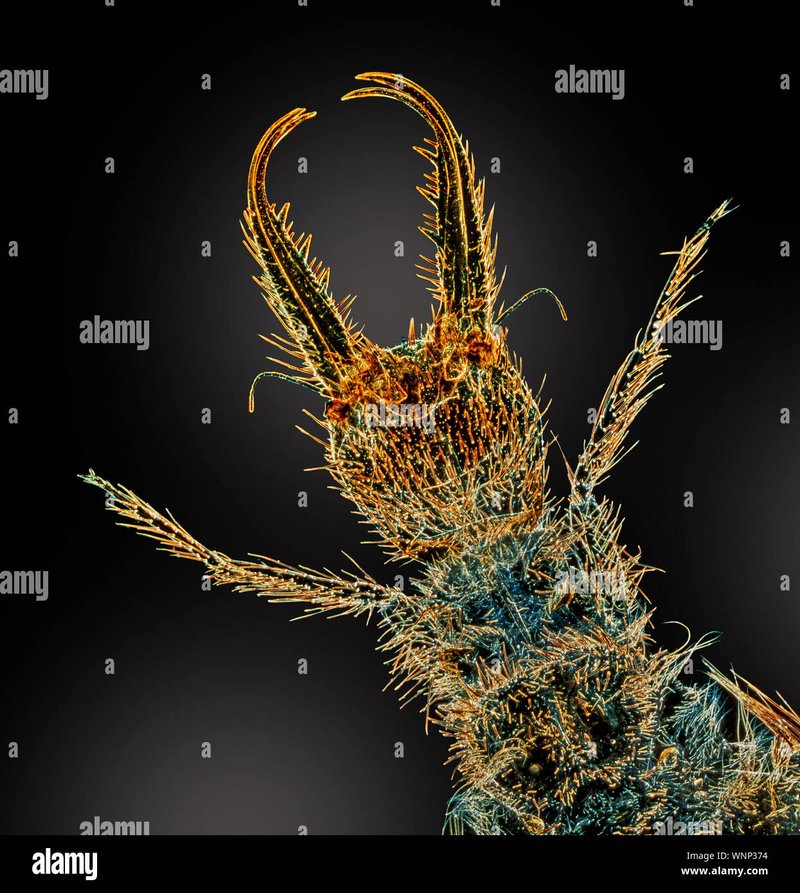
Ant lion larvae are part of a larger ecosystem that includes all sorts of microfauna, like tiny insects, worms, and even microorganisms. You might wonder how these little hunters interact with their surroundings and the other inhabitants of their mini-world. Just like any good drama, there’s more than one character to consider. From the prey they capture to the competitors and symbiotic relationships they form, understanding these interactions reveals the complex tapestry of life at a microscopic level. So, grab your coffee as we dive deeper into the captivating world of ant lion larvae and their interactions with other microfauna.
What Are Ant Lion Larvae?
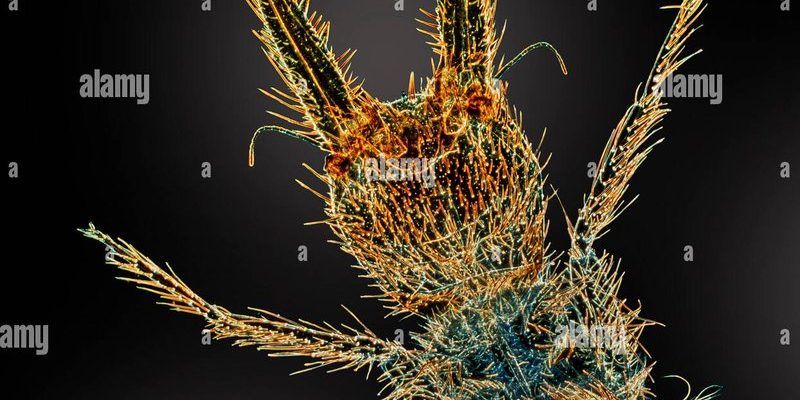
Ant lion larvae belong to the family Myrmeleontidae, and they’re best known for their unique predatory behavior. These larvae often dwell in sandy soil, using their specialized body structure to create funnel-shaped traps. When an unlucky insect, like an ant, wanders too close, it slips into the sandy pit. The ant lion larva quickly strikes, using its elongated jaws to grab the prey. It’s a clever strategy that showcases the adaptation of these fascinating creatures.
