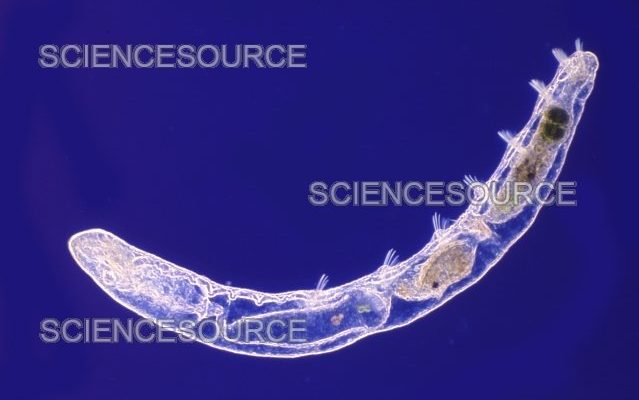
So, what exactly is an oligochaete? Simply put, they’re a class of segmented worms that includes familiar types like *Lumbricus terrestris*, commonly known as the earthworm. In freshwater habitats, oligochaetes can be found living in mud, sediment, or among aquatic plants. Their habitat preferences are fascinating and can give us great insight into the health and quality of freshwater environments. Let’s dive in and explore these little creatures and their preferred homes!
What Are Freshwater Oligochaetes?
Freshwater oligochaetes are a subgroup of annelids, which are segmented worms. This group thrives in diverse aquatic habitats, from rivers and lakes to ponds and streams. They can be found buried in sediment or swimming freely in the water. These worms have soft bodies that can vary in color from pale to dark brown, depending on their environment.
You might be wondering what makes oligochaetes so special. For starters, they play a crucial role in breaking down organic matter, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem. They’re also a food source for many larger animals, ranging from fish to birds. Honestly, without these little guys, many aquatic systems wouldn’t function as efficiently.
Natural Habitat Conditions
Freshwater oligochaetes have specific habitat preferences that ensure their survival. They thrive in environments with certain physical and chemical conditions. Here are some key elements of their ideal habitat:
- Substrate Type: Oligochaetes prefer soft sediments, such as mud and silt, where they can burrow and feed easily. These substrates provide protection and ample food sources.
- Oxygen Levels: Like many living organisms, oligochaetes need oxygen to survive. They thrive in well-aerated waters, but can also tolerate low oxygen levels if necessary.
- pH Levels: These worms generally prefer a neutral to slightly alkaline pH range (around 6.5 to 8.5). Extreme pH levels can be harmful to their health.
Understanding these conditions helps scientists monitor freshwater ecosystems. It’s like having a weather report for the health of our waters!
Role of Water Quality
Water quality significantly impacts the presence and population of freshwater oligochaetes. When water quality is compromised, you can often see a decline in oligochaete populations. Pollutants, high nutrient loads, and sedimentation can decrease their numbers, creating a ripple effect throughout the ecosystem.
Here’s the thing: if you notice fewer oligochaetes in a pond, it may indicate issues like pollution or habitat degradation. Regular monitoring of these organisms can help environmental scientists assess the health of a water body. For instance, a high number of oligochaetes suggests good water quality, while low numbers may raise a red flag.
Proper water management is vital for maintaining these delicate ecosystems. This includes keeping pollutants out and ensuring the habitat remains intact. It’s a team effort between nature and humans, and every tiny creature counts.
Preferred Habitats: Streams vs. Lakes
When it comes to specific habitats, freshwater oligochaetes show a range of preferences. Let’s compare two common environments: streams and lakes.
Streams: These flowing waters often have higher oxygen levels due to constant movement. Oligochaetes here tend to burrow into the sediment along the riverbed, where they can feed on organic debris. They also adapt to varying flow rates, which can keep their populations robust.
Lakes: In contrast, lakes can allow for larger populations of oligochaetes, especially in areas with rich nutrient levels. They often thrive in the soft, organic-rich mud found at the bottom of lakes. You might commonly find them hanging out near decaying plant matter, which serves as their buffet.
Both habitats have their charm, and oligochaetes adapt beautifully to their surroundings. Whether they’re drifting with the current or lurking in lake mud, these worms know how to find their place in the world.
Human Impact on Freshwater Habitats
Unfortunately, human activities can significantly impact the habitats of freshwater oligochaetes. Pollution from agricultural run-off, industrial waste, and urban development leads to habitat degradation. This can disrupt the delicate balance that these creatures rely on.
For example, excess nutrients from fertilizers can cause algal blooms, which deplete oxygen levels in the water. This puts pressure on oligochaete populations and can lead to their decline. Think about it: if their food sources diminish, the entire ecosystem suffers.
Restoration projects are crucial. These initiatives can help rehabilitate affected areas, bringing back not just oligochaetes but entire aquatic communities. It’s about working together to ensure the health and sustainability of these ecosystems for future generations.
Ecological Importance of Oligochaetes
The ecological role of freshwater oligochaetes goes beyond just being a food source. They are vital in nutrient cycling and soil formation within aquatic environments. As they break down organic matter, they release nutrients back into the water, benefiting plants and other organisms in the ecosystem.
You might think of them as nature’s recyclers. Their presence contributes to healthy sediment dynamics, ensuring that the bottom of lakes and rivers remains productive. This process supports a diverse community of aquatic life, which is essential for maintaining ecological balance.
Moreover, oligochaetes can act as bioindicators, helping scientists assess environmental conditions. By studying their populations, researchers can gauge the health of freshwater ecosystems, making them crucial allies in conservation efforts.
Freshwater oligochaetes might be small, but their impact on aquatic ecosystems is anything but insignificant. From nutrient recycling to serving as a food source, they play a vital role in keeping our freshwater habitats healthy.
It’s essential for us to understand their habitat preferences and the factors that influence their populations. By doing so, we can take action to protect these remarkable creatures and the ecosystems they inhabit. Whether through clean-up efforts or mindful water management, we can help ensure that freshwater oligochaetes thrive.
Let’s remember: every small worm contributes to a larger picture. So, the next time you see a body of freshwater, think about the hidden world beneath the surface—where oligochaetes are busy doing their important work!