Hookworms are fascinating because they show us how interconnected life can be. They’re not just about making humans unwell; they have a bigger picture role in the environment. Imagine them as tiny players in a vast game of survival, not just for themselves but for various other organisms and even the soil or water they inhabit. Grab your coffee, and let’s unravel the mystery of hookworms and their ecological importance!
What Are Hookworms?
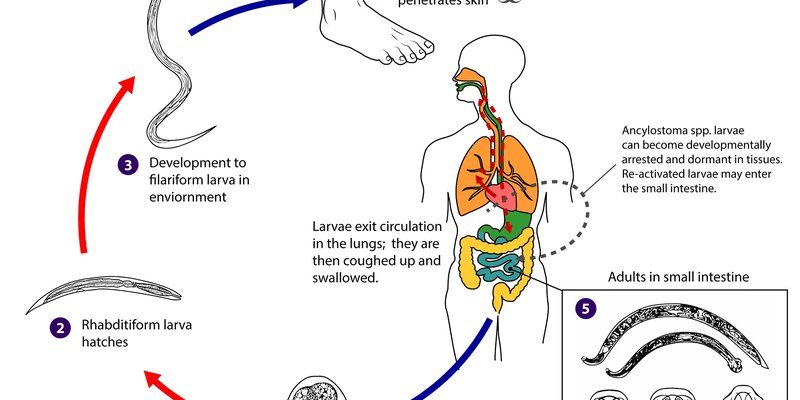
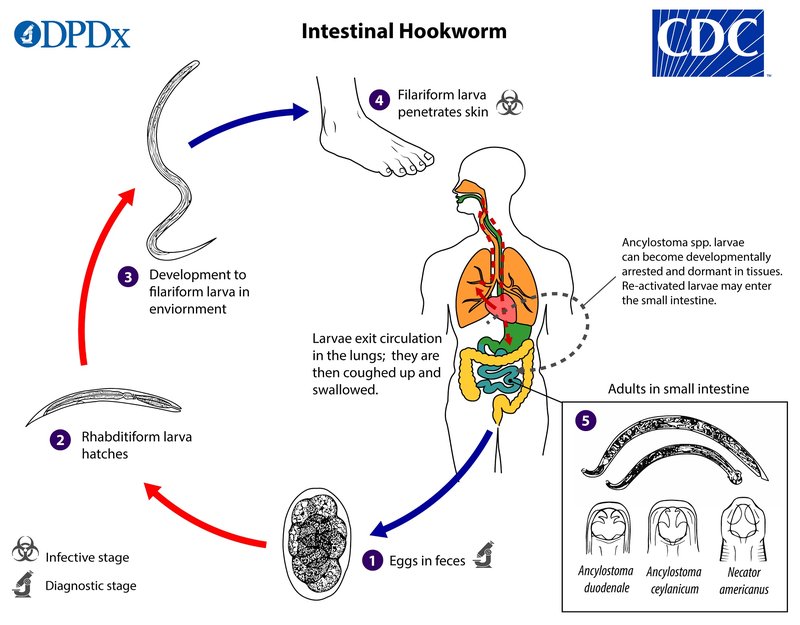
Hookworms are parasitic roundworms that belong to the family Ancylostomatidae. You might be wondering where they get their name from. Well, they have a hook-like mouth that helps them attach to the intestines of their host—often humans and other mammals. There are several species of hookworms, but the two most common are *Necator americanus* and *Ancylostoma duodenale*. They’re quite small, usually just a few millimeters long, but don’t let their size fool you!
These creatures enter their hosts through the skin, often via bare feet. Does that make you cringe a bit? It’s a reminder that our connection to nature can come with unexpected surprises. Once hooked, they feed on the blood of their hosts, which can lead to anemia and various health issues if left untreated. But this is just one side of the story.