But it’s not just about being a good hunter. Ant lion larvae also have a significant role in their ecosystem. As they consume insects, they help maintain the balance of populations in their environment. If ant lion larvae were to disappear, we might see an overpopulation of certain insect species—which could be detrimental to the ecosystem. Their hunting prowess allows them to contribute to the health of their habitat while also ensuring their own survival.
Interactions With Prey
The relationship between ant lion larvae and their prey is a classic predator-prey dynamic. When an ant or other small insect falls into one of their traps, it’s not just a meal; it’s a crucial part of the life cycle. Without a steady stream of prey, ant lion larvae wouldn’t thrive. They rely on these creatures for nutrition and energy, making their hunting tactics essential.
While it might seem cruel from our perspective, this interaction is vital for the overall health of the ecosystem. Consider it a natural form of pest control. The larvae help keep populations of small insects in check, which prevents overgrazing of plant life and supports the growth of other flora. This balance is crucial for the sustainability of their entire habitat.
Competition With Other Microfauna
Ant lion larvae don’t operate in a vacuum. They share their environment with a variety of other microfauna, which can lead to competition for resources. Other predators, like spiders or beetles, might also be hunting the same prey. This competitive aspect is fascinating because it shows how resources are limited, even in small ecosystems.
You might be wondering what happens when two predators go head-to-head. In many cases, ant lions are well-adapted to their hunting strategy, with traps that are hard to escape. However, there are times when they might lose out to a quicker spider or a more agile beetle. It’s a constant battle for survival, and the struggles between these creatures contribute to the ever-changing dynamics of their ecosystem.
Symbiotic Relationships
Not all interactions in the ant lion larvae’s world are about competition. Some relationships are symbiotic, meaning both parties benefit from the interaction. For instance, certain species of fungi or bacteria may live in the same sandy habitat as the ant lion larvae. These microorganisms can help break down organic matter, enriching the soil and promoting plant growth.
In return, ant lion larvae may help create a more favorable environment for these microorganisms by aerating the soil with their movement and feeding activities. This mutualistic relationship highlights the interconnectedness of all life forms within an ecosystem and shows how even the smallest creatures can have a significant impact on their surroundings.
The Role of Environmental Factors
The interactions of ant lion larvae don’t just depend on their behavior and relationships; they’re also influenced by environmental factors. Elements like moisture, temperature, and soil type can significantly affect how these larvae interact with their surroundings. For instance, in drier areas, their traps might dry out faster, limiting their hunting success.
Additionally, changes in weather patterns or human activities can disrupt their habitats. If the soil becomes too compacted or contaminated, it can impact the larvae’s ability to build traps or capture prey. This connection between environmental health and the survival of ant lion larvae emphasizes the need for sustainable practices in managing natural areas.
Impacts of Human Activity
Sadly, human activity has an impact on the lives of ant lion larvae and their ecosystems. Habitat destruction through urban development, agriculture, and pollution can diminish the natural environments they rely on. This loss of habitat not only threatens the larvae but also disrupts the food web in which they operate.
On a broader scale, the decline of ant lion populations can lead to imbalances in the ecosystem, allowing certain insect populations to swell unchecked. This not only harms the local flora but can also affect larger animals that depend on a balanced ecosystem. Protecting these tiny predators is essential for maintaining biodiversity and the overall health of our planet’s ecosystems.
In the grand scheme of things, ant lion larvae may seem small and insignificant. However, their complex interactions with other microfauna highlight their critical role within their ecosystems. From their predatory habits to their competitive relationships and contributions to the health of their habitats, these tiny hunters are more important than they appear.
As we look closely at the intricate web of life that surrounds us, it’s crucial to remember that every creature, however small, plays a part in maintaining the balance of nature. By understanding and appreciating the role of ant lion larvae, we can better advocate for the conservation of their habitats and ensure a thriving ecosystem for all its inhabitants. So, next time you’re outside, take a moment to consider the ant lions and all the unseen interactions that keep our world buzzing with life.