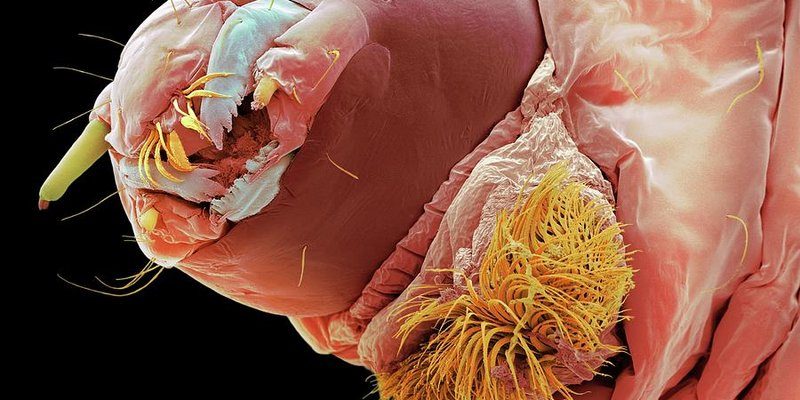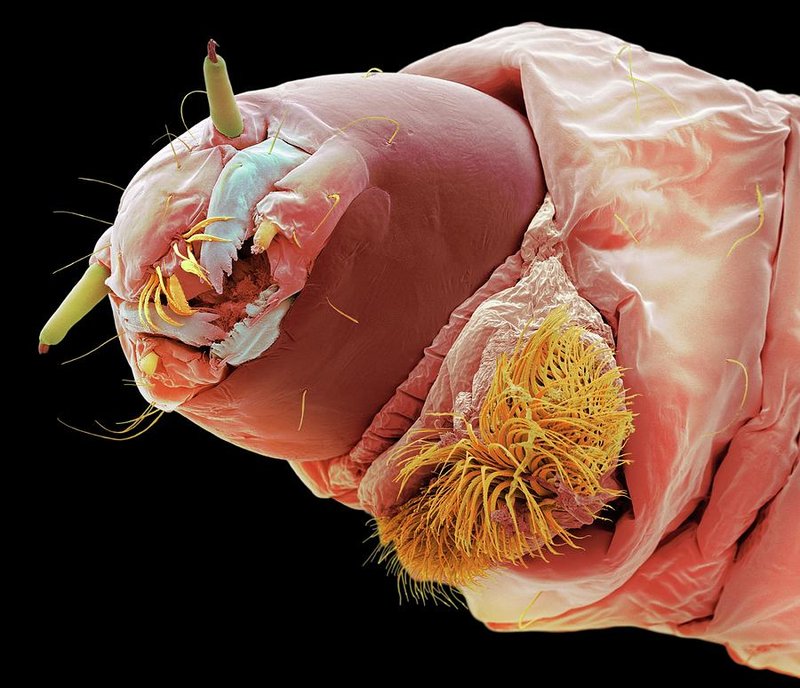
Picture the lifecycle of bloodworms like a movie, with each season representing a different act. From their vibrant spring emergence to their subdued winter dormancy, these worms have a fascinating story to tell. Whether you’re an aquarist, a fisherman, or just someone curious about nature, understanding how bloodworm activity changes with the seasons can help you appreciate these remarkable creatures even more.
In this article, we’ll dive into the seasonal behaviors of bloodworms, explore why they matter, and offer practical tips for monitoring their activity all year round.
What Are Bloodworms, Exactly?
Bloodworms are the larval stage of a type of midge, specifically the genus *Chironomus*. Although they might not look like much at first glance, they play a huge role in aquatic ecosystems. You might be surprised to learn that bloodworms are often favored fish food—especially for species like trout and perch.
The name “bloodworm” comes from their striking reddish color, which is due to the hemoglobin present in their bodies. This hemoglobin allows them to thrive in low-oxygen environments. Think of bloodworms as the tough little survivors of the water world. When oxygen levels are low, they still manage to get by, making them an essential part of any healthy aquatic habitat.
You might be wondering why these worms are so important. Understanding their life cycle and seasonal activity is crucial for anyone interested in aquaculture or fishing. A healthy population of bloodworms can indicate good water quality and a balanced ecosystem, which benefits numerous other species.
Spring: The Bloom of Activity
As the chill of winter fades away, spring is when bloodworms really start to come alive. With rising temperatures and increasing daylight, their activity increases. You can often find them in shallow waters, where they begin to feed and grow.
