutrient cycling.
In essence, bristle worms act like tiny farmers, tilling the soil and enriching it with nutrients. This not only benefits their immediate surroundings but also supports the broader marine ecosystem.
The Importance of Biodiversity
Biodiversity in marine ecosystems is crucial for maintaining balance. Bristle worms play a critical part in this web of life. They’re not just essential nutrient recyclers; they also serve as food for various marine animals, including fish and crustaceans. If you think about it, when a system has rich biodiversity, it creates a more resilient environment.
When bristle worm populations are stable, they help ensure that nutrients remain available for other organisms. However, if their numbers decline, it can disrupt the nutrient cycle. This can lead to issues like algal blooms or a drop in overall marine health, so their presence is more critical than it might seem.
Here’s the thing: a healthy ocean relies on the interactions between many species, including bristle worms. By supporting biodiversity, we can help maintain the essential functions that keep our oceans thriving.
How Human Activities Impact Bristle Worms
Unfortunately, human activities can have a significant impact on bristle worm populations and, by extension, nutrient cycling in the ocean. Pollution, habitat destruction, and overfishing are just a few factors that can disrupt their delicate balance.
– **Pollution**: Chemicals and waste products can contaminate marine environments, affecting the health of bristle worms. Toxic substances may kill them directly or hinder their ability to perform their ecological roles.
– **Habitat Destruction**: Coastal development and dredging can destroy the sediments where bristle worms live, leading to population declines. Without their habitat, these tiny recyclers can’t thrive.
– **Overfishing**: Removing too many fish and other marine species can disrupt the food chain. Bristle worms rely on dead organic material from these creatures, and if their populations diminish, it can affect nutrient cycling.
To protect bristle worms and support healthy marine ecosystems, we need to be mindful of our impact. Sustainable practices and conservation efforts can help maintain these vital worm populations and, in turn, the overall health of the ocean.
Conservation Efforts and Their Benefits
Conservation efforts focused on marine ecosystems are essential for protecting bristle worms and ensuring the sustainability of nutrient cycling. Here are a few ways we can contribute:
1. **Reducing Pollution**: Proper waste management and reducing the use of harmful chemicals can help minimize pollution in marine environments. Supporting legislation aimed at protecting oceans can also make a significant difference.
2. **Responsible Fishing Practices**: Choosing sustainably sourced seafood and supporting responsible fisheries can help maintain the balance of marine life. When fish populations are managed effectively, it allows for healthier ecosystems, including thriving bristle worm populations.
3. **Restoration Projects**: Participating in or donating to restoration projects that aim to rehabilitate coastal ecosystems can be incredibly beneficial. These initiatives often focus on restoring habitats that support diverse marine life, including bristle worms.
By taking these actions, we can help create healthier oceans that support all creatures, big and small. Protecting bristle worms is just one piece of the larger puzzle, but it’s a crucial one.
The Future of Bristle Worms and Ecosystem Health
As we look to the future, understanding and protecting the role of bristle worms in nutrient cycling is essential for maintaining vibrant marine ecosystems. Our oceans face numerous challenges, but by promoting healthy ecosystems, we can ensure that these tiny yet mighty creatures continue to thrive.
Keeping an eye on the health of bristle worm populations can serve as an indicator of overall ocean health. If these creatures are flourishing, it’s a good sign that nutrient cycling is in balance. So the next time you think about our oceans, remember the little bristle worms doing their important work beneath the surface.
In conclusion, bristle worms may be small, but their role in nutrient cycling is anything but insignificant. By supporting the health of these creatures and the ecosystems they inhabit, we can contribute to a thriving marine environment. It’s a simple yet effective way to make a lasting impact on our oceans.