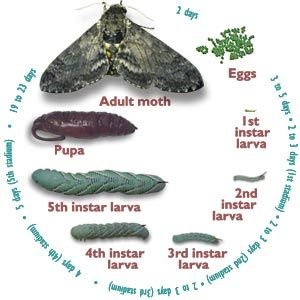
Let’s connect this to something we can all understand. Think of the hornworm’s lifecycle like a dramatic movie. Each stage represents a different act, filled with challenges, growth, and transformation. Here’s the thing: while many people might know the moth, not everyone is familiar with the journey it takes to become one. So grab your favorite drink, and let’s dive into the intriguing world of hornworms!
What is a Hornworm?
Hornworms, also known as tomato hornworms, are the larvae of several species of moths, specifically from the Sphingidae family. These caterpillars are notorious for their voracious appetites, often munching on tomato plants and other vegetables. They can grow to a hefty size, reaching up to 4 inches long, and they’re easy to spot thanks to their bright green bodies and distinctive horn-like protrusion on their rear end.
But why should you care about these pests? Well, while they can wreak havoc on your garden, understanding their lifecycle can help you manage them effectively. Think of it as armoring yourself with knowledge so you can protect your plants without resorting to harsh chemicals.
The Egg Stage
The lifecycle of the hornworm begins with the egg stage, which is a short but crucial phase. Female moths lay their eggs on the underside of leaves, typically on host plants like tomatoes, peppers, and eggplants. These tiny eggs are usually pale green and blend in well with the leaves, making them nearly invisible to predators.
After about a week, the eggs hatch into tiny larvae. This is like the trailer of the movie: it sets the stage for the adventure that’s about to unfold. You might be wondering how these little beings know when to emerge. Well, their development is pretty much timed with the right environmental conditions, like warmth and humidity, which means they’re ready for action when the conditions are just right.
The Larval Stage
Once the hornworm hatches, it enters the larval stage, also known as the caterpillar phase. This is where the real action begins! During this phase, they engage in a feeding frenzy, munching their way through leaves at an astonishing rate. They can eat up to 4 times their body weight in a single day!
This intense feeding is crucial for their growth. As they consume leaves, they store energy for their transformation into moths. Honestly, it’s like they’re bulking up for a big performance. It’s during this phase that they also undergo several molts, shedding their skin as they grow. Each molt brings them closer to their final form.
With their insatiable hunger, they can quickly devastate a garden. So if you spot one, it’s wise to keep an eye on their population, or you might end up losing your prized tomatoes!
Pupation: The Transformation Begins
After a few weeks of eating and growing, the hornworm reaches its full size and prepares for its metamorphosis. This marks the beginning of the pupation stage. The caterpillar will seek out a safe, sheltered location, often hiding under leaves or burrowing into the soil, where it forms a protective casing around itself called a chrysalis.
Inside the chrysalis, an incredible transformation takes place. The caterpillar’s body breaks down, reorganizing itself into the structure of a moth. It’s a bit like a caterpillar version of a makeover show, where they emerge looking completely different than when they went in. This stage can last anywhere from a few days to a couple of weeks, depending on environmental conditions.
Here’s a fun fact: the size of the moth that emerges from the chrysalis can be influenced by the conditions it faced during its larval stage. So, if a hornworm has plenty of food and a safe environment, it’s likely to emerge as a larger, healthier moth.
The Adult Moth Stage
Finally, after a period of waiting, the adult moth emerges from the chrysalis, ready to take flight! Adult hornworms, now called sphinx moths or hawk moths, have large wings and a streamlined body, making them powerful fliers. Their appearance often surprises those who only knew them as caterpillars; they’re striking with their muted colors and impressive wingspan.
Adult moths play an essential role in the ecosystem. They are pollinators, meaning they help plants reproduce while they search for nectar. You might be surprised to find out that they can even be active during the daytime, unlike many moths that prefer the night.
This stage is short-lived, usually lasting only a few weeks to months, depending on the species and environment. During this time, moths mate, and the cycle starts anew as females lay eggs.
Impact on the Garden
Now that you know the lifecycle of the hornworm, you might be curious about their impact on gardening. Hornworms can devastate a garden in just a few days, but understanding their lifecycle can empower you to take action.
Here are some effective strategies to manage hornworm populations:
- Handpicking: If you see them, just pick them off your plants. It’s simple and effective!
- Natural Predators: Encourage birds, wasps, and other predators that feed on hornworms.
- Neem Oil: This natural pesticide can deter hornworms without harming beneficial insects.
By keeping an eye on them and acting swiftly, you can protect your plants from these munching machines while witnessing the beauty of their lifecycle.
The lifecycle of the hornworm is a reminder of nature’s wonders—how something so small can grow into a beautiful moth, even if it does have a bit of a munching reputation first. By understanding this process, you not only gain appreciation for these creatures but also learn how to manage them effectively in your garden.
So, the next time you spot a hornworm, remember: it’s not just a pest; it’s part of a larger story of growth, change, and the beauty of life cycles. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, knowing the journey from egg to moth can help you cultivate a healthy garden and appreciate the natural world around you.
