Inchworms might not be the first thing that comes to mind when discussing forest ecology, but they are crucial in maintaining the balance of life in these habitats. As they munch on leaves, inchworms provide energy and nutrients to a variety of forest inhabitants. So, grab your coffee, sit tight, and let’s dive into the fascinating world of inchworms and their role in forest ecology.
What Are Inchworms?
Inchworms are the larval stage of certain moths, primarily from the family Geometridae. They’re named for their unique way of moving, which looks like they’re measuring their way along the branches and leaves. Unlike typical caterpillars that have several pairs of prolegs, inchworms only have prolegs at both ends, which gives them that signature “inching” motion.
These little creatures can vary in color and size depending on their species, but they often blend in with their surroundings, making them hard to spot. This camouflage helps them avoid predators. You might find them munching on leaves, which is their primary food source. As they grow, inchworms can become significant consumers in the forest ecosystem.
The Role of Inchworms in the Food Web
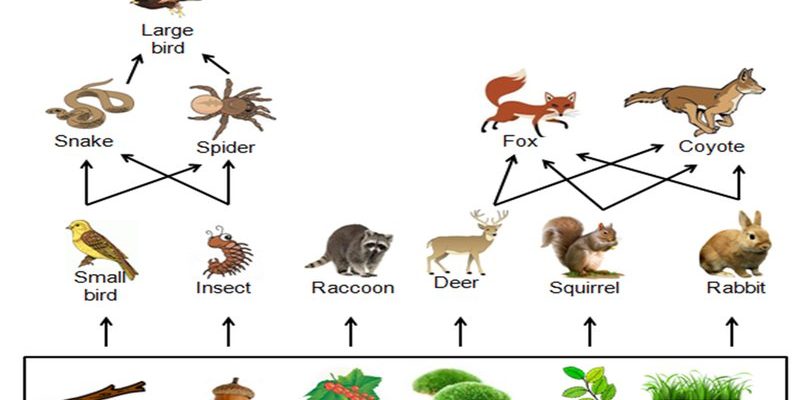
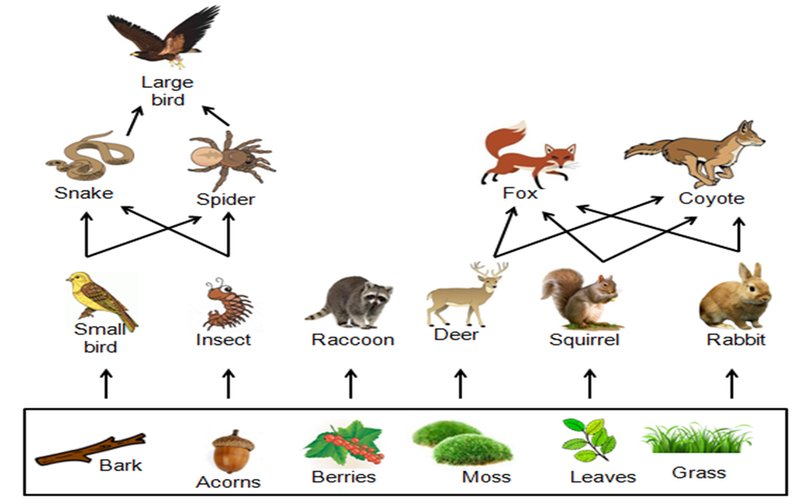
Inchworms are a critical link in the forest food web. They primarily feed on the leaves of trees and shrubs, influencing the plant community available in their habitats. By feeding on these leaves, inchworms regulate plant growth and health. Healthy plants provide shelter and food for other forest species, creating a thriving environment.
Here’s the thing: when inchworms consume leaves, they’re not just munching away without consequences. They become a food source for a range of predators, including birds, small mammals, and even larger insects. This interaction helps maintain the balance between plant growth and herbivore populations. Without inchworms, there could be an overabundance of foliage, which may lead to issues like disease in plants or limiting the resources available for other herbivores.
How Inchworms Support Bird Populations
One of the most notable relationships in the forest is between inchworms and birds. Many birds depend on these soft-bodied caterpillars as a primary food source, especially during the spring and early summer when they are abundant. Baby birds, which require high-protein diets for growth, often feast on inchworms.
Birds like warblers, chickadees, and woodpeckers will actively hunt for inchworms by peeking into the foliage. This predation helps control inchworm populations, which can sometimes explode if left unchecked, leading to defoliation in trees. The presence of inchworms leads to a thriving bird community, which in turn brings more biodiversity to the forest.
Inchworms as Indicators of Forest Health
You might be wondering how inchworms relate to the overall health of a forest ecosystem. They serve as excellent indicators of forest health because their populations can reflect changes in the environment. For instance, a sudden increase in inchworm numbers might signal that there are enough food resources available, or it might indicate a disruption in predator populations.
Conversely, a decline in inchworm numbers can suggest problems like habitat destruction or pesticide use, which can threaten their survival. By studying inchworm populations, ecologists can gather valuable data on the state of the forest and make informed decisions about conservation efforts.
Inchworms and Plant Management
Inchworms play a significant role in managing forest vegetation. By feeding on leaves, they help prune trees and shrubs, promoting new growth. This natural pruning can be beneficial for the overall health of the forest. When plants are pruned regularly, it encourages stronger, more vigorous growth.
However, unchecked inchworm populations can lead to overconsumption, resulting in defoliation. This could severely impact tree health, leading to weakened plants that are more susceptible to diseases and pests. Forest managers often keep an eye on inchworm populations to maintain a balance between their beneficial and detrimental effects.
The Interconnectedness of Ecosystems
The role of inchworms in forest ecology exemplifies the interconnectedness of ecosystems. They are just one small piece of a much larger puzzle. Each organism, from the plants they consume to the birds that feed on them, plays a vital part in the health and stability of the forest.
Inchworms demonstrate how a single species can have far-reaching effects. When researchers study these creatures, they gain insight into the dynamics of food webs, population control, and biodiversity. This understanding is crucial for conservation efforts and maintaining healthy ecosystems.
Inchworms may seem small and insignificant, but their role in forest ecology is anything but. As herbivores, they support plant management and serve as a vital food source for many animals, particularly birds. By maintaining a balance between their populations and the plants they consume, inchworms help shape the forests we cherish.
So, the next time you’re out in nature and spot an inchworm inching along, take a moment to appreciate its part in the bigger picture. Each tiny creature, no matter how small, plays a crucial role in sustaining the environment we call home. It’s a beautiful reminder of how everything in nature is interconnected, and how even the least conspicuous players can have a significant impact on the world around us.