These tiny creatures, which can fit on the tip of your finger, engage in various interactions with other microorganisms, affecting everything from nutrient cycling to disease transmission. In this article, we’ll explore how pinworms interact with other microfauna in their ecosystem. Don’t worry if some of the terms sound too scientific; I’ll break it down for you step by step.
Understanding Pinworms: The Basics
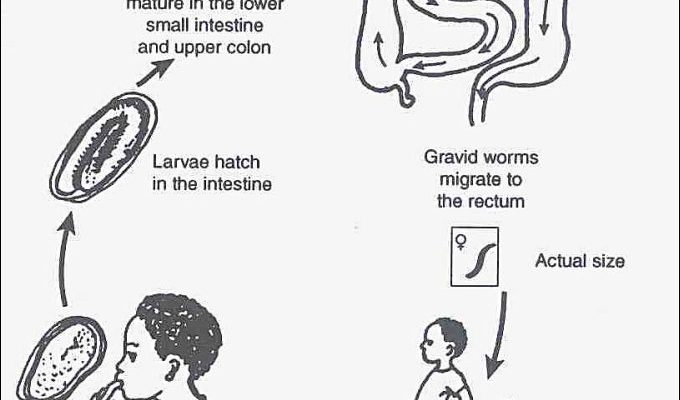
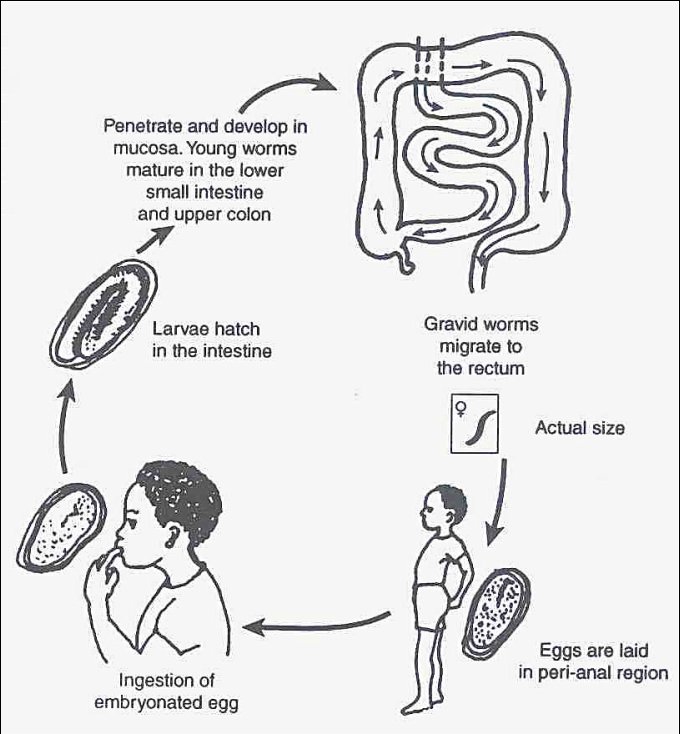
Let’s start with some foundational knowledge about pinworms. Scientifically known as *Enterobius vermicularis*, pinworms are small, white worms that primarily infect humans. They thrive in the intestines, where they lay their eggs, typically at night. If you’ve ever had to deal with them, you know how unpleasant the itching can be! It’s like having an annoying little itch that just won’t go away.
But why do pinworms matter in their ecosystem? Well, these critters are more than just a nuisance. They interact with many other microfauna, including bacteria, protozoa, and even fungi. This is important because it influences the health of their environment and can even impact human health.
The Role of Microfauna in Ecosystems
Microfauna, which include tiny organisms like bacteria and protozoa, play crucial roles in any ecosystem. They help break down organic matter, recycle nutrients, and maintain soil health. In the context of humans, they also form part of our gut microbiome, which is essential for digestion and overall health.
These tiny players act like a team, working together to create an environment that supports life. When pinworms enter the mix, they can influence the balance of this ecosystem. For instance, if there are too many pinworms, they might alter the composition of the gut microbiome, potentially leading to digestive issues.
