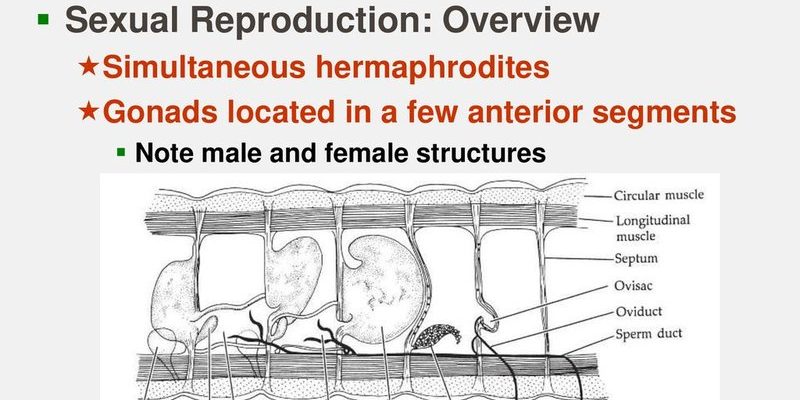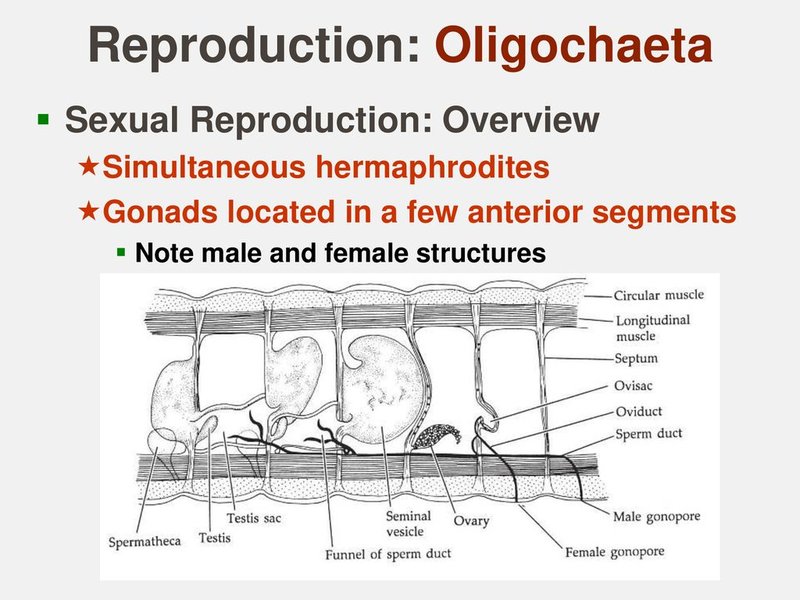
Imagine a hidden world beneath the surface of a pond or river, where these lively worms are busy with their romantic endeavors. From mating rituals that would make any soap opera jealous to the delicate way they lay their eggs, oligochaetes have a unique approach to reproduction. So, let’s dive into this watery world and explore the intriguing sex lives of these segmented wonders!
What Are Freshwater Oligochaetes?
Before we jump into their reproduction, let’s take a moment to understand what freshwater oligochaetes are. Oligochaetes belong to the phylum Annelida, which means “little rings” in Latin, a reference to their segmented bodies. They are mostly found in soil and freshwater but can also thrive in marine environments.
These worms typically have a soft, elongated body that can vary in color from earth tones to more vibrant shades depending on their habitat. They’re also equipped with tiny bristles called setae, which help them move through their environment. Think of them as nature’s little gardeners, aerating the soil and breaking down organic matter. This makes them essential for healthy ecosystems!
Mating Habits of Oligochaetes
So, how do these little worms find love? Oligochaetes are hermaphroditic, meaning each individual has both male and female reproductive organs. This fascinating aspect of their biology allows them to mate with any other oligochaete they encounter.
