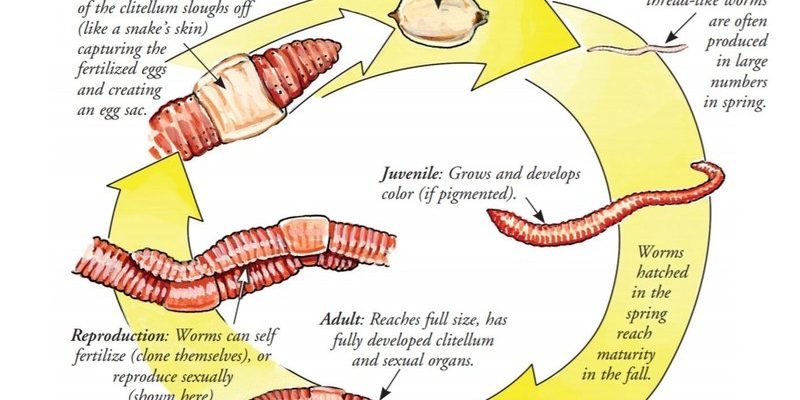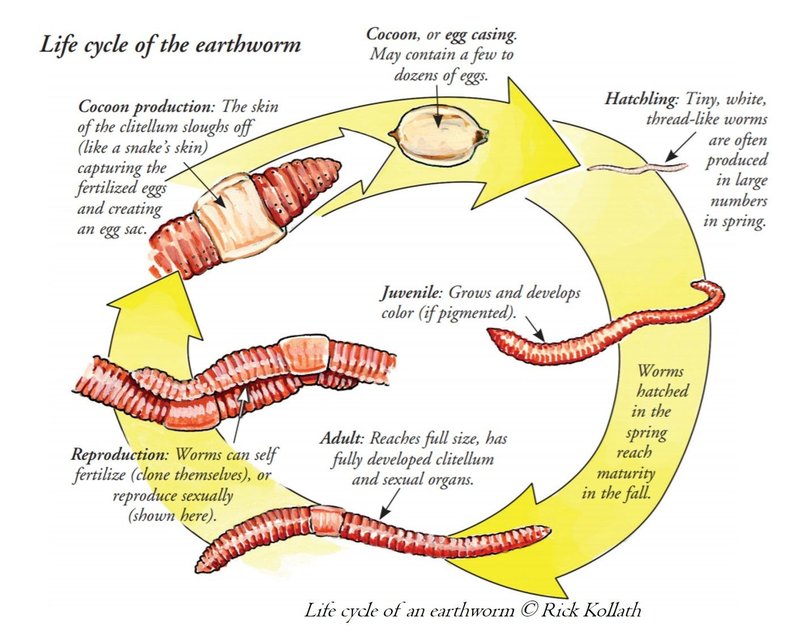
Let’s take a closer look at the life cycle of the Giant Gippsland Earthworm. Understanding these stages and their behavior not only helps you appreciate them as nature’s wonders but also sheds some light on how they contribute to our environment. So, grab your coffee, and let’s dig into the life of these incredible creatures!
What Is the Giant Gippsland Earthworm?
The Giant Gippsland Earthworm (Megascolides australis) is one of the largest earthworm species in the world, found mainly in the Gippsland region of Victoria, Australia. They have a distinct blue to purple coloration and a smooth body that can measure up to 3 meters in length. These earthworms live in deep burrows and prefer moist environments—rainy days are their favorite!
You might be wondering why these worms are important. They play a crucial role in aerating the soil and recycling nutrients. By breaking down organic matter, they help maintain a healthy ecosystem, making them a vital part of the local habitats.
The Life Stages of the Giant Gippsland Earthworm
The life cycle of the Giant Gippsland Earthworm can be broken down into several stages: egg, juvenile, and adult. Each stage is significant and showcases the worm’s adaptation to its environment.
Egg Stage
The life of a Giant Gippsland Earthworm begins in the egg stage. Adult worms lay their eggs in a cocoon, which is usually found in the soil. Each cocoon can contain several eggs, but not all will survive due to environmental conditions and predation.
Once laid, these eggs typically incubate for a few weeks to several months. The exact duration often depends on the temperature and moisture in the soil. Here’s a fun fact: the eggs are very resilient and can survive harsh conditions, which increases the chances of the species continuing to thrive.
Juvenile Stage
After hatching, the young worms emerge as tiny juveniles. These little critters are about the size of a fingernail! At this stage, they remain close to their burrows, feeding on decaying organic matter, which provides them with essential nutrients for growth.
As juveniles, they’re particularly vulnerable to predators and environmental changes. They need moist, rich soils to survive and grow. If conditions are right, these juvenile worms can grow rapidly, reaching adulthood in about 2 to 4 years!
Adult Stage
Once they reach adulthood, Giant Gippsland Earthworms can live for over a decade. Their behavior changes significantly as they become more independent and less reliant on their immediate environment. Adult worms can burrow deep into the soil—sometimes more than 2 meters down!
In addition to burrowing, adults are known to breed. During mating, two worms exchange sperm, and then they go on to produce their cocoons. This fascinating reproductive behavior helps ensure that their population continues, even in changing environments.
Behavior Patterns of the Giant Gippsland Earthworm
Understanding the behavior of the Giant Gippsland Earthworm gives us insight into how they interact with their surroundings. They are generally nocturnal creatures, meaning they come out mostly at night. This helps them avoid predators and stay moist.
Feeding Habits
These worms primarily feed on decomposing plant matter and organic material in the soil. You could think of them as nature’s recyclers! They play a vital role in breaking down tough plant fibers while enriching the soil with nutrients.
As they move through the soil, they create channels that help with aeration and moisture retention. This makes the soil healthier for plants and other organisms. So, while they may not seem like much at first glance, their feeding habits significantly impact the ecosystem.
Burrowing Behavior
Burrowing is another key aspect of their behavior. Giant Gippsland Earthworms create complex tunnel systems in the soil, which not only provides them with shelter but also helps in breaking up compacted soil. This makes it easier for roots to penetrate and absorb water.
Interestingly, they can modify their burrowing depth based on moisture levels. During dry spells, they may go deeper down into the soil to find moisture, while they come closer to the surface during damp conditions. This adaptability is crucial for survival.
Predation and Defense
Despite their size, Giant Gippsland Earthworms face threats from various predators like birds, mammals, and even larger insects. Their moist skin is vulnerable to drying out, especially during hot weather, so they must stay in their burrows when it’s too dry.
To defend themselves, these worms can secrete a slime that deters some predators. This protective layer not only acts as a barrier but also keeps their skin moist, which is vital for their survival.
The Importance of Conservation
Given their unique traits and the role they play in the ecosystem, it’s crucial to protect the Giant Gippsland Earthworm. Habitat destruction and climate change pose significant risks to their populations.
Conservation efforts are underway to preserve their natural habitats. Education also plays a key role in raising awareness about their importance in the ecosystem. By protecting this species, we contribute to the overall health of our environment.
The life cycle and behavior of the Giant Gippsland Earthworm are as fascinating as they are vital. From their humble beginnings as eggs to their impressive adult stage, these creatures showcase resilience and adaptability. They remind us of the interconnectedness of life—how even the smallest beings play crucial roles in our ecosystem.
If you ever have the chance to learn more about these worms or see them in their natural habitat, take a moment to appreciate their contributions. Whether it’s aerating the soil, recycling nutrients, or simply being a part of the natural landscape, they deserve our respect and protection. So the next time you think about earthworms, remember the Giant Gippsland Earthworm—not just for its size, but for its incredible life story!