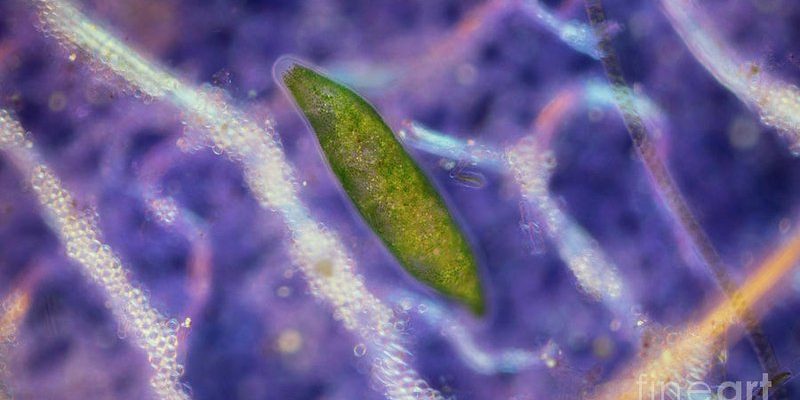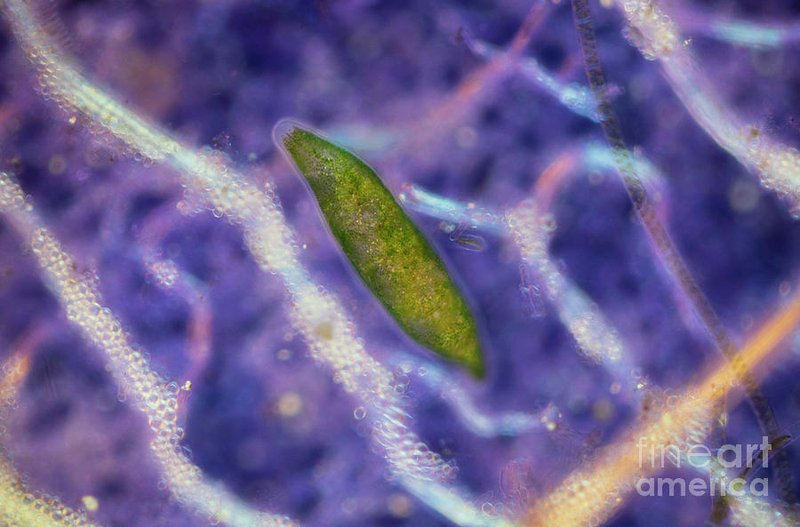
Flatworms are more than just simple organisms; they are complex and interesting creatures. You might not realize it, but they have a reputation among their fellow microfauna for being both predators and prey. It’s a bit like a high-stakes game of tag, where everyone has a role to play. This article will explore how flatworms interact with other microfauna, what their relationships look like, and why they matter in their ecosystems.
The Role of Flatworms in Their Ecosystem
Flatworms are often referred to as *trophic cascades* in their ecosystems. What does that mean? Essentially, they sit in the middle of the food web. They eat smaller organisms, like nematodes and other tiny invertebrates, and, in turn, become food for larger predators, like certain fish or amphibians. This balancing act keeps the population of microfauna in check, ensuring that no one species dominates the ecosystem.
Flatworms also contribute to nutrient cycling. As they feed and decompose, they break down organic matter. This process releases nutrients back into the soil or water, fostering a healthier environment for the plants and microbes that depend on these nutrients. Without flatworms, this nutrient cycling could slow down, impacting everything from plant growth to the health of the entire ecosystem.
You might be wondering, just how many types of flatworms are there? Well, there are thousands of species, ranging from marine to freshwater and terrestrial environments, each with its own unique interactions. In this rich tapestry of life, flatworms are key players, gently knitting together the complex relationships that define their world.
Flatworm Predation and Competition
One of the most interesting aspects of flatworms is how they interact with other microfauna through predation. They have a varied diet that includes detritus, bacteria, and smaller protozoans. This means they often compete with other microfauna for food, leading to a dynamic relationship among species.
Flatworms are not picky eaters. They can consume a broad range of organisms, allowing them to thrive in various environments. This adaptability gives them an advantage in terms of survival. In a freshwater pond, for example, a flatworm might feast on tiny rotifers and protozoa. The competition can be fierce, especially when food is scarce. That’s where strategy comes in—flatworms can sometimes rely on camouflage or speed to get their next meal before someone else does.