When it’s time to mate, two oligochaetes will come together, aligning their bodies side by side. During this process, they exchange sperm, which is later used for fertilization. Often, they will also exchange a mucus ring that helps them exchange sperm more effectively. It’s like a cozy, slippery handshake!
Once the mating is complete, each worm holds onto the sperm until it is time to lay eggs. This strategy maximizes the chances of reproduction since they can use sperm from any partner, making sure their genetic material mixes well.
Egg-Laying Process
After a successful mating session, it’s time for the oligochaetes to become parents. The egg-laying process is quite remarkable. Instead of simply dropping their eggs, oligochaetes create a special structure known as a cocoon.
This cocoon is produced by a specialized gland in their body. It’s kind of like creating a little protective pouch for their future babies. The worm will slide out of the cocoon, which then hardens in the water, ensuring the eggs are safe from predators and environmental stresses. Typically, a single cocoon can hold anywhere from a few to dozens of eggs, depending on the species and environmental conditions.
You might be wondering how long it takes for the eggs to hatch. Generally, it can take several weeks to a few months, depending on the water temperature and conditions. This means that oligochaetes are quite patient parents, waiting for the right moment to welcome their little ones into the world.
What Happens Next? The Larvae Stage
Once the eggs hatch, the larvae enter what is known as the juvenile stage. These tiny worms are miniature versions of their parents, equipped with all the essential parts to thrive in their environment.
At this stage, they usually stay close to the substrate, feeding on decomposing organic matter and microorganisms. As they grow, they continuously molt, shedding their outer skin to accommodate their increasing size. This is similar to how some animals, like snakes or crabs, shed their shells.
Interestingly, the growth rate can vary based on environmental factors such as food availability and water quality. Warmer temperatures generally speed up their growth, while cooler conditions may slow it down. It’s like nature’s way of ensuring every oligochaete has the best chance to thrive.
Factors Influencing Oligochaete Reproduction
The reproduction of freshwater oligochaetes is influenced by several factors in their environment. Let’s break down the major ones:
- Water Quality: Clean water with adequate oxygen levels supports healthy oligochaete populations. Polluted or low-oxygen environments can hinder their reproduction.
- Temperature: Oligochaetes prefer moderate temperatures. Extreme heat or cold can stress them and negatively impact their reproductive success.
- Food Availability: A rich supply of organic matter boosts the health of oligochaetes. Healthy worms are more likely to reproduce successfully.
- Population Density: High densities can lead to increased competition for resources, which may affect their mating habits.
Understanding these factors is crucial, especially for environmentalists and researchers who study the health of freshwater ecosystems. Protecting these worms is vital not just for their survival, but for the health of the entire aquatic community.
Why Oligochaete Reproduction Matters
You might be thinking, “Why should I care about the reproduction of oligochaetes?” Well, let me explain. These worms play a critical role in nutrient cycling and organic matter decomposition in freshwater ecosystems. When they reproduce successfully, they help maintain a balanced ecosystem.
Their feeding habits help break down sediment and recycle nutrients, making them available for other organisms. This means that healthy oligochaete populations contribute to the overall health of the water bodies they inhabit. In turn, this supports fish, amphibians, and various other creatures that rely on clean, nutrient-rich water to thrive.
Moreover, studying oligochaete reproduction can provide insights into environmental changes. If researchers notice shifts in oligochaete populations, it could signal changes in water quality or habitat conditions, acting as an early warning system for ecosystem health.
In the grand tapestry of freshwater ecosystems, oligochaetes might not be the star of the show, but their reproductive habits are certainly noteworthy. From their unique hermaphroditic mating practices to the careful production of cocoons, every aspect reflects their incredible adaptability and resilience.
Next time you glance at a pond or stream, remember that beneath the surface, these tiny worms are busy contributing to the health of the environment. Their life cycle may not be the flashiest, but it’s undeniably fascinating. So, whether you’re a budding biologist or just someone who appreciates nature, take a moment to celebrate the wonders of freshwater oligochaete reproduction!