As you sip that coffee, let’s take a dive into the worms’ classification journey in the Nemertea phylum. From their unique body structures to their ecological roles, these creatures tell us a lot about marine life and how living organisms are categorized. If you’re curious about how scientists put these fascinating organisms into specific groups, you’re in the right place.
What Are Bootlace Worms?
Bootlace worms, scientifically known as *Lineus longissimus*, are remarkable creatures with long, slender bodies that can reach lengths of up to 30 meters (that’s around 98 feet!). If you could picture a giant piece of spaghetti swimming through the ocean, you’d get a sense of what these worms look like. They are mostly found in the shallow coastal waters of Europe, where they wriggle through sand and mud.
Classified under the phylum Nemertea, bootlace worms are part of a group known for their soft, elongated bodies. They possess a unique ability to stretch and contract, allowing them to navigate through their habitats with ease. This phylum includes over 1,200 species, showcasing the incredible diversity found in these marine worms.
You might be wondering why they have such a strange name. The term “bootlace” comes from their long, thin shape, reminiscent of the laces you’d find on shoes. This fascinating visual gives us a fun peek into how common language can shape our understanding of species in the animal kingdom.
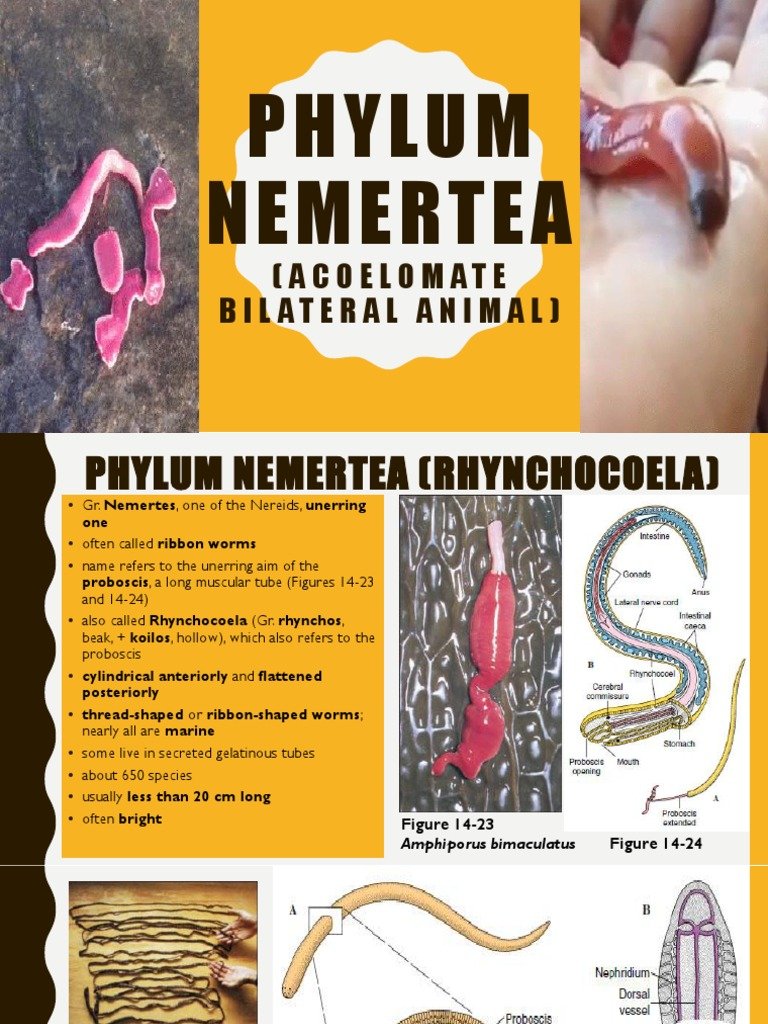
The Phylum Nemertea: An Overview
So, what exactly is *Nemertea*? It’s a phylum that includes some of the most interesting and lesser-known creatures in the ocean. Members of this group, known as ribbon worms, have a variety of fascinating characteristics that can sometimes surprise you! For instance, they possess a specialized structure called a “proboscis,” which allows them to capture prey efficiently.