During this time, bloodworms play a critical role in nutrient cycling. They feed on organic matter and help break it down, returning nutrients to the ecosystem. This process not only benefits the worms but also supports other aquatic life, like fish and insects that depend on these nutrients.
If you’re keen on monitoring bloodworm activity in spring, look for areas with rich organic matter or shallow ponds. Using methods like sediment sampling can be quite effective. Just scoop up some sediment and see how many bloodworms you can find. This can give you a good idea of their population density.
Summer: Peak Population
Summer is the prime season for bloodworms. The warm temperatures and abundant sunlight create ideal conditions for them to thrive. You’ll often see a surge in their population, which can lead to a higher availability of food for fish and other wildlife.
Bloodworms often congregate in areas with plenty of algae and decaying matter, which provide a feast for them. For those involved in fishing, summer is a key time to monitor bloodworm activity. Observing when fish are most active can give you clues about when to cast your line.
To track bloodworm numbers in summer, consider using a seine net. This tool helps you catch a larger sample size, making it easier to gauge their presence. Just remember that during this peak activity, bloodworms are often a hot commodity for hungry fish!
Fall: Preparing for Dormancy
As the days grow shorter and temperatures start to drop, bloodworms enter a phase of preparation for winter. Although they still remain active, their numbers may begin to dwindle as they slow down. This is an essential time for them to stock up on nutrients before the colder months.
Interestingly, bloodworms can still be found in greater abundance in the fall, especially in areas where there’s still organic matter to feed on. Monitoring their activity during this time can offer insights into how well they’re preparing for winter.
Look for changes in their feeding behavior. Are they still congregating in large numbers, or do they seem to be drifting away? Observing these changes can help gauge the health of your local water body. For aquarists, maintaining a balance of bloodworms can support the health of your fish as they prepare for winter.
Winter: Dormancy and Resilience
When winter arrives, bloodworm activity takes a noticeable hit. Cold temperatures cause these creatures to slow down significantly. Many tend to burrow deeper into the sediment to find a more stable, warmer environment. This dormancy is nature’s way of helping them survive until spring returns.
During winter, it’s more challenging to find active bloodworms as they are less visible. However, if you’re curious, you can still conduct sediment sampling to check their presence. You might not find them in the same numbers as in spring or summer, but knowing they’re down there is reassuring.
While it may seem like a quiet time, winter is vital for bloodworm populations. It’s a period where they are resting and conserving energy, allowing them to bounce back when temperatures rise again. This resilience is what keeps their populations stable year after year.
Monitoring Techniques for Bloodworms
Monitoring bloodworm activity isn’t just for researchers; it can be a fun and educational hobby for anyone interested in nature. Here are some effective techniques to keep tabs on these little creatures:
- Sediment Sampling: This is the most direct method. Scoop up some sediment from your local pond and look for bloodworms. Make sure to return any samples carefully to avoid disrupting their habitat.
- Using a Seine Net: This tool is excellent for capturing a larger number of bloodworms in a designated area. It’s particularly useful during peak seasons like summer.
- Visual Observations: Simply watching the water surface during peak activity times can yield clues about bloodworm populations. Look for fish feeding or distinct red hues in the water.
Each of these methods offers a unique way to engage with bloodworm monitoring. Whether you’re doing it for scientific purposes or just for fun, it’s a great way to connect with the life in your waters.
Why Monitoring Matters
So, why should you care about monitoring bloodworm activity across the seasons? Well, it’s about understanding the health of our aquatic ecosystems. High bloodworm populations often indicate good water quality, while declines might signal problems like pollution or habitat loss.
For fishermen, knowing when and where bloodworms are active can improve your catch. For aquarists, monitoring can help maintain a balanced environment for your fish. Plus, being in tune with nature can deepen your appreciation for the ecosystems around you.
In a world where environmental issues are on the rise, every small effort counts. Monitoring bloodworms serves as a window into the larger health of our water bodies and can inform better practices for conservation and sustainability.
In conclusion, bloodworms may be tiny, but they pack a significant punch in the health of our ecosystems. By understanding their seasonal activity, you can become more engaged with the natural world and contribute to better aquatic health. So, whether you’re observing them in your backyard pond or studying them in a research setting, remember that you’re part of a larger story—one that connects us all. So grab your net, head out to the water, and start your monitoring adventure!