Imagine you’re in a long tube, and your friends are at the other end. If everyone squeezes and releases in a wave-like motion, you’d all move toward the exit. That’s a bit like what happens with bootlace worms. These creatures are experts at pushing their bodies forward using muscle contractions in a coordinated rhythm. This unique technique not only helps them travel through soil and water but also has a role in their feeding habits and overall survival.
So, let’s dive deeper into this wormy world. Here, we’ll explore how bootlace worms utilize peristalsis for movement and why it matters for their existence.
What is Peristalsis?
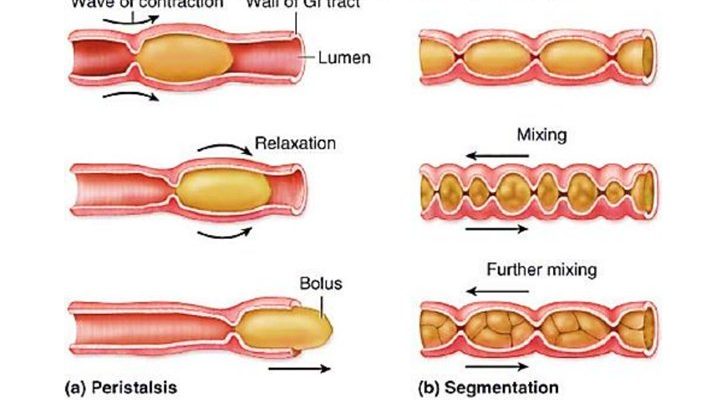
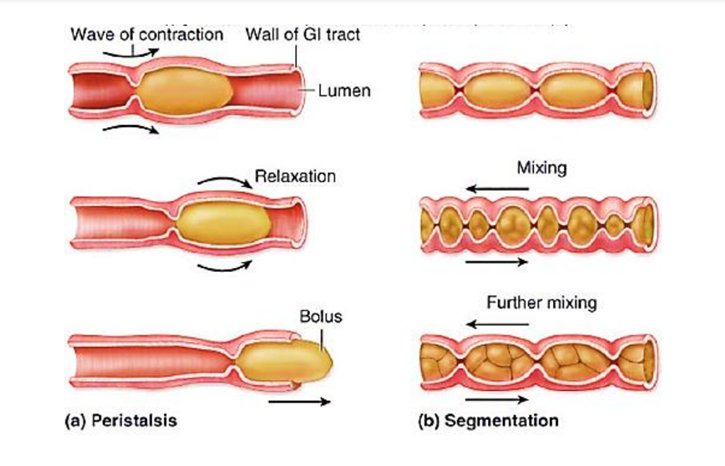
To understand how bootlace worms move, we first need to grasp what *peristalsis* is. In simple terms, it’s the contraction and relaxation of muscles in a wave-like fashion. This is a common method of movement in the animal kingdom, particularly among soft-bodied animals like worms and some types of snails.
When peristalsis occurs in a bootlace worm, it starts with the muscles in the worm’s body contracting. Imagine a long balloon: when you squeeze one end, the air shifts and pushes out the other end. Bootlace worms have flexible bodies made up of many segments that can expand or contract. By alternating the contraction of these muscles along their length, they can push themselves forward through their environment. It’s like a wave traveling through a string; as one part moves, it creates a ripple effect that helps the entire structure advance.
Why Is Peristalsis Important for Movement?
You might be wondering, why is this way of moving so beneficial for bootlace worms? Well, the answer lies in their environment. Bootlace worms often live in narrow spaces like mud, sand, or even deep sea beds, where traditional walking or crawling wouldn’t cut it. Peristalsis allows them to navigate through tight spots without getting stuck.
Additionally, this movement method helps them efficiently search for food. As they inch through the soil or water, they can absorb nutrients and organic materials from their surroundings. So, not only does peristalsis get them where they need to go, but it also plays a crucial role in their feeding process.
The Anatomy of Bootlace Worms
One key feature that enables bootlace worms to perform peristalsis is their anatomy. These worms have a soft, elongated body that’s divided into many segments. Each segment contains muscle fibers that can contract independently and in unison, allowing for that wave-like movement.
Their body is also lined with a protective outer layer called the *cuticle*, which helps them retain moisture and navigate through different terrains without losing water. The combination of their segmented body structure and the flexible cuticle gives bootlace worms the tools they need to thrive in various environments.
Muscle Composition and Arrangement
Bootlace worms have two main types of muscles that aid in peristalsis: circular and longitudinal muscles.
– **Circular muscles** wrap around each segment. When they contract, the segment becomes narrower and longer, pushing the worm forward.
– **Longitudinal muscles** run along the length of the worm. When these contract, the worm shortens and thickens, creating movement in the opposite direction.
You can think of this muscle arrangement as a perfectly synchronized dance. The circular and longitudinal muscles work together, contracting and relaxing to create a smooth, flowing motion that propels the worm through mud or water.
Comparing Movement in Bootlace Worms and Other Animals
It’s interesting to see how different animals move. While bootlace worms rely on peristalsis, other creatures have their own unique methods. Take snakes, for instance. They use a combination of muscle contractions and their flexible spine to slither and climb. Fish, on the other hand, use their fins and tails to swim through water, utilizing a side-to-side motion.
What’s fascinating about bootlace worms is that their peristaltic movement is very efficient in their specific environment. Unlike many animals that may rely on limbs or rigid structures, bootlace worms have evolved to thrive in tight spaces, giving them an advantage when scavenging for food or escaping predators.
Movement Variability in Bootlace Worms
Not all movements are created equal! Bootlace worms can adapt their peristaltic movements based on what they need to do. For example, if they’re trying to burrow deeper into the mud, they might use slower, more deliberate muscle contractions. On the other hand, if they’re trying to escape a threat, they can contract rapidly to dart away.
This adaptability not only showcases their survival skills but also allows them to interact with their ecosystem in various ways. By changing their movement patterns, bootlace worms can find better feeding grounds or avoid becoming someone else’s lunch.
The Role of Peristalsis in Feeding
Here’s the thing: movement isn’t just about getting from point A to point B for bootlace worms. It’s strongly tied to how they feed. As they move through the sediment or water, these worms are constantly filtering and absorbing nutrients from their environment.
Peristalsis plays a crucial role in this process. As they inch along, they can bring food particles into their bodies and use their specialized mouthparts to consume tiny organic matter like detritus, algae, and microorganisms. This not only sustains them but also keeps the ecosystem healthy by recycling nutrients.
Feeding Method and Adaptations
Bootlace worms typically have a *pharynx*, a muscular structure that helps suck in food. When they feel food nearby, the rhythmic peristaltic movements help guide them toward it. It’s like having a built-in vacuum that draws in everything delicious as they move.
Thanks to their efficient feeding method, bootlace worms can thrive in environments that may not seem hospitable to other creatures. Their ability to process organic materials enhances soil quality and provides nutrients for other organisms, contributing to the balance of their ecosystem.
Understanding how bootlace worms use peristalsis for movement gives us a unique glimpse into the marvels of nature. Their ability to move efficiently through tight spaces, coupled with their adaptable feeding methods, illustrates the wonders of evolution and survival.
Next time you see a worm or think about the critters beneath our feet, remember the incredible journey they undertake and the roles they play in the ecosystem. It’s just one of those fascinating reminders that even the smallest creatures have big stories to tell. Whether you’re a nature enthusiast or just curious about the world around you, bootlace worms and their use of peristalsis are a captivating topic worth exploring.