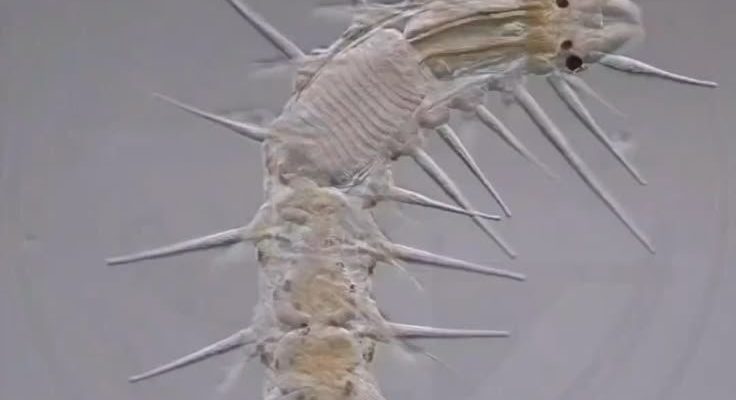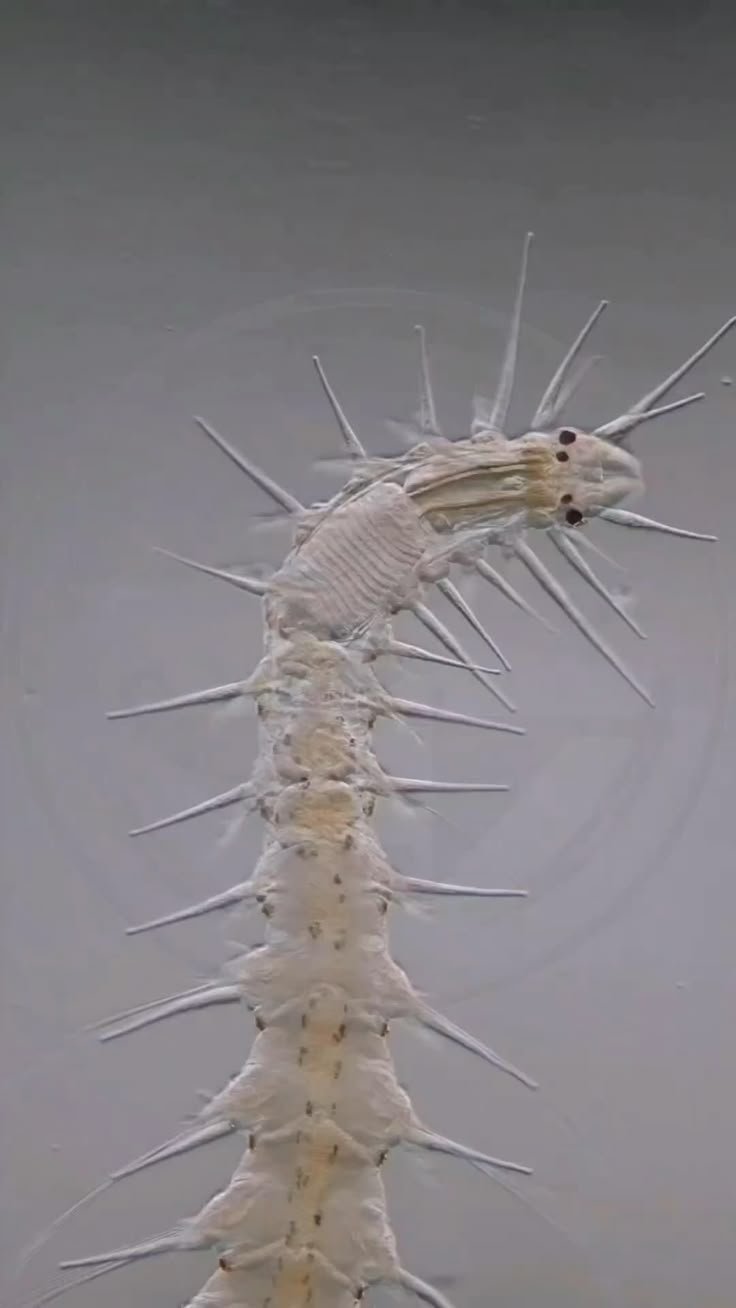
Marine polychaetes are an essential part of the aquatic food web, interacting with all sorts of microfauna, which refers to tiny organisms that call the ocean home. By exploring these interactions, we can understand more about how these creatures contribute to their environments. So, grab your metaphorical snorkel, and let’s dive into the world of marine polychaetes and their fascinating relationships with other microfauna.