Hookworms in Soil Ecosystems
In soil ecosystems, hookworms can actually play a positive role. They help break down organic matter, which is vital for maintaining soil health. As they feed and grow, they release nutrients back into the soil, enriching it. This process supports plant growth, creating a more vibrant ecosystem.
You might think of hookworms as tiny recyclers of nutrients. They consume decaying organic material and, through their life cycle, contribute to the nutrient cycle. Healthy soil is crucial for agriculture, as it supports the plants that feed us. So, it’s true—hookworms, in moderation, can be beneficial for soil health!
The Balance of Nature
Here’s the thing: every organism in an ecosystem plays a role, and hookworms are no exception. They help control the population of other soil microorganisms, ensuring no single species dominates. This balance is crucial for maintaining biodiversity. A diverse ecosystem is more resilient and can better withstand changes, whether they come from climate change or human activity.
Imagine walking through a lush garden. The healthy plants, the thriving soil life, and yes, even the tiny hookworms contribute to that beauty. They might not seem glamorous, but they’re part of the team that keeps our environment thriving.
Hookworms in Aquatic Ecosystems
Now let’s shift our focus to aquatic ecosystems. While hookworms are more commonly associated with soil, they can also impact water environments. When they are present in areas where animals or humans defecate into the water, they can lead to increased nutrient levels. This scenario can seem a bit tricky, as it involves the delicate balance of aquatic life.
When hookworm eggs or larvae enter water sources, they can affect the health of aquatic plants and animals. Their presence can indicate a level of nutrient pollution, which can lead to algal blooms. These blooms can suffocate fish and other aquatic life, creating an imbalance in the ecosystem.
The Ripple Effect
Think about this: if a small change happens, like the introduction of hookworms into a water source, it can lead to a chain reaction. Fish populations might decline, affecting species that feed on them, and thus altering the entire food web. It’s a reminder of how interconnected everything is—every little change matters.
Hookworms and Nutrient Cycling
A key aspect of hookworms’ role in ecosystems is their contribution to nutrient cycling. When they feed, they digest nutrients that can later be released back into the environment. This cycling process is essential for healthy ecosystems because it provides the necessary elements for plant growth and sustenance of other organisms.
In a way, you can call hookworms nature’s little fertilizers. Just like how we use compost to enrich our gardens, hookworms contribute to the natural composting process. As they break down organic material and recycle nutrients, they help build a robust and thriving ecosystem.
Why Nutrient Cycling Matters
Nutrient cycling is vital for maintaining environmental health. Without it, soil can become depleted and unable to support plant life. The same goes for aquatic environments—over time, without healthy nutrient cycling, these ecosystems can struggle to flourish. It’s like trying to grow a garden in poor soil; you won’t get very far!
Human Impact on Hookworm Populations
Sadly, human activity can significantly impact hookworm populations and their roles in ecosystems. Overuse of fertilizers in agriculture can alter soil composition and nutrient balance, potentially leading to an increase in hookworm populations due to enriched habitats.
Conversely, improved sanitation and healthcare have led to a decrease in hookworm infections among humans. This decline can affect soil health and nutrient cycling in regions where hookworms had previously contributed positively. The balance between maintaining health and preserving ecological roles is a delicate dance.
Finding a Middle Ground
So, how do we find a balance? It’s all about understanding the nuances of ecology. Education and awareness can lead to better practices in farming and waste management. By working together, we can find ways to keep our environments healthy without inadvertently harming the delicate balance hookworms help maintain.
In the grand tapestry of life, even the smallest threads—like hookworms—play a role. By understanding their function in soil and aquatic ecosystems, we can appreciate the complexity of nature around us. Hookworms might not be the cutest or most charming organisms, but they do their part in maintaining the balance of our environment.
So next time you hear about these tiny parasites, remember that they’re more than just slackers in the ecosystem. They’re contributors to nutrient cycling and soil health. Recognizing this complexity encourages us to embrace the beauty of interconnected life. After all, every creature, big or small, has its place in nature’s intricate web.