How Pinworms Interact with Bacteria
One of the primary players in any ecosystem is bacteria. Pinworms can affect the diversity and abundance of bacterial communities in the gut. You might be wondering: how does that happen?
When pinworms are present, they can create an environment that favors certain types of bacteria over others. This occurs through the release of waste products and by altering the pH levels in their surroundings. Some studies suggest that a higher pinworm load could lead to a decrease in beneficial bacteria, which can affect overall gut health.
Interestingly, some bacteria might even benefit from the presence of pinworms. For instance, certain strains may thrive on the nutrients provided by pinworm waste. This tug-of-war between pinworms and bacteria illustrates the complexities of their interactions.
Pinworms and Protozoa: A Complicated Relationship
Protozoa are another type of microfauna that can be influenced by pinworms. These single-celled organisms often exist in environments where nutrients are plentiful. Like bacteria, protozoa play an essential role in breaking down organic material, which helps recycle nutrients.
When pinworms infest the intestines, they can disrupt the habitat for protozoa. Some protozoa may become more or less abundant due to changes in the microbial environment. For instance, if pinworms consume a certain type of food source, it could impact the protozoa that rely on that source for survival.
The interplay between pinworms and protozoa is an excellent example of how these tiny creatures can have far-reaching effects on one another within their ecosystem.
Pinworms and Their Impact on Fungi
Let’s not forget about fungi! While they might not be the first thing that comes to mind when thinking about pinworms, they too play a significant role in ecosystems. Fungi help decompose organic matter and can affect the nutrient cycling in the environment.
Pinworms can influence fungal populations in a couple of ways. First, their waste products might provide nutrients that some fungi can utilize, helping them flourish. On the flip side, the presence of pinworms might also create competition for resources. This can lead to shifts in the fungal community, impacting how effectively nutrients are recycled in the ecosystem.
Disease Transmission: A Microfauna Concern
One of the more concerning aspects of pinworms is their potential role in disease transmission within their microfauna community. When pinworms infest a host, they can affect not just the host but also the surrounding microbial community.
For instance, if a host becomes ill due to the imbalance caused by pinworms, this can create an environment for harmful bacteria or pathogens to thrive. Consequently, the overall health of the microbiome could decline, leading to further complications.
This highlights the interconnectedness of microfauna. Changes in one group can ripple through the ecosystem, affecting the health and diversity of other organisms.
Implications for Human Health
Understanding how pinworms interact with other microfauna is crucial, especially when it comes to human health. If these interactions disrupt the balance of gut microorganisms, it could lead to various health issues.
People with pinworm infections may experience digestive problems, which could stem from a disrupted microbiome. Moreover, the imbalances created by pinworms might also impact nutrient absorption, leading to deficiencies over time.
Taking care of gut health is vital. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in fiber and probiotics can help support a healthy microbiome, which in turn can help combat the effects of pinworms and other pathogens.
How to Manage Pinworm Infections
If you or someone in your household is dealing with a pinworm infection, managing it effectively is essential. Here are some steps you can take:
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: If you suspect a pinworm infection, seeking medical advice is crucial.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash hands frequently, especially before meals and after using the bathroom, to prevent spreading eggs.
- Clean Living Spaces: Regularly wash bedding, towels, and clothes in hot water to eliminate any pinworm eggs.
- Consider Over-the-Counter Treatments: Medication is often effective in treating pinworm infections and can help restore balance to the gut microbiome.
The Bigger Picture: Ecosystem Balance
In conclusion, pinworms are a small part of a larger ecosystem filled with other microfauna. Their interactions with bacteria, protozoa, and fungi illustrate a web of relationships that impacts not just their immediate environment but the health of humans as well.
Understanding these dynamics can help us appreciate the importance of maintaining ecosystem balance. By taking measures to manage pinworm infections, we can support not just our health but also the health of the tiny creatures living in our gut.
So next time you think about pinworms, remember that they’re not just tiny nuisances. They’re part of a complex, interconnected ecosystem that deserves our attention and understanding!