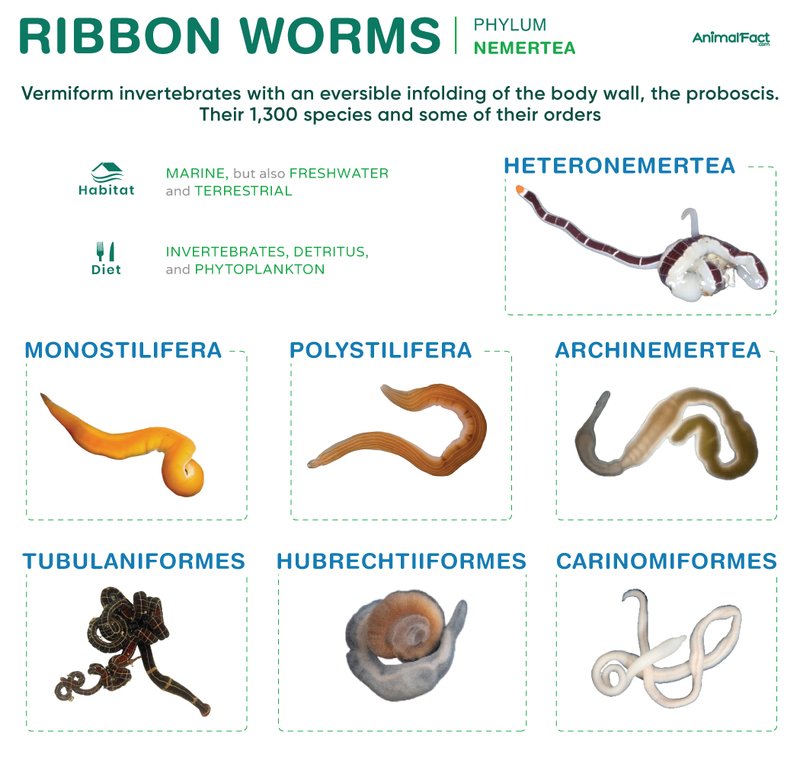
When we dive deeper into the world of ribbon worms, it’s like peeling back layers of an onion, revealing how these creatures thrive in different environments. Whether it’s the soft, sandy bottoms or the coarse, rocky surfaces of the sea, ribbon worms show a surprising adaptability and preference that plays a crucial role in their survival. Let’s explore the ins and outs of ribbon worm burrowing and their substrate favorites!
What Are Ribbon Worms?
Ribbon worms, or *Nemertea*, are a fascinating group of invertebrates known for their long, flattened bodies. They can range from a few centimeters to several meters in length. Imagine a spaghetti noodle sliding through the ocean; that’s essentially what a ribbon worm looks like! These critters are typically found in marine environments, and their lifestyle often involves burrowing into various substrates.
One of the standout characteristics of ribbon worms is their ability to extend their bodies remarkably. With specialized structures, they can burrow into sand, mud, or even rocky surfaces. This unique ability isn’t just a quirk; it’s a survival mechanism. By hiding from predators and environmental changes, ribbon worms can thrive in diverse marine ecosystems.
The Importance of Burrowing
You might be wondering, why do ribbon worms burrow in the first place? Well, burrowing serves several vital functions. First, it provides protection. Just like how we feel safer in our homes, ribbon worms use their burrows to shield themselves from predators. They can retreat into these tunnels when danger approaches, making it harder for predators to spot them.
Second, burrowing helps in feeding. Many ribbon worms are carnivorous, preying on small mollusks and other marine animals. By creating burrows, they can ambush their prey, making them more efficient hunters. It’s like having a secret hideout from which they can launch surprise attacks!
Lastly, burrowing contributes to nutrient cycling in the ocean floor. As ribbon worms dig through the substrate, they disturb the sediment, allowing oxygen to penetrate deeper layers. This process helps sustain a healthier ecosystem, benefiting not just ribbon worms but other marine life as well.
Substrate Preferences of Ribbon Worms
When it comes to choosing a substrate, ribbon worms are not just picky; they have specific preferences that influence their habitat. In general, these worms favor environments that offer a balance between stability and accessibility. Let’s break down some common substrate types they prefer:
- Sandy substrates: Ribbon worms are often found in fine to medium-grained sand. This type of substrate is easy for them to burrow into, allowing them to create intricate tunnels quickly.
- Soft mud: Some species thrive in muddy environments, where they can dig deeper and find ample food sources. The softness of the mud allows for easier burrowing, making it a favorite.
- Rocky substrates: In contrast, certain ribbon worms prefer coarser, rocky areas where they can cling onto surfaces. These habitats often offer a unique feeding opportunity, allowing them to capture prey hiding in crevices.
Understanding these substrate preferences is essential for conservation efforts. When we know where ribbon worms are likely to thrive, we can better protect their habitats from pollution and other threats.
How Ribbon Worms Burrow
Now that we know where ribbon worms like to live, let’s take a closer look at *how* they actually burrow. The process is nothing short of fascinating. Ribbon worms use a combination of muscular contractions and secretion of mucus to create their burrows. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how they do it:
1. **Anchor body**: Ribbon worms first anchor themselves to the substrate with their muscular bodies.
2. **Contraction**: They then contract their bodies to push against the substrate, breaking it apart.
3. **Secretion of mucus**: While burrowing, they secrete a slimy mucus that helps them slide through the particles and keeps the burrow walls stable.
4. **Extension and retraction**: Through a series of extensions and contractions, they expand their burrow, creating a network of tunnels.
This unique burrowing technique showcases how ribbon worms adapt to their environments. It also allows them to create a safe haven tailored to their needs.
Impact of Environmental Changes on Burrowing Behavior
Environmental changes can significantly influence ribbon worm behavior, particularly their burrowing habits. Factors like temperature, salinity, and substrate availability can compel these worms to adapt or shift their burrowing strategies. Here’s how:
1. **Temperature**: If the ocean warms up, it can affect the metabolic rates of ribbon worms. Warmer temperatures might encourage them to burrow deeper for cooler conditions. On the flip side, extreme heat could make them more vulnerable to predators.
2. **Salinity**: Changes in salinity can impact their ability to thrive. Increased salinity might push ribbon worms to seek out more suitable locations.
3. **Substrate Availability**: If their preferred substrate becomes scarce due to erosion or human activities, ribbon worms may have to compromise and adapt to less ideal conditions. This could lead to increased competition with other species for resources.
Being aware of these changes is essential for the conservation of ribbon worms and the ecosystems they inhabit.
Conservation and Future of Ribbon Worms
Finally, as we look towards the future, it’s crucial to acknowledge the role of ribbon worms in our oceans. They may seem small and insignificant, but their burrowing activities contribute to the overall health of marine ecosystems. Sadly, factors like pollution, climate change, and habitat destruction threaten their populations.
Conservation efforts must focus on protecting their habitats and understanding the intricate relationships they hold within marine ecosystems. By protecting the environments that ribbon worms thrive in, we can preserve their ecological contributions, ensuring the health of our oceans for future generations.
So there you have it—a deep dive into the world of ribbon worms and their burrowing and substrate preferences. These seemingly simple creatures play a vital role in our oceans, reminding us of the interconnectedness of life beneath the waves. Understanding their behaviors and habitats helps us appreciate the delicate balance of marine ecosystems, pushing us to advocate for their protection. Let’s cherish their hidden lives and work towards a healthier ocean for all!