Nemerteans can be found in diverse habitats, ranging from shallow coastal waters to deep-sea environments. Most of them are benthic, meaning they live on the ocean floor, but some are active swimmers. Their adaptability and ecological versatility make them vital parts of marine ecosystems.
You might be curious about how Nemertea fits into the broader classification scheme within the animal kingdom. It sits higher up (more primitive) than more familiar phyla, like Annelida (segmented worms) or Mollusca (snails and clams). This gives scientists valuable insight into the evolutionary history of life on Earth.
Classifying Bootlace Worms
When it comes to classifying bootlace worms, scientists consider several factors. Primarily, they look at genetic traits, physical characteristics, and ecological roles. Bootlace worms fall into various classes within the phylum Nemertea, with two primary groups being Anopla and Enopla.
The distinguishing factor between these classes is the presence or absence of a “proboscis.” Anopla have a simpler structure, while Enopla features a more developed one with specialized functions for hunting and feeding. This classification helps researchers understand the relationships between different species and their adaptations.
You might be wondering why classification matters. By categorizing organisms, scientists can study their evolution, behaviors, and ecological contributions more effectively. Bootlace worms, for instance, play essential roles in controlling prey populations and contributing to the nutrient cycle in marine ecosystems.
Characteristics of Bootlace Worms
Understanding the unique characteristics of bootlace worms can help clarify why they belong to the Nemertea phylum. One fascinating feature is their soft-bodied structure, which allows them to be incredibly flexible. This flexibility is crucial for their survival as they navigate through their sandy habitats.
Another key trait is their body covering, which is mainly composed of a protective layer of skin that helps prevent desiccation and damage from predators. You could liken this to a suit of armor that keeps them safe as they move through the ocean floor.
Moreover, bootlace worms are fascinating because they exhibit a form of regeneration. If they lose a part of their body, they have the remarkable ability to regrow it. This characteristic not only highlights their resilience but also makes them a subject of interest in scientific research regarding regeneration mechanisms.
Ecological Role of Bootlace Worms
Bootlace worms may not be household names, but they play crucial roles in the marine ecosystem. As predators, they feed on small invertebrates, helping maintain balanced populations in their habitats. By consuming a variety of prey, they contribute to the dynamic interactions within marine food webs.
Additionally, bootlace worms can release nutrients back into the ecosystem through their waste, which provides food for other marine organisms. This nutrient cycling is vital for the health of ocean environments, reminding us that even the smallest creatures can have significant impacts on their surroundings.
You might also find it interesting that bootlace worms can be indicators of ecological health. Their presence in a particular habitat can signal good environmental conditions, making them valuable indicators of water quality and ecosystem balance.
Studying Bootlace Worms: Why It Matters
Studying bootlace worms and their classification in the phylum Nemertea goes beyond mere curiosity. Understanding these creatures can inform us about biodiversity, evolution, and ecosystem health. As we face global changes like climate change and pollution, knowing more about the organisms that inhabit our oceans can guide conservation efforts.
Researchers are also looking into how these worms’ unique biological traits can inspire innovations in various fields, from medicine to biotechnology. Their regenerative properties, for example, are drawing interest for potential applications in human health.
By understanding bootlace worms and their place in the larger picture of marine life, we can appreciate the intricate tapestry that is our planet’s biodiversity. Each thread, no matter how small, contributes to the overall strength and beauty of the ecosystem.
Bootlace worms remind us how interconnected life can be in the vast oceans of our planet. From their classification in the phylum Nemertea to their ecological roles, these remarkable creatures deserve a spot in the spotlight. Their unique adaptations, complex interactions, and contributions to marine ecosystems illustrate the beauty of biological diversity.
As we learn more about these intriguing organisms, we gain insights that could benefit both our understanding of the marine environment and potential innovations in various scientific fields. So, the next time you think about the vast ocean, remember the bootlace worm and the secrets it holds beneath the waves.