Interestingly, the presence of flatworms can impact the behavior of other microfauna. For example, when flatworm populations are high, some smaller organisms may adapt by becoming less active during the day, essentially hiding from their potential predators. This constant push and pull between species showcases the intricate balance of life in micro-ecosystems.
Symbiotic Relationships: A Mutual Benefit
Not all flatworm interactions are about competition and predation. Some flatworms establish symbiotic relationships with other microfauna. These relationships can benefit both parties involved. For instance, some flatworms might host microorganisms or algae on their bodies. In return for a safe space, these microorganisms help the flatworms by providing extra nutrients through photosynthesis.
This kind of relationship is like a partnership where both sides have something to gain. The flatworm gets an extra food source, while the microorganisms get a secure place to grow and thrive. These symbiotic interactions highlight the importance of cooperation in ecosystems, even among organisms that might seem very different from one another.
Another example can be seen in freshwater habitats, where flatworms may interact with certain types of bacteria that contribute to breaking down organic material. Together, they create a more sustainable ecosystem. By understanding these partnerships, we gain insight into how ecosystems function as a whole.
Flatworm’s Role in Decomposition
Speaking of partnerships, flatworms play an essential role in the process of *decomposition*. They help break down organic matter, which includes dead plants and animals, converting it into nutrients that other organisms can use. In a way, they are nature’s recyclers.
When flatworms consume decomposing material, they break it down into smaller particles, which then become accessible to bacteria and fungi. This breakdown is crucial for maintaining soil health and ensuring that nutrients are available for new plant growth. Without flatworms, the decomposition process would slow down significantly, leading to nutrient shortages in the ecosystem.
Imagine walking through a forest and seeing piles of leaves and dead plant matter. Thanks to flatworms and their fellow decomposers, this organic material doesn’t stay piled up for long. Instead, it becomes a rich source of nutrients for the soil, fostering new life and growth in the process.
Every time you see a vibrant garden or a flourishing patch of grass, you can bet that organisms like flatworms have played their part behind the scenes.
Coexistence and Diversity in Microfaunal Communities
Flatworms exemplify how diverse microfauna communities can thrive. In habitats like soil, freshwater, or marine environments, different species coexist and interact in complex ways. The flatworm’s adaptability allows it to take on various roles within these communities, whether as a predator, prey, or partner.
When flatworms share their habitat with other microfauna, this diversity enhances the resilience of the ecosystem. Different species often have specialized niches, meaning they each contribute something unique. For instance, flatworms might coexist with roundworms and tardigrades, each playing different roles in nutrient cycling and energy flow.
This diversity also means greater stability. If one species faces a decline due to disease or environmental changes, others can help maintain ecosystem balance. Flatworms, with their versatile nature, are crucial in keeping these communities thriving. The next time you see a small flatworm, remember that it’s part of a larger story of coexistence and interdependence.
The Impact of Environmental Changes on Flatworm Interactions
Environmental changes, like pollution or habitat destruction, can disrupt flatworm interactions with other microfauna. Flatworms are sensitive to changes in their surroundings, and their health often reflects the overall health of the ecosystem. If pollution rises in a body of water, for example, flatworm populations may dwindle, leading to imbalances in the food web.
When flatworm interactions are disrupted, whole ecosystems can cascade into chaos. Less predation means a burst in the populations of their prey, which can lead to overgrazing on bacteria and microorganisms. This imbalance can impact nutrient cycling and overall ecosystem health, rippling through the entire community.
Understanding these impacts is vital for conservation efforts. By protecting the habitats where flatworms and other microfauna live, we safeguard the intricate web of life that keeps our ecosystems functioning smoothly. It serves as a reminder that even the smallest creatures have a big part in maintaining the balance of nature.
Why Flatworms Matter
So, why should we care about flatworms and their interactions with other microfauna? The answer is simple: they are essential to the health of ecosystems. Flatworms play multiple roles, from predators to partners in symbiosis, and they help maintain balance through nutrient cycling and decomposition.
Their presence reflects the condition of their environment. When flatworm populations thrive, it’s often a sign that the ecosystem is healthy. Conversely, a decline in flatworm populations can raise red flags about environmental issues that need attention.
In a world that’s increasingly impacted by climate change and pollution, understanding these interactions can help us make better choices for conservation. The story of flatworms is a reminder that we must protect even the smallest players, as they are vital to the well-being of our planet.
As we wrap up this exploration of flatworms and their microfaunal interactions, remember that it’s not just about these tiny creatures. It’s about the interconnectedness of life. When we learn more about the role of flatworms, we’re really gaining insight into the bigger picture of our ecosystems and the importance of maintaining biodiversity for a sustainable future.