So, how do they manage this? It’s all about adaptation. Living in their watery homes, these worms have evolved to make digestion efficient and effective, even without a typical digestive system. Let’s dive into the world of bootlace worms and explore their unique digestive process, which is as intriguing as it is efficient.
Understanding Bootlace Worms
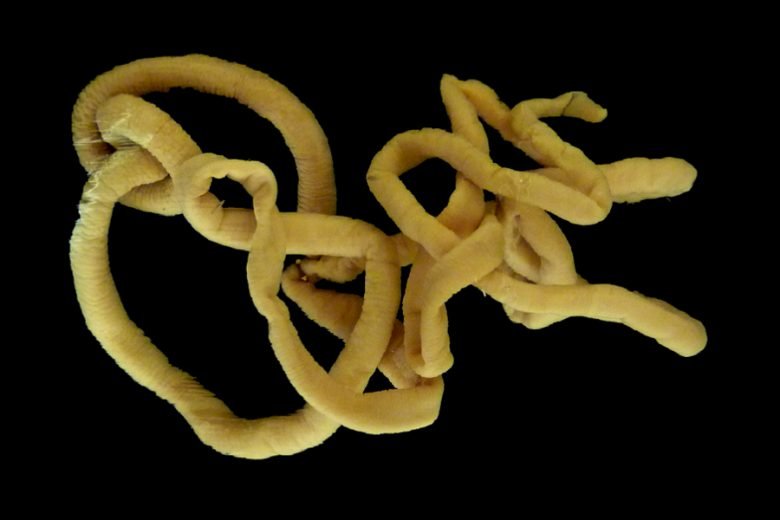
Bootlace worms, scientifically known as *Lineus longissimus*, are among the longest animals on the planet. Imagine a living spaghetti strand, stretching over 30 meters long! These worms roam the waters, often hiding in crevices or amongst seaweed. What makes them truly special isn’t just their length, but their ability to digest prey without a well-defined stomach.
These fascinating creatures thrive in shallow waters, where they can hunt for food. They primarily feed on smaller marine animals, like crustaceans, which they capture with their slim, flexible bodies. So, you might be wondering, how do they consume and digest their meals without a traditional stomach? Let’s break it down.
How Bootlace Worms Capture Their Prey
The first step in any digestion process is capturing the food, and bootlace worms have perfected this art. Instead of using jaws or teeth like many animals, these worms employ a method called **contraction and expansion**.
When a bootlace worm encounters a small prey item, it can rapidly contract its body to envelop the prey. Imagine a rubber band snapping around a small toy! This allows them to catch and hold on to their meal firmly. Once they’ve secured their prey, the real magic happens.
Bootlace worms release enzymes that start breaking down the prey’s tissues right in their own bodies. This brings us to the next part of their unique digestion process.
The Role of Enzymes in Digestion
Enzymes are like tiny workers that help break down food into smaller, more manageable pieces. In bootlace worms, these enzymes are secreted directly from their skin rather than coming from a stomach. This means digestion occurs externally, as the worm slowly absorbs the nutrients.
You can think of it like a sponge soaking up water. When the enzymes mix with the prey, they begin to liquefy it into a soupy substance. This is a remarkable adaptation that allows the bootlace worm to make the most out of its meals without the need for a complex internal system.
Once the prey is broken down, the worm can absorb the nutrients through its skin, feeding off the digestible parts. This is simple yet incredibly effective!
Advantages of This Unique Digestive Process
You might be wondering, why would a bootlace worm evolve such a peculiar way to digest food? There are several advantages to this method.
- Efficiency: By digesting food outside its body, the worm can quickly absorb nutrients without having to wait for food to pass through a lengthy digestive system.
- Adaptation to Environment: Living in water, this method suits their habitat perfectly. They can feed on various prey types, even those that are too large to swallow whole.
- Energy Conservation: Not having to expend energy on complex digestive processes allows the worm to survive in nutrient-poor environments where food might be scarce.
In the grand scheme of things, this method of digestion represents a clever survival strategy that has allowed bootlace worms to thrive in their watery homes.
Exploring Related Digestive Strategies in Other Animals
Bootlace worms aren’t the only creatures with unique ways of digesting food. For instance, some other marine animals, like sea cucumbers, also digest their meals differently. Sea cucumbers can eviscerate parts of their bodies to escape predators, using the remaining parts to digest food.
Another interesting comparison comes from animals like birds, which have a gizzard—an internal organ that grinds up food. While it’s a different method altogether, it highlights the diversity of digestive strategies in the animal kingdom.
When you look at these various methods, it becomes clear that evolution shapes digestion based on environmental needs and available resources. Each species has found its own way to survive and thrive.
The Importance of Studying Bootlace Worms
Understanding how bootlace worms digest their prey can offer insights into marine biology and ecosystems. These worms play a role in nutrient cycling within their habitats. By breaking down prey and recycling nutrients, they contribute to the overall health of their environment.
Moreover, research on these unique creatures can pave the way for innovations in science and medicine. For example, studying their enzymes could lead to advances in biological research or even industrial applications. It’s incredible to think that by examining a simple worm, we might unlock secrets that benefit humanity!
Bootlace worms are a perfect case study of how nature adapts to different challenges. Their ability to digest prey without a traditional stomach showcases the ingenuity of evolution. By using enzymes to break down food externally, these remarkable creatures have found a way to thrive in their aquatic environments.
Next time you think about digestion, remember this little worm and its impressive skills. Nature has an endless capacity for innovation, and the bootlace worm is just one example of how even the simplest organisms can teach us about the complex web of life. So raise a glass to these fascinating creatures and their unique approach to survival!