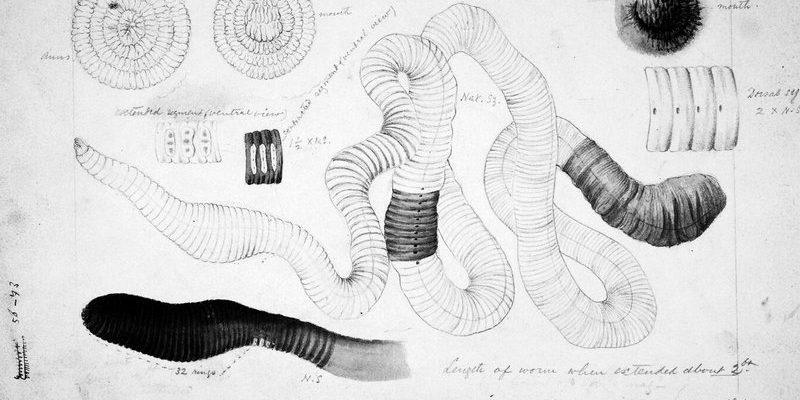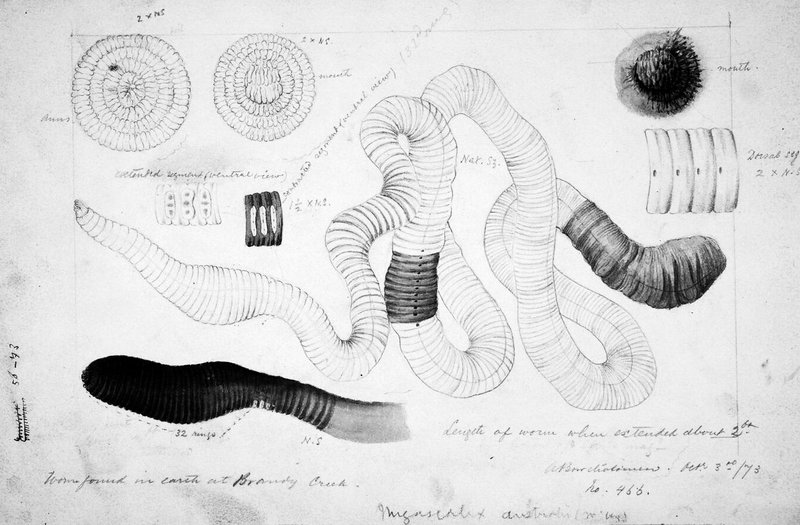
You might be wondering, why should we care about such an obscure creature? Well, just like a symphony depends on each instrument to create a harmonious piece of music, ecosystems rely on the interactions between various species. The Giant Gippsland Earthworm’s interactions with other soil microfauna are crucial for soil health, nutrient cycling, and even plant growth. Let’s dig deeper—pun intended—and explore how these giant worms work alongside their tiny neighbors to keep their ecosystem thriving.
The Role of the Giant Gippsland Earthworm
The Giant Gippsland Earthworm isn’t just your average earthworm; it’s an essential component of its habitat. Living primarily in the rich soils of southeastern Australia, these worms aerate the soil, allowing air and water to penetrate deeper. This, in turn, promotes better plant growth. By burrowing through the earth, they leave behind tunnels that help prevent soil compaction.
But what makes these worms unique is their diet. They primarily feed on decaying organic matter, which may include anything from leaves to decomposing animals. As they consume this material, they break it down into smaller particles, enriching the soil with valuable nutrients. You might think of them as nature’s recyclers, ensuring that nothing goes to waste.
Moreover, these earthworms help improve soil structure. Their expansive burrowing creates space for other organisms to thrive. This means that they don’t operate in isolation; rather, they contribute to a bustling micro-ecosystem that supports countless other species, making their function vital.
Interactions with Bacteria
Let’s dive into the microscopic world of bacteria. You might not always see them, but they’re everywhere—especially in soil. The Giant Gippsland Earthworm interacts closely with various bacteria that play a critical role in nutrient cycling. When worms consume organic matter, they also ingest bacteria. Through their digestive process, they help release nutrients back into the soil, making them available for plants and other organisms.