What Are Marine Polychaetes?
Marine polychaetes are a class of annelid worms, which means they have a segmented body structure. With over 10,000 species found mainly in marine environments, they come in various shapes, sizes, and colors. You could think of them as the little soldiers of the sea, each equipped with bristle-like structures called *chaetae* that help them move through sediment and capture food.
These worms can be found in diverse habitats—ranging from deep ocean floors to tide pools—making them a crucial part of the benthic zone. They act as scavengers and predators, feeding on organic matter and smaller organisms. Their ability to burrow into sediments helps aerate the substrate, which is vital for the health of the ecosystem.
But why should we care about them? Well, their interactions with other organisms can tell us a lot about the state of marine environments and the health of the ocean overall.
The Role of Marine Polychaetes in Nutrient Cycling
One of the most important ways marine polychaetes interact with other microfauna is through nutrient cycling. Think of them as nature’s recyclers. They consume decaying organic matter, which not only helps keep the environment clean but also turns this waste into nutrients that support the growth of other organisms.
When marine polychaetes break down organic material, they release nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus back into the water. These nutrients are essential for *phytoplankton*—tiny plant-like organisms that form the base of many aquatic food webs. Without marine polychaetes, these nutrients would accumulate, leading to a depletion of available resources for other microfauna.
In this way, marine polychaetes help maintain ecosystem stability. So, the next time you see a vibrant school of fish, remember that their health might be linked to these little worms working tirelessly below the surface.
Interactions with Other Microfauna
Marine polychaetes don’t just exist in a vacuum; they interact with various other microfauna, forming intricate relationships. You might be wondering how these interactions play out. For instance, polychaetes often share their habitat with bacteria, *protozoa*, and even other worms.
These relationships can be competitive or symbiotic. For example, certain polychaetes may compete with other microfauna for food resources. Still, they can also benefit from one another. Some studies show that the presence of polychaetes can enhance the microbial community in sediments, leading to better overall health in the ecosystem.
It’s kind of like a neighborhood potluck—everyone brings something to the table. Marine polychaetes help enrich their environment, allowing other species to thrive alongside them.
Predatory Relationships: Polychaetes as Hunters
On the flip side of their relationships, marine polychaetes are also predators. Many species hunt smaller microfauna, including crustaceans, mollusks, and even other worms. This predatory behavior keeps populations in check, ensuring that no single species dominates the ecosystem.
For example, the *nereid* family of polychaetes is known for its active hunting style. They can detect vibrations and chemical signals in the water, allowing them to locate prey effectively. Their hunting not only provides them with food but also contributes to the overall balance of the ecosystem.
So, you see, marine polychaetes serve as both prey and predator. Their role helps maintain a diverse community of microfauna, contributing to the resilience of marine ecosystems.
Impact of Environmental Changes on Polychaete Interactions
Environmental changes can significantly impact marine polychaete interactions with other microfauna. Factors like pollution, climate change, and habitat destruction can disrupt food webs and alter these delicate relationships. For example, increased nitrogen levels from agricultural runoff can lead to eutrophication, which depletes oxygen in the water and creates dead zones where few organisms can survive.
As a result, polychaetes may struggle to find food, leading to a decline in their populations. This decline can have a ripple effect, impacting the species that depend on them for food and nutrient cycling. Scientists are particularly interested in studying these relationships to predict and mitigate the impacts of human activity on marine environments.
It’s like a domino effect—when one piece falls, others follow. Protecting marine polychaetes means protecting the intricate web of life that depends on them.
How to Support Marine Ecosystems
If you’re inspired to help support marine ecosystems and the invaluable roles that marine polychaetes play, there are several simple steps you can take:
- Reduce plastic usage. Plastic waste can harm marine life and pollute habitats.
- Support sustainable fishing practices to ensure that marine ecosystems remain balanced.
- Participate in beach clean-ups to remove debris that can impact marine organisms.
- Advocate for policies that protect marine habitats from pollution and development.
By making mindful decisions in our daily lives, we can contribute to the health of our oceans. Remember, every little bit helps!
Marine polychaetes are more than just tiny worms; they’re vital players in the health of ocean ecosystems. Their interactions with other microfauna—through nutrient cycling, predation, and symbiotic relationships—underscore the complexity of life beneath the waves.
Understanding these interactions helps us appreciate the delicate balance within marine environments. By protecting marine polychaetes and their ecosystems, we ensure a healthier future for our oceans and all the life they support. So next time you think about the marine world, remember those little worms working diligently beneath the surface, holding together the fabric of ocean life!