In turn, bacteria can also benefit from these interactions. The environment inside a Giant Gippsland Earthworm’s gut is quite hospitable. Nutrients are plentiful, and the conditions are favorable for bacterial growth. As they multiply, these bacteria help break down organic matter even further, making it easier for both worms and plants to access essential nutrients.
This relationship is a classic example of mutualism, where both parties benefit. The worms receive nutrient-rich food, while the bacteria gain a safe place to thrive. Honestly, when you think about it, it’s a win-win situation!
Interactions with Fungi
Just like bacteria, fungi form a significant part of the soil ecosystem. The Giant Gippsland Earthworm’s interactions with fungi are similarly essential. Fungi are great at decomposing complex organic materials, breaking them down into simpler forms that worms can consume.
When worms move through the soil, they help distribute fungal spores. This can lead to fungal networks spreading throughout the soil, which is beneficial for plant health. Fungi form symbiotic relationships with plant roots through structures called mycorrhizae. These partnerships allow plants to absorb water and nutrients more effectively, often with the help of nutrients processed by earthworms.
Imagine a forest floor where earthworms and fungi work hand in hand to create a lush environment. The worms help the fungi grow, and in return, the fungi help nourish the plants. Without this cooperation, the ecosystem would struggle to thrive.
Interactions with Other Soil Fauna
In addition to bacteria and fungi, the Giant Gippsland Earthworm interacts with a variety of other microfauna, like nematodes and protozoa. These tiny creatures might be small, but they play crucial roles in the soil ecosystem. For example, nematodes help control the population of bacteria by preying on them.
When earthworms break down organic matter, they create an environment that supports these other organisms. By doing so, they indirectly contribute to a more balanced soil ecosystem. This balance is crucial for nutrient cycling and maintaining soil health.
You might be surprised to learn that the presence of earthworms can actually increase the diversity of microfauna in their environment. It’s like throwing a party; the more the merrier! The Giant Gippsland Earthworm sets the stage for various soil organisms to thrive, creating a lively and healthy ecosystem.
The Impact of Environmental Changes
Environmental changes, like climate change and land use practices, can significantly impact the interactions between the Giant Gippsland Earthworm and other microfauna. For example, soil compaction or chemical fertilizers can disrupt the delicate balance within this ecosystem.
When soil becomes overly compacted, it reduces the movement of worms and the aeration they provide. This leads to less interaction with bacteria, fungi, and other soil organisms, creating a cycle that can degrade soil health over time. It’s a bit like throwing a wrench in the works of a well-oiled machine.
On the other hand, when the environment is conducive—like maintaining organic farming practices that support worms—the benefits are clear. This leads to increased biodiversity and healthier soil. We should be mindful of how our actions impact the Giant Gippsland Earthworm and its web of interactions, as these tiny changes can have a ripple effect on the entire ecosystem.
Conservation Efforts for Giant Gippsland Earthworm
Given the vital role of the Giant Gippsland Earthworm and its interactions with other microfauna, conservation efforts are crucial. These worms face threats from habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change. Protecting their natural habitat ensures that the balance of their ecosystem remains intact.
Local organizations work tirelessly to promote soil health and biodiversity. By engaging in practices like sustainable farming and reducing chemical use, we can help create an environment where the Giant Gippsland Earthworm can thrive.
Moreover, public awareness campaigns highlight the importance of these earthworms in maintaining soil health. When communities understand the significance of such creatures, they are more likely to support conservation efforts. It’s all about working together—just like the Giant Gippsland Earthworm and its microfauna friends!
So, what have we learned about the Giant Gippsland Earthworm and its interactions with other microfauna? These intriguing creatures contribute so much more to our ecosystems than we might initially realize. They aid in nutrient cycling, promote soil health, and support a variety of life in the soil.
Understanding these relationships helps us appreciate what’s happening beneath our feet. With ongoing conservation efforts and sustainable practices, we can ensure that the Giant Gippsland Earthworm continues to thrive alongside its tiny companions. In the end, it’s about harmony—every creature, big or small, plays its part in the grand scheme of